Working with lists
R For SAS Users

Melinda Higgins, PhD
Research Professor/Senior Biostatistician Emory University
Create list by combining other objects
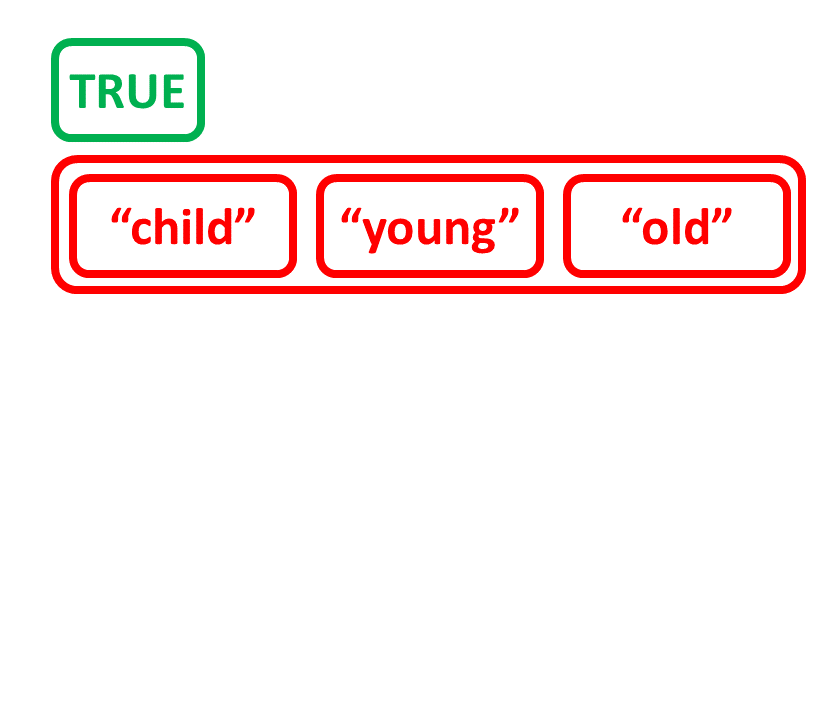
# Create logical scalar
logic_scalar <- TRUE
logic_scalar
[1] TRUE

Create list by combining other objects
# Create character vector age_charvec
age_charvec <- c("child", "young", "old")
age_charvec
[1] "child" "young" "old"
Create list by combining other objects
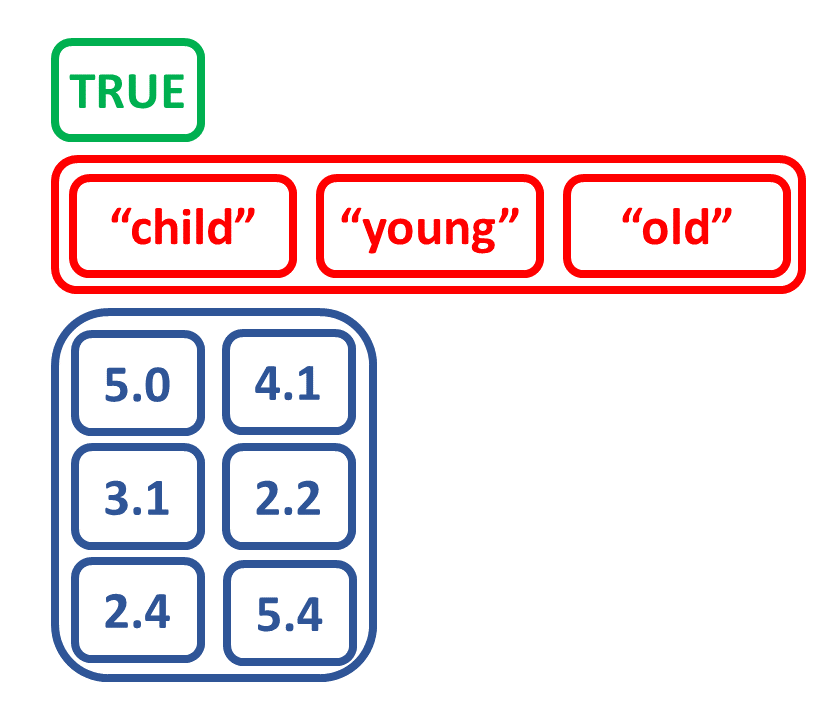
# Create matrix num_matrix
a <- c(5.0, 3.1, 2.4)
b <- c(4.1, 2.2, 5.4)
num_matrix <- matrix(c(a, b),
nrow = 3,
ncol = 2)
num_matrix
[,1] [,2]
[1,] 5.0 4.1
[2,] 3.1 2.2
[3,] 2.4 5.4
Create list by combining objects of different types
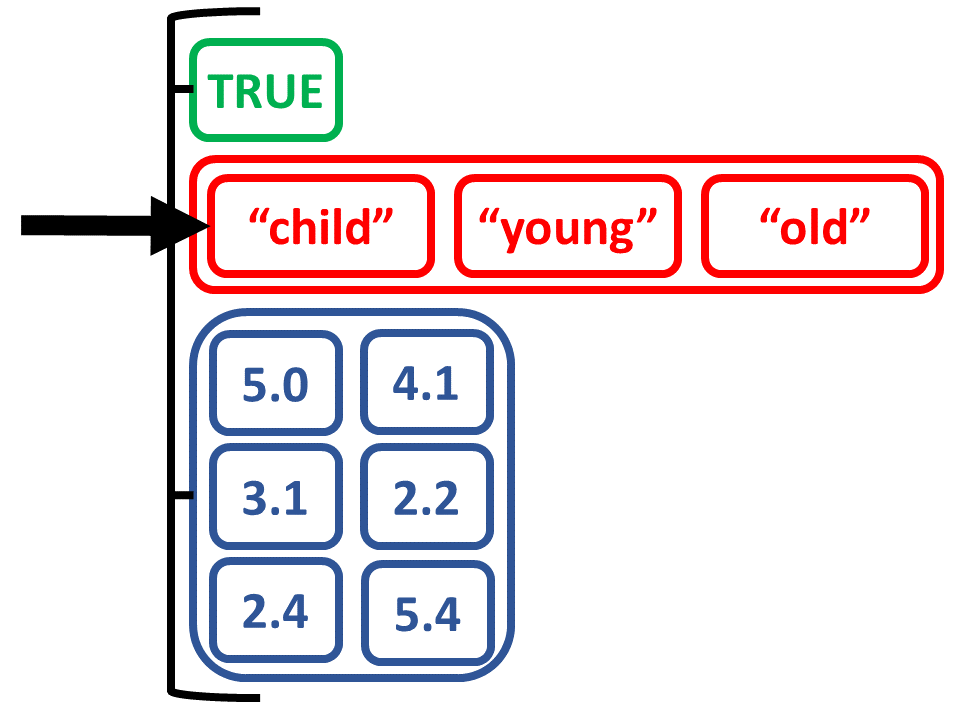
# Create list from scalar, vector, matrix
list_logicagemtx <-
list(logic_scalar, age_charvec, num_matrix)
list_logicagemtx
[[1]]
[1] TRUE
[[2]]
[1] "child" "young" "old"
[[3]]
[,1] [,2]
[1,] 5.0 4.1
[2,] 3.1 2.2
[3,] 2.4 5.4

Named list elements
# Name the elements of the list, view names
names(list_logicagemtx) <- c("logicalValue", "ageDescription", "numericMatrix")
