Descriptive statistics with R
R For SAS Users

Melinda Higgins, PhD
Research Professor/Senior Biostatistician Emory University
Loading external CSV datasets
- Abalone dataset contains 9 measurements:
- length
- diameter
- height
- whole weight
- shucked weight
- shell weight
- viscera weight
- sex (infants, females, males)
- number of rings

- For 4177 abalones
Loading external CSV datasets
abalonedataset available in CSV (comma separated value) formatread_csv()function fromreadrpackage used to load CSV data

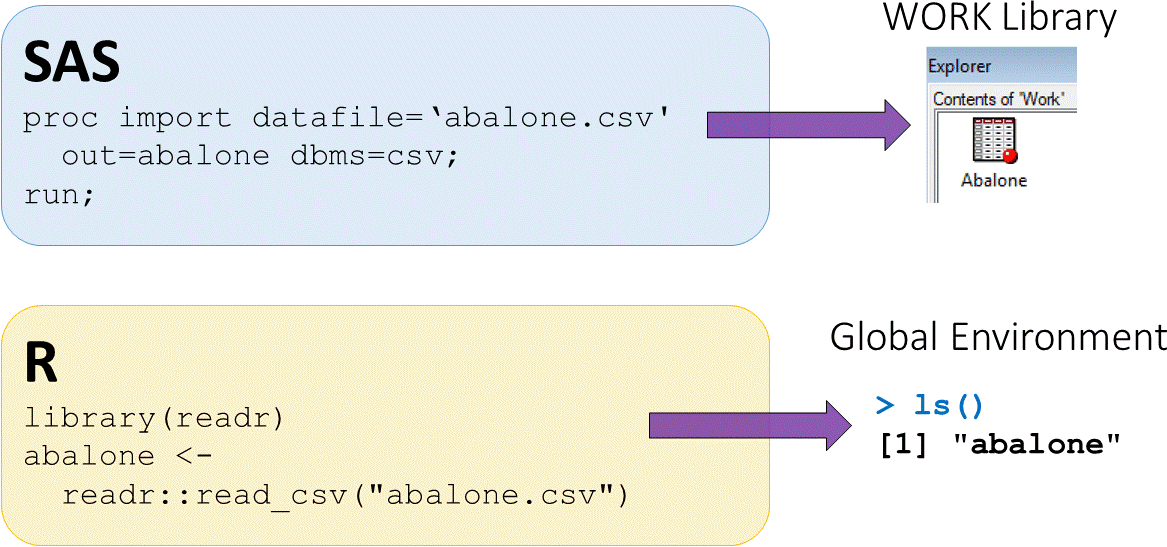
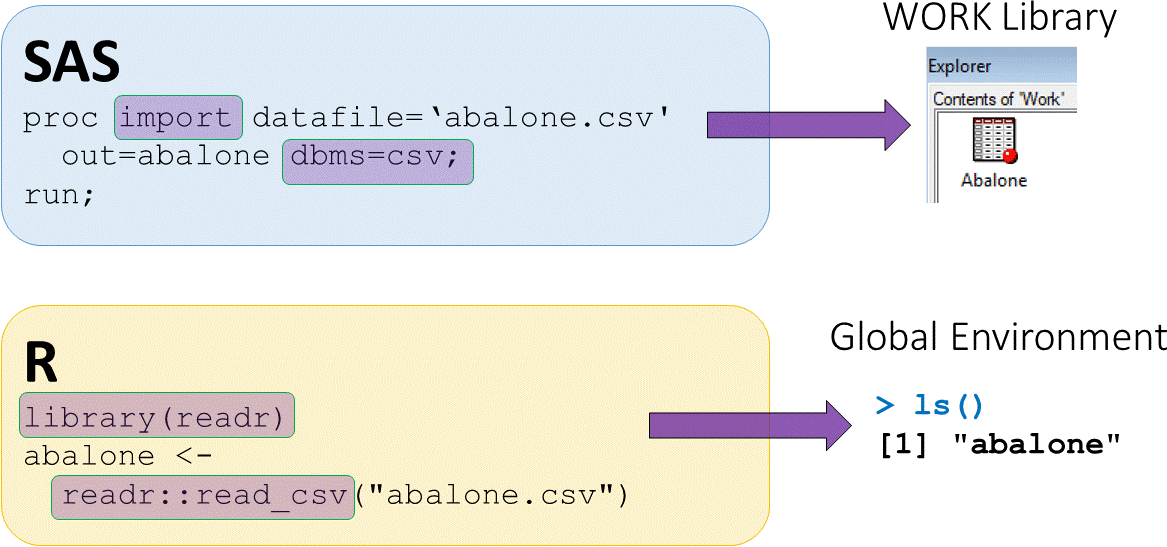
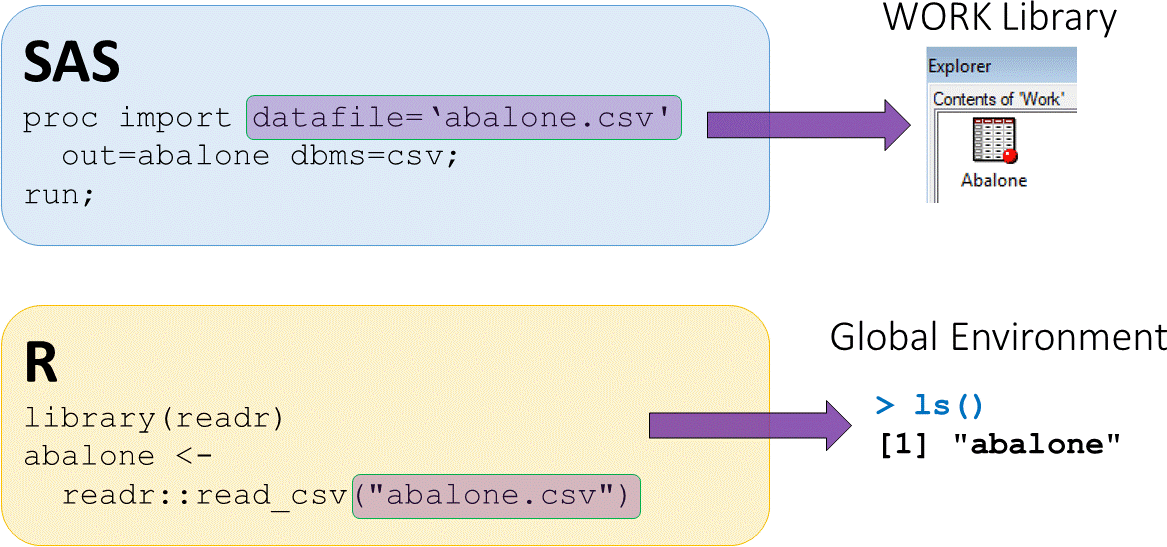
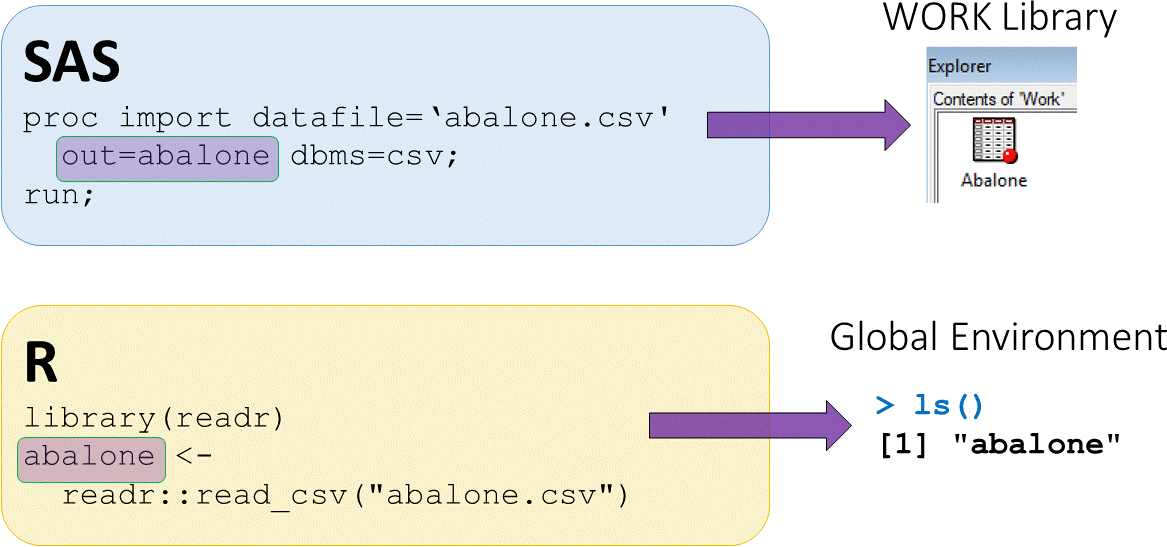
- The assign operator
<-puts output fromreadr::read_csvinto an objectabalone abaloneis now saved in the global environment
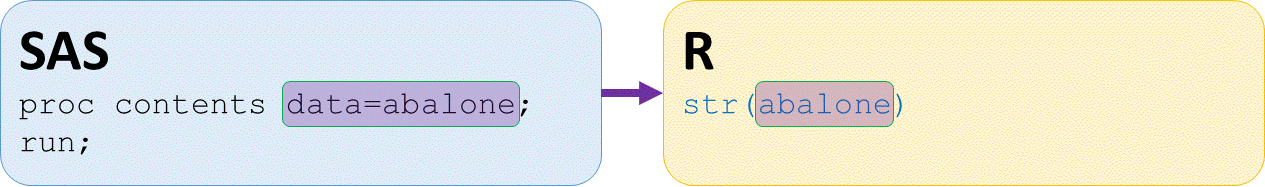
str(abalone)
Classes ‘tbl_df’, ‘tbl’ and 'data.frame': 4177 obs. of 9 variables:
$ sex : chr "M" "M" "F" "M" ...
