The white noise (WN) model
Time Series Analysis in R

David S. Matteson
Associate Professor at Cornell University
White noise
White Noise (WN) is the simplest example of a stationary process.
A weak white noise process has:
- A fixed, constant mean.
- A fixed, constant variance.
- No correlation over time.
White noise
Time series plots of White Noise:
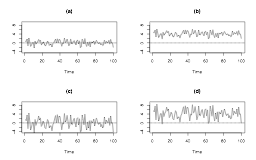
White noise
Time series plots of White Noise?
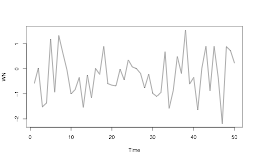
# Simulate n = 50 observations from the WN model
WN_1 <- arima.sim(model = list(order = c(0, 0, 0)), n = 50)
head(WN_1)
-0.005052984 0.042669765 3.261154066
2.486431235 0.283119322 1.543525773
ts.plot(WN_1)
# Simulate from the WN model with mean = 4, sd = 2
WN_2 <- arima.sim(model = list(order = c(0, 0, 0)),
n = 50, mean = 4, sd = 2)
ts.plot(WN_2)

Estimating white noise
# Fit the WN model with
# arima()
arima(WN_2,
order = c(0, 0, 0))
Coefficients:
intercept
4.0739
s.e. 0.2698
sigma^2 estimated as 3.639
# Calculate the sample
# mean and sample variance
# of WN
mean(WN_2)
4.0739
var(WN_2)
3.713
Let's practice!
Time Series Analysis in R