names(list_logicagemtx)
[1] "logicalValue" "ageDescription" "numericMatrix"
# Get structure of list_logicagemtx
str(list_logicagemtx)
List of 3
$ logicalValue : logi TRUE
$ ageDescription: chr [1:3] "child" "young" "old"
$ numericMatrix : num [1:3, 1:2] 5 3.1 2.4 4.1 2.2 5.4
Select elements from list by name
# Select ageDescription with $
list_logicagemtx$ageDescription
[1] "child" "young" "old"
# Check class of the ageDescription element
class(list_logicagemtx$ageDescription)
[1] "character"
# Confirm vector class
is.vector(list_logicagemtx$ageDescription)
[1] TRUE
Hmisc output
# Run Hmisc::describe() for sex and bmi
davisHmisc <- daviskeep %>%
select(sex, bmi) %>%
Hmisc::describe()
# Structure of Hmisc::describe() output
str(davisHmisc)
List of 2
$ sex:List of 5
..$ descript: chr "sex"
..$ units : NULL
..$ format : NULL
..$ counts : Named num [1:3] 199 0 2
.. ..- attr(*, "names")= chr [1:3] "n" "missing" "distinct"
..$ values :List of 2
.. ..$ value : chr [1:2] "F" "M"
.. ..$ frequency: num [1:2(1d)] 111 88
..- attr(*, "class")= chr "describe"
$ bmi:List of 6
..$ descript: chr "bmi"
... rest of output omitted ...
