Features with missing values or little variance
Dimensionality Reduction in Python

Jeroen Boeye
Head of Machine Learning, Faktion
Creating a feature selector
print(ansur_df.shape)
(6068, 94)
from sklearn.feature_selection import VarianceThreshold sel = VarianceThreshold(threshold=1)sel.fit(ansur_df) mask = sel.get_support() print(mask)
array([ True, True, ..., False, True])
Applying a feature selector
print(ansur_df.shape)
(6068, 94)
reduced_df = ansur_df.loc[:, mask]
print(reduced_df.shape)
(6068, 93)
Variance selector caveats
buttock_df.boxplot()
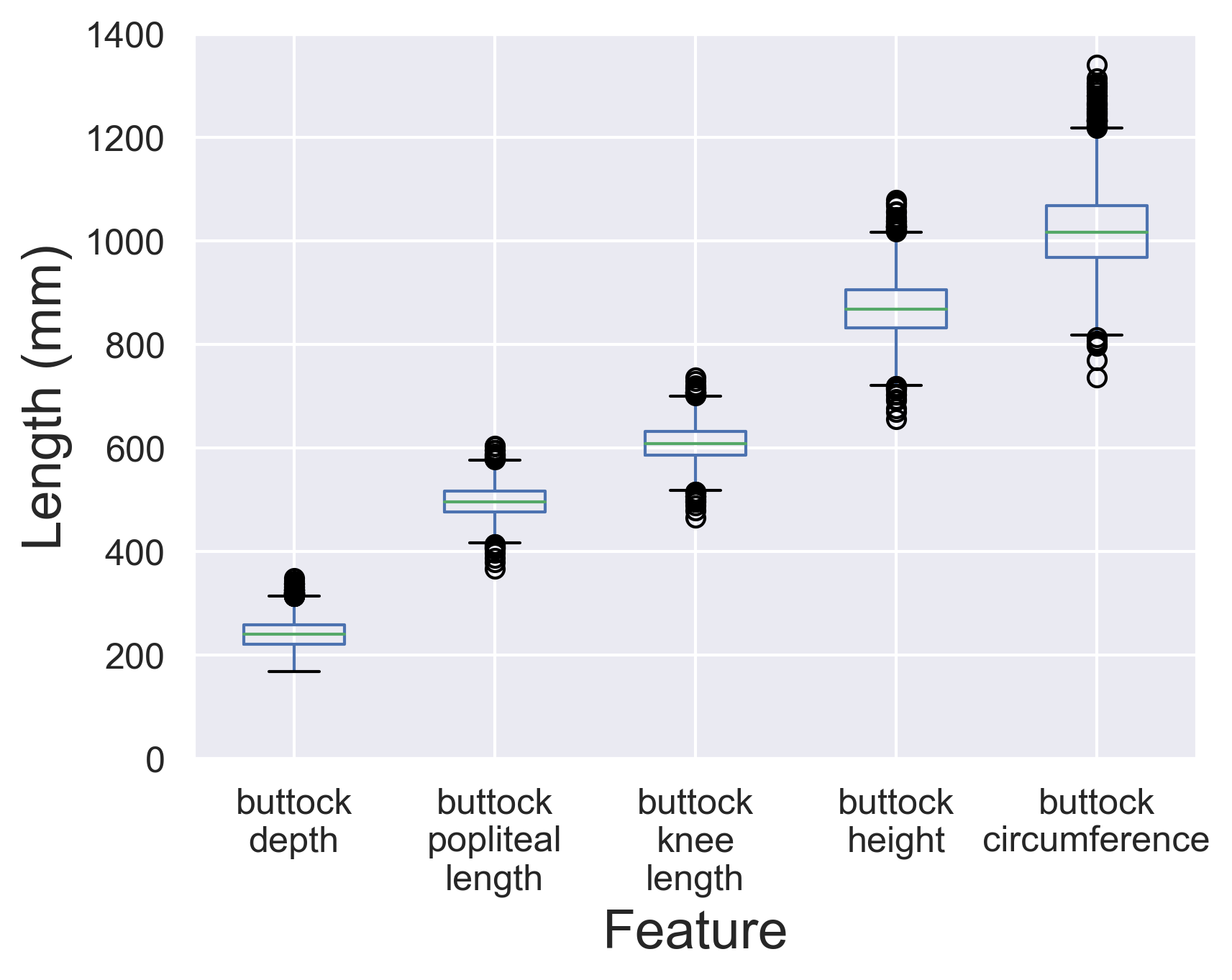
Normalizing the variance
from sklearn.feature_selection import VarianceThreshold sel = VarianceThreshold(threshold=0.005) sel.fit(ansur_df / ansur_df.mean())mask = sel.get_support() reduced_df = ansur_df.loc[:, mask] print(reduced_df.shape)
(6068, 45)
Missing value selector
Missing value selector
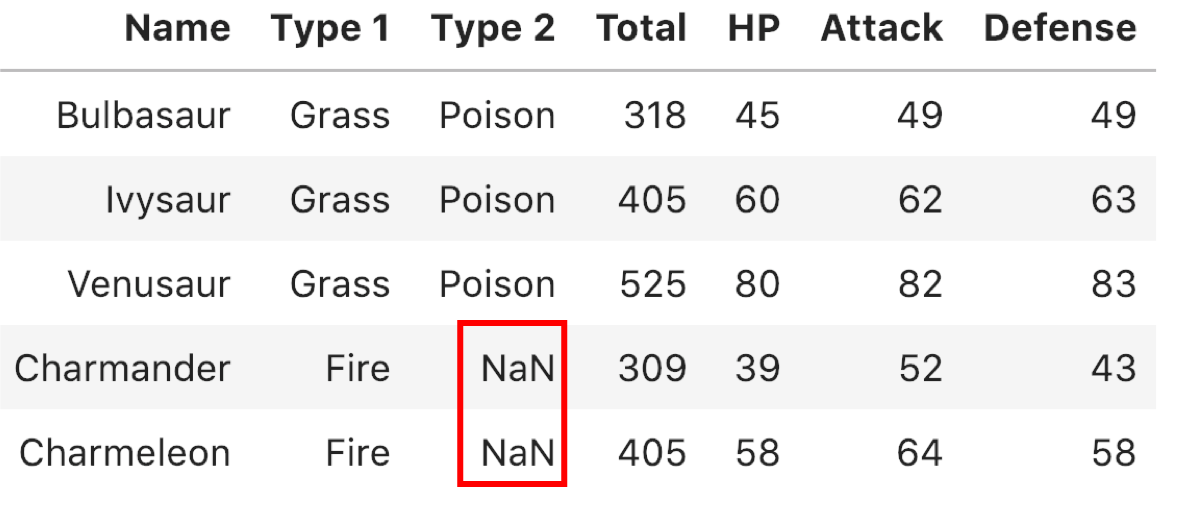
Identifying missing values
pokemon_df.isna()
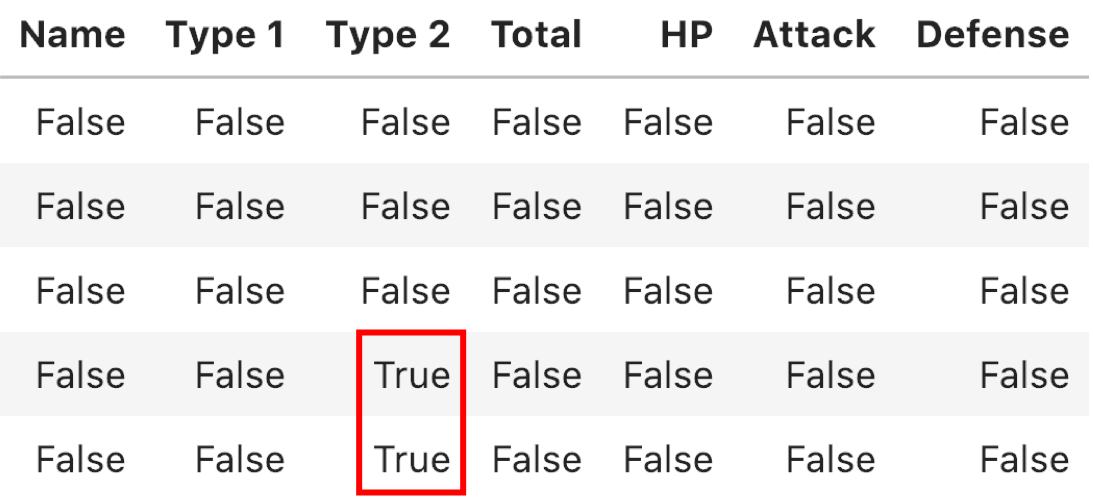
Counting missing values
pokemon_df.isna().sum()
Name 0
Type 1 0
Type 2 386
Total 0
HP 0
Attack 0
Defense 0
dtype: int64
