Correlations and t-tests
R For SAS Users

Melinda Higgins, PhD
Research Professor/Senior Biostatistician Emory University
Correlations compare SAS and R
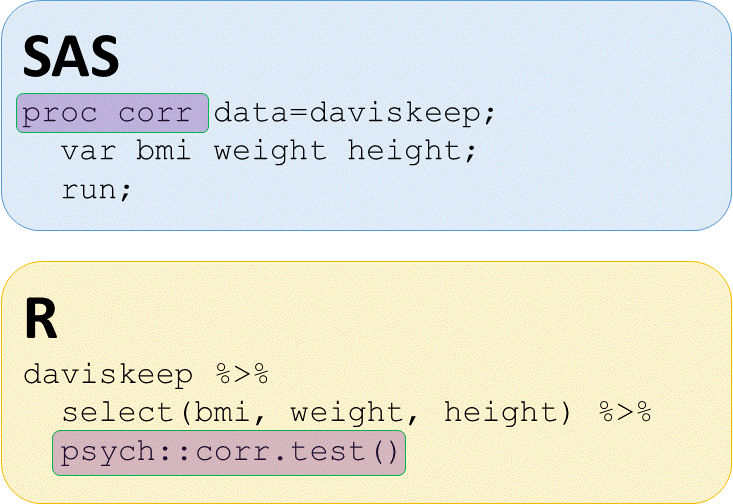
Correlations with psych package
# Correlations with psych::corr.test()
daviskeep %>%
select(bmi, weight, height) %>%
psych::corr.test()
Call:psych::corr.test(x = .)
Correlation matrix
bmi weight height
bmi 1.00 0.88 0.38
weight 0.88 1.00 0.77
height 0.38 0.77 1.00
Sample Size
[1] 199
Probability values (Entries above the
diagonal are adjusted for multiple tests.)
bmi weight height
bmi 0 0 0
weight 0 0 0
height 0 0 0
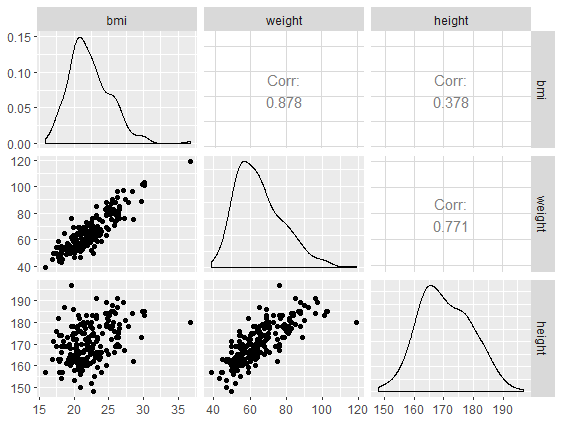
Scatterplot matrix SAS and R
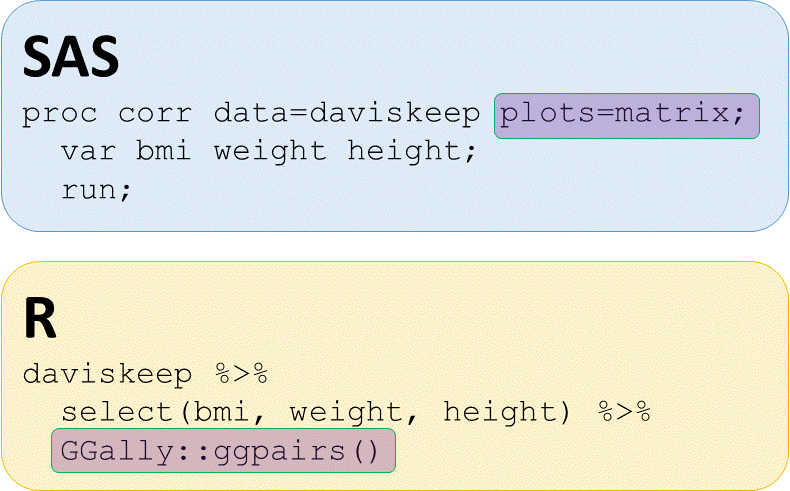
Scatterplot matrix - GGally::ggpairs() function
# Matrix plot with GGally::ggpairs()
daviskeep %>%
select(bmi, weight, height) %>%
GGally::ggpairs()
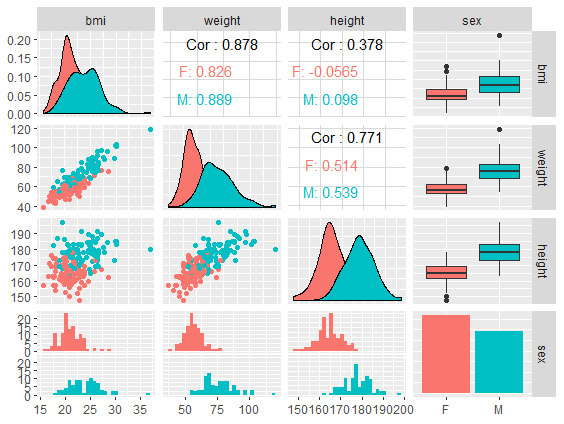
Scatterplot matrix - ggpairs by group
# Color points by sex group
daviskeep %>%
select(bmi, weight, height, sex) %>%