$ length : num 0.455 0.35 0.53 0.44 0.33 0.425 0.53 0.545 ...
$ diameter : num 0.365 0.265 0.42 0.365 0.255 0.3 0.415 0.425 ...
$ height : num 0.095 0.09 0.135 0.125 0.08 0.095 0.15 0.125 ...
$ wholeWeight : num 0.514 0.226 0.677 0.516 0.205 ...
$ shuckedWeight: num 0.2245 0.0995 0.2565 0.2155 0.0895 ...
$ visceraWeight: num 0.101 0.0485 0.1415 0.114 0.0395 ...
$ shellWeight : num 0.15 0.07 0.21 0.155 0.055 0.12 0.33 0.26 ...
$ rings : int 15 7 9 10 7 8 20 16 9 19 ...
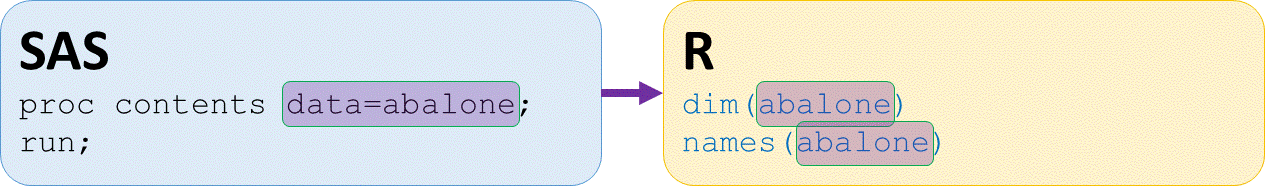
# Display dimensions of abalone dataset
dim(abalone)
4177 9
# Elements or variables in abalone dataset
names(abalone)
"sex" "length" "diameter" "height" "wholeWeight"
"shuckedWeight" "visceraWeight" "shellWeight" "rings"
Dataset contents and variable types
head()andtail()show top and bottom 6 rows respectively by default- Change the number of rows shown by adding a second argument to the function
# Show bottom 7 rows of abalone
tail(abalone, 7)
# A tibble: 7 x 9
sex length diameter height wholeWeight shuckedWeight visceraWeight shellWeight rings
<chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 M 0.55 0.43 0.13 0.840 0.316 0.196 0.240 10
2 M 0.56 0.43 0.155 0.868 0.4 0.172 0.229 8
3 F 0.565 0.45 0.165 0.887 0.37 0.239 0.249 11
4 M 0.59 0.44 0.135 0.966 0.439 0.214 0.260 10
5 M 0.6 0.475 0.205 1.18 0.526 0.288 0.308 9
6 F 0.625 0.485 0.15 1.09 0.531 0.261 0.296 10
7 M 0.71 0.555 0.195 1.95 0.946 0.376 0.495 12
Working with data using dplyr approach

In this course, you will use these dplyr functions:
%>%is a pipe operator from themagrittrpackage included withdplyrarrange()will sort the data by one or more variablespull(x)will pull one columnxvariable out of the datasetselect(x,y,z)will select more than one variable out of the dataset
dplyr arrange function and pipe %>% approach

dplyr arrange function and pipe %>% approach

dplyr arrange function and pipe %>% approach
dplyr arrange function and pipe %>% approach
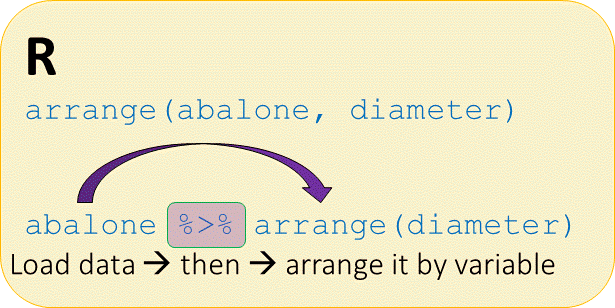
Arrange abalones by diameter
# Arrange abalone dataset by diameter dimension
abalone %>%
arrange(diameter)
# A tibble: 4,177 x 9
sex length diameter height wholeWeight shuckedWeight visceraWeight shellWeight rings
<chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 I 0.075 0.055 0.01 0.002 0.001 0.0005 0.0015 1
