Stationary processes
Time Series Analysis in R

David S. Matteson
Associate Professor at Cornell University
Stationarity
- Stationary models are parsimonious.
- Stationary processes have distributional stability over time.
Observed time series:
- Fluctuate randomly.
- But behave similarly from one time period to the next.
Weak stationarity - I
Weak stationary: mean, variance, covariance constant over time.
$Y_1, Y_2$, ...is a weakly stationary process if:
- Mean $ \mu $ of $ Y_t$ is same (constant) for all $t$.
- Variance $ \sigma ^2$ of $ Y_t$ is same (constant) for all $t$.
- And….
Weak stationarity - II
Covariance of $ Y_t$ and $ Y_s$ is same (constant) for all $ \vert t - s \vert = h$, for all$ h$.
$$ Cov(Y_2, Y_5) = Cov(Y_7, Y_{10})$$
since each pair is separated by three units of time.
Stationarity: why?
A stationary process can be modeled with fewer parameters.
For example, we do not need a different expectation for each $ Y_t$; rather they all have a common expectation, $ \mu$.
- Estimate $ \mu$ accurately by $ \bar y $.
Stationarity: when?
Many financial time series do not exhibit stationarity, however:
- The changes in the series are often approximately stationary.
- A stationary series should show random oscillation around some fixed level; a phenomenon called mean-reversion.
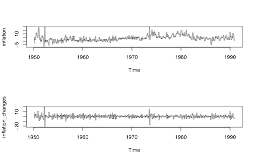
Stationarity example
Inflation rates and changes in inflation rates:
Let's practice!
Time Series Analysis in R