GGally::ggpairs(aes(color = sex))
Descriptive stats by group
No group counts
# Get mean and sd for bmi by sex
daviskeep %>% group_by(sex) %>%
select(sex, bmi) %>%
summarise(across(everything(),
list(mean = ~ mean(.x),
sd = ~ sd(.x))))
# A tibble: 2 × 3
sex bmi_mean bmi_sd
<fct> <dbl> <dbl>
1 F 21.0 2.18
2 M 23.9 3.12
With group counts
# Add N = n(), get mean, sd for bmi by sex
daviskeep %>% group_by(sex) %>%
select(sex, bmi) %>%
summarise(across(everything(),
list(mean = ~ mean(.x),
sd = ~ sd(.x))),
N = n())
# A tibble: 2 × 4
sex bmi_mean bmi_sd N
<fct> <dbl> <dbl> <int>
1 F 21.0 2.18 111
2 M 23.9 3.12 88
1 https://dplyr.tidyverse.org/reference/context.html
T-tests SAS and R
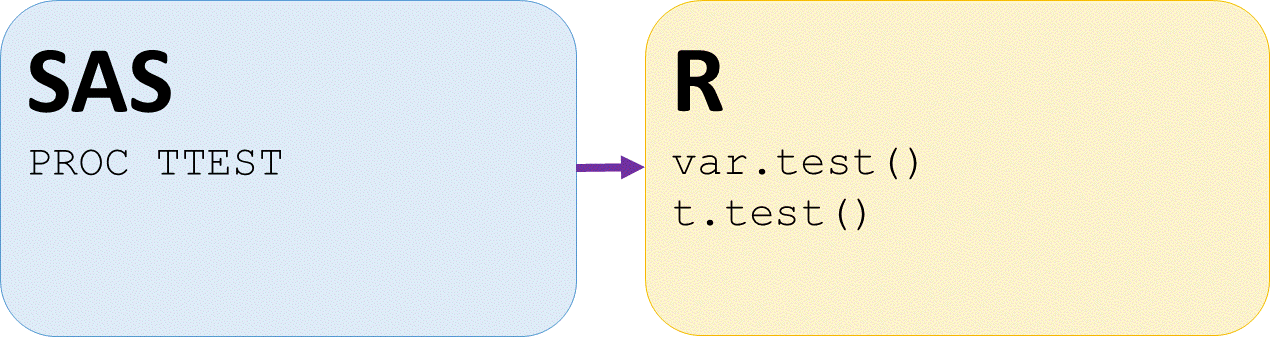
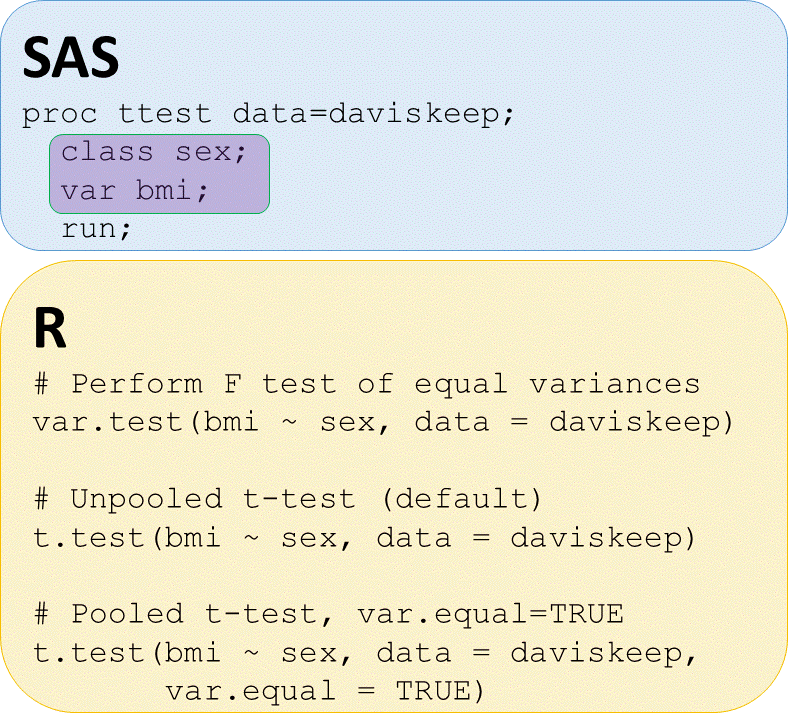
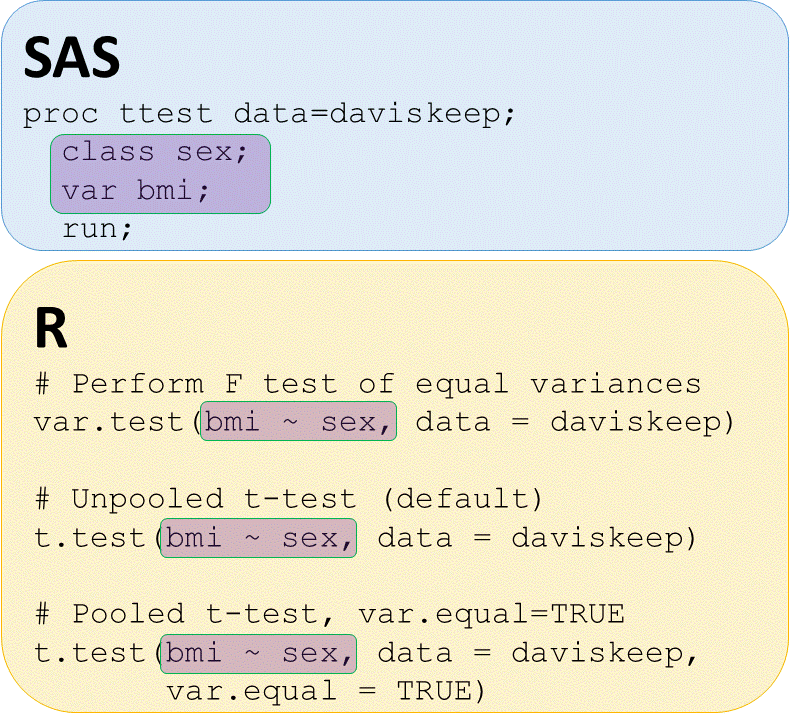
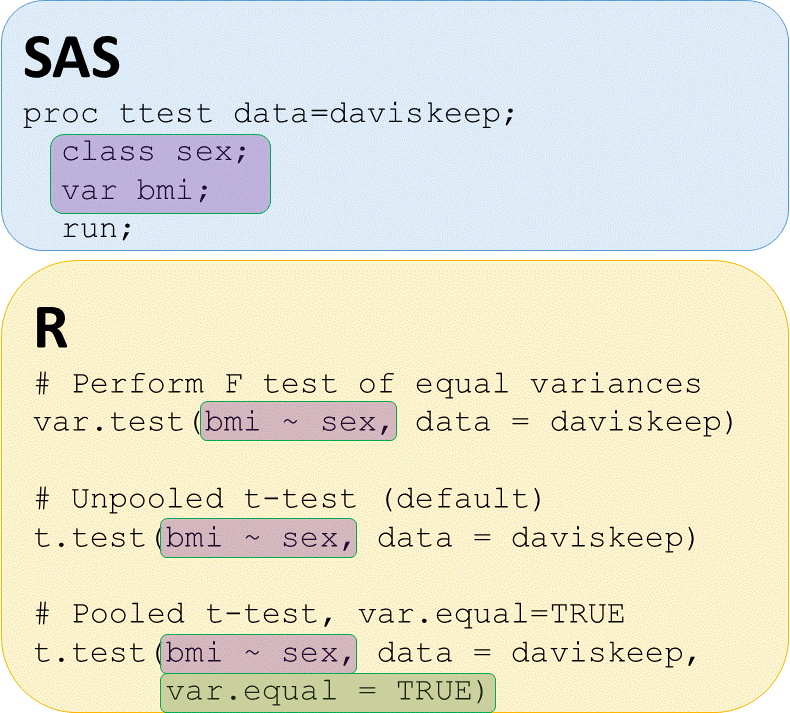
T-tests - check for equal variances
# Perform equal variance test
var.test(bmi ~ sex, data = daviskeep)
F test to compare two variances
data: bmi by sex
F = 0.48637, num df = 110, denom df = 87, p-value = 0.0003668
alternative hypothesis: true ratio of variances is not equal to 1
95 percent confidence interval:
0.3244691 0.7221946
sample estimates:
ratio of variances
0.4863699
T-tests - pooled and unpooled
# UNPOOLED t-test bmi by sex
t.test(bmi ~ sex,
data = daviskeep)
Welch Two Sample t-test
data: bmi by sex
t = -7.5158, df = 149.45,
p-value = 4.819e-12
alternative hypothesis: true difference
in means is not equal to 0
95 percent confidence interval:
-3.716353 -2.169035
sample estimates:
mean in group F mean in group M
20.95632 23.89901
# POOLED t-test bmi by sex
t.test(bmi ~ sex, data = daviskeep,
var.equal = TRUE)
Two Sample t-test
data: bmi by sex
t = -7.8239, df = 197,
p-value = 3.055e-13
alternative hypothesis: true difference
in means is not equal to 0
95 percent confidence interval:
-3.684428 -2.200960
sample estimates:
mean in group F mean in group M
20.95632 23.89901
Let's explore bivariate relationships in abalones!
R For SAS Users