Counting missing values
pokemon_df.isna().sum() / len(pokemon_df)
Name 0.00
Type 1 0.00
Type 2 0.48
Total 0.00
HP 0.00
Attack 0.00
Defense 0.00
dtype: float64
Applying a missing value threshold
# Fewer than 30% missing values = True value
mask = pokemon_df.isna().sum() / len(pokemon_df) < 0.3
print(mask)
Name True
Type 1 True
Type 2 False
Total True
HP True
Attack True
Defense True
dtype: bool
Applying a missing value threshold
reduced_df = pokemon_df.loc[:, mask]
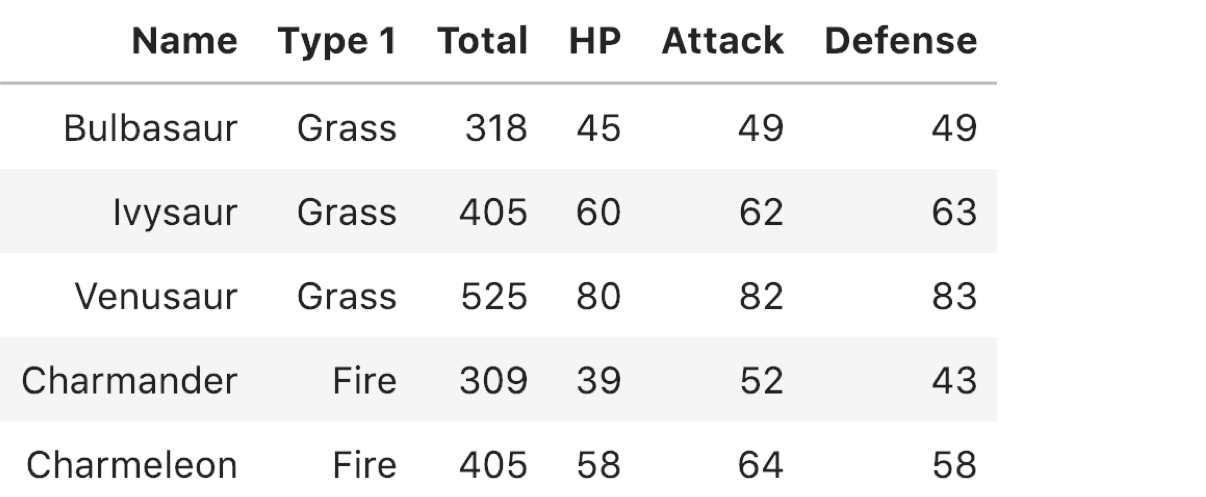
reduced_df.head()
Let's practice
Dimensionality Reduction in Python