2 I 0.11 0.09 0.03 0.008 0.0025 0.002 0.003 3
3 I 0.13 0.095 0.035 0.0105 0.005 0.0065 0.0035 4
4 I 0.13 0.1 0.03 0.013 0.0045 0.003 0.004 3
5 I 0.15 0.1 0.025 0.015 0.0045 0.004 0.005 2
6 I 0.155 0.105 0.05 0.0175 0.005 0.0035 0.005 4
7 I 0.14 0.105 0.035 0.014 0.0055 0.0025 0.004 3
8 I 0.17 0.105 0.035 0.034 0.012 0.0085 0.005 4
9 I 0.14 0.105 0.035 0.0145 0.005 0.0035 0.005 4
10 M 0.155 0.11 0.04 0.0155 0.0065 0.003 0.005 3
Extract one variable from abalone
Let's extract shuckedWeight from abalone using pull() from dplyr
# Pull out shuckedWeight variable from abalone
abalone %>%
pull(shuckedWeight)
[1] 0.2245 0.0995 0.2565 0.2155 0.0895 0.1410 0.2370 0.2940 0.2165 0.3145 0.1940 0.1675
[13] 0.2175 0.2725 0.1675 0.2580 0.0950 0.1880 0.0970 0.1705 0.0955 0.0800 0.4275 0.3180
[25] 0.5130 0.3825 0.3945 0.3560 0.3940 0.3930 0.3935 0.6055 0.5515 0.8150 0.6330 0.2270
[37] 0.5305 0.2370 0.3810 0.1340 0.1865 0.3620 0.0315 0.0255 0.0175 0.0875 0.2930 0.1775
[49] 0.0755 0.3545 0.2385 0.1335 0.2595 0.2105 0.1730 0.2565 0.1920 0.2765 0.0420 0.2460
[61] 0.1800 0.3050 0.3020 0.1705 0.2340 0.2340 0.3540 0.4160 0.2135 0.0630 0.2640 0.1405
[73] 0.4800 0.4740 0.4810 0.4425 0.3625 0.3630 0.2820 0.4695 0.3845 0.5105 0.3960 0.4080
[85] 0.3800 0.3390 0.4825 0.3305 0.2205 0.3135 0.3410 0.3070 0.4015 0.5070 0.5880 0.5755
[97] 0.2690 0.2140 0.2010 0.2775 0.1050 0.3280 0.3160 0.3105 0.4975 0.2910 0.2935 0.2610
...remaining output removed...
Compute mean and median shucked weight
# Compute mean shuckedWeight
abalone %>%
pull(shuckedWeight) %>%
mean()
0.3593675
# Compute median shuckedWeight
abalone %>%
pull(shuckedWeight) %>%
median()
0.336
Select two variables from abalone
# Select two variables length and height
abalone %>%
select(length, height)
# A tibble: 4,177 x 2
length height
<dbl> <dbl>
1 0.455 0.095
2 0.35 0.09
3 0.53 0.135
4 0.44 0.125
5 0.33 0.08
6 0.425 0.095
7 0.53 0.15
8 0.545 0.125
# ... with 4,169 more rows
Get summary statistics of length and height
summary() outputs min, max, mean, median and 25th and 75th quartiles
# Get summary stats of length and height
abalone %>%
select(length, height) %>%
summary()
length height
Min. :0.075 Min. :0.0000
1st Qu.:0.450 1st Qu.:0.1150
Median :0.545 Median :0.1400
Mean :0.524 Mean :0.1395
3rd Qu.:0.615 3rd Qu.:0.1650
Max. :0.815 Max. :1.1300
Let's go find out about abalones
R For SAS Users