Hmisc output
# View sex element of Hmisc describe output
davisHmisc$sex
sex
n missing distinct
199 0 2
Value F M
Frequency 111 88
Proportion 0.558 0.442
# Confirm the describe class is also a list
is.list(davisHmisc$sex)
[1] TRUE
Hmisc output
# View names of elements in davisHmisc$sex
names(davisHmisc$sex)
[1] "descript" "units" "format" "counts" "values"
# Use $ selector again to display counts for sex
davisHmisc$sex$counts
n missing distinct
199 0 2
Correlation tests output
# Save output from psych::corr.test()
daviscorr <- daviskeep %>%
select(bmi, weight, height) %>%
psych::corr.test()
# View names of 11 elements in psych::corr output
names(daviscorr)
[1] "r" "n" "t" "p" "se"
[6] "sef" "adjust" "sym" "ci" "ci.adj"
[11] "Call"
Correlation tests output
daviscorr$p
bmi weight height
bmi 0.000000e+00 2.569508e-64 3.628533e-08
weight 8.565028e-65 0.000000e+00 4.017148e-40
height 3.628533e-08 2.008574e-40 0.000000e+00
daviscorr$ci
lower r upper p
bmi-weght 0.8410885 0.8775201 0.9060257 8.565028e-65
bmi-heght 0.2524241 0.3782344 0.4914688 3.628533e-08
weght-heght 0.7074835 0.7707306 0.8217303 2.008574e-40
T-tests output
# UNPOOLED t-test bmi by sex
davisunpooled <- t.test(bmi ~ sex,
data = daviskeep)
class(davisunpooled)
[1] "htest"
is.list(davisunpooled)
[1] TRUE
names(davispooled)
[1] "statistic" "parameter"
[3] "p.value" "conf.int"
[5] "estimate" "null.value"
[7] "alternative" "method"
[9] "data.name"
Chi-square tests output
# Create table object of bmigt25 by sex and view table
tablebmisex <- daviskeep %>%
with(table(bmigt25, sex))
daviscs <- chisq.test(tablebmisex)
class(daviscs)
[1] "htest"
names(daviscs)
[1] "statistic" "parameter" "p.value" "method" "data.name" "observed"
[7] "expected" "residuals" "stdres"
Output of htest list class
T-test output
davisunpooled$statistic
davisunpooled$parameter
davisunpooled$p.value
t
-7.515792
df
149.4533
[1] 4.818621e-12
Chi-square test output
daviscs$observed
sex
bmigt25 F M
1. underwt/norm 107 54
2. overwt/obese 4 34
daviscs$expected
sex
bmigt25 F M
1. underwt/norm 89.80402 71.19598
2. overwt/obese 21.19598 16.80402
Let's work with list output objects to customize your abalone analysis results.
R For SAS Users

