Loss functions Part I
Designing Machine Learning Workflows in Python

Dr. Chris Anagnostopoulos
Honorary Associate Professor
The KDD '99 cup dataset
kdd.iloc[0]
kdd.iloc[0]
duration 51
protocol_type tcp
service smtp
flag SF
src_bytes 1169
dst_bytes 332
land 0
...
dst_host_rerror_rate 0
dst_host_srv_rerror_rate 0
label good
False positives vs false negatives
Binarize label:
kdd['label'] = kdd['label'] == 'bad'
Fit a Gaussian Naive Bayes classifier:
clf = GaussianNB().fit(X_train, y_train)
predictions = clf.predict(X_test)
results = pd.DataFrame({
'actual': y_test,
'predicted': predictions
})

False positives vs false negatives
Binarize label:
kdd['label'] = kdd['label'] == 'bad'
Fit a Gaussian Naive Bayes classifier:
clf = GaussianNB().fit(X_train, y_train)
predictions = clf.predict(X_test)
results = pd.DataFrame({
'actual': y_test,
'predicted': predictions
})

False positives vs false negatives
Binarize label:
kdd['label'] = kdd['label'] == 'bad'
Fit a Gaussian Naive Bayes classifier:
clf = GaussianNB().fit(X_train, y_train)
predictions = clf.predict(X_test)
results = pd.DataFrame({
'actual': y_test,
'predicted': predictions
})

False positives vs false negatives
Binarize label:
kdd['label'] = kdd['label'] == 'bad'
Fit a Gaussian Naive Bayes classifier:
clf = GaussianNB().fit(X_train, y_train)
predictions = clf.predict(X_test)
results = pd.DataFrame({
'actual': y_test,
'predicted': predictions
})

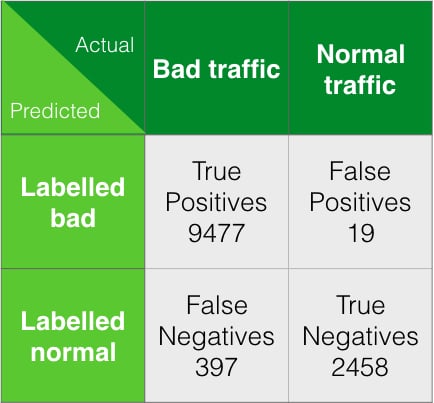
The confusion matrix
conf_mat = confusion_matrix(
ground_truth, predictions)
array([[9477, 19],
[ 397, 2458]])
tn, fp, fn, tp = conf_mat.ravel()
(fp, fn)
(19, 397)
Scalar performance metrics
accuracy = 1-(fp + fn)/len(ground_truth)recall = tp/(tp+fn)fpr = fp/(tn+fp)precision = tp/(tp+fp)f1 = 2*(precision*recall)/(precision+recall)
accuracy_score(ground_truth, predictions)
recall_score(ground_truth, predictions)
precision_score(ground_truth, predictions)
f1_score(ground_truth, predictions)
False positives vs false negatives
Classifier A:
tn, fp, fn, tp = confusion_matrix(
ground_truth, predictions_A).ravel()
(fp,fn)
(3, 3)
cost = 10 * fp + fn
33
Classifier B:
tn, fp, fn, tp = confusion_matrix(
ground_truth, predictions_B).ravel()
(fp,fn)
(0, 26)
cost = 10 * fp + fn
26
Which classifier is better?
Designing Machine Learning Workflows in Python

