Model complexity and overfitting
Designing Machine Learning Workflows in Python

Dr. Chris Anagnostopoulos
Honorary Associate Professor
What is model complexity?
RandomForestClassifier() takes additional arguments, like max_depth:
help(RandomForestClassifier)
Help on class RandomForestClassifier in module sklearn.ensemble.forest:
...
| max_depth : integer or None, optional (default=None)
| The maximum depth of the tree. If None, then nodes are expanded until
| all leaves are pure or until all leaves contain less than
| min_samples_split samples.
m2 = RandomForestClassifier( max_depth=2) m2.fit(X_train, y_train)m2.estimators_[0]
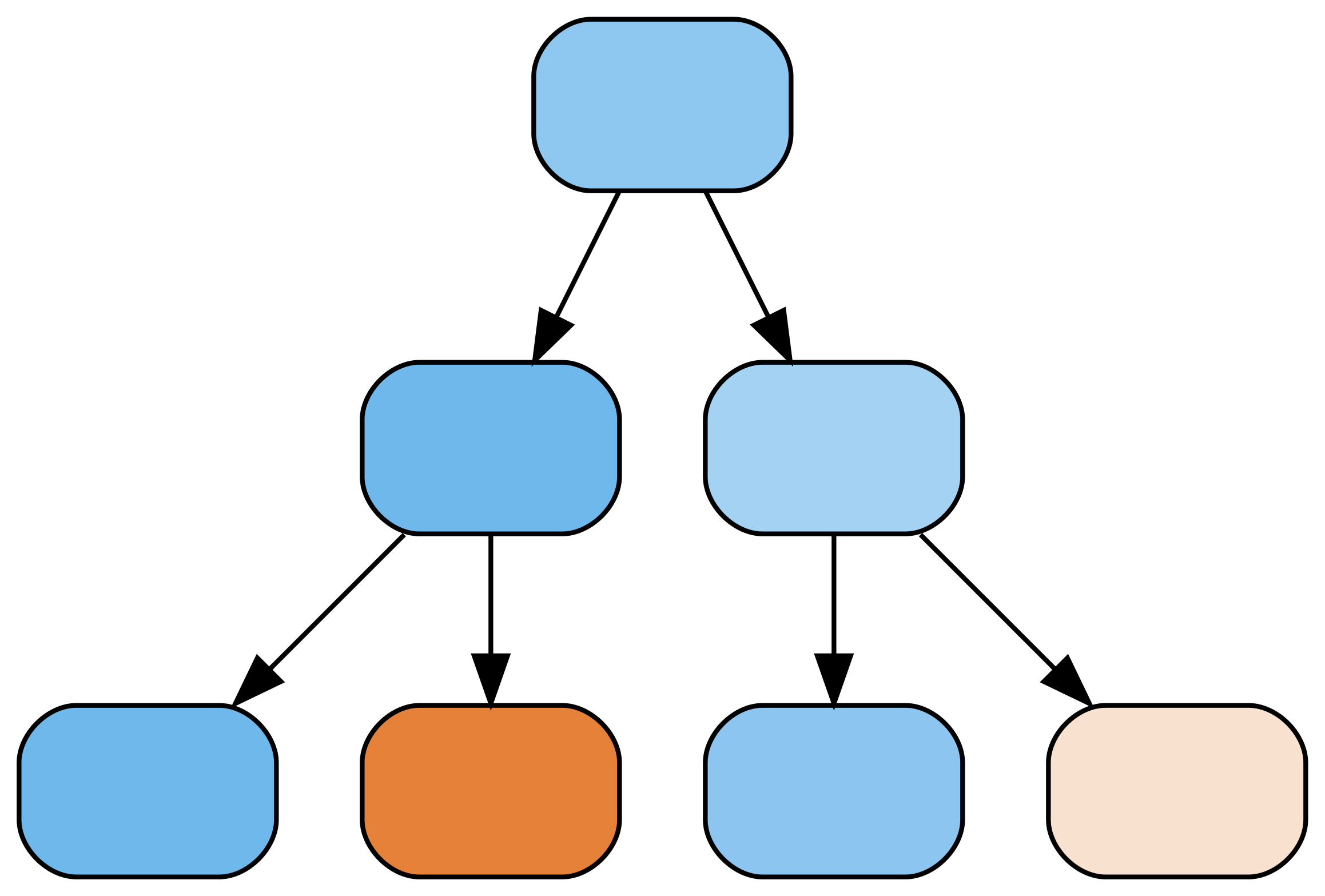
m4 = RandomForestClassifier( max_depth=4) m4.fit(X_train, y_train)m4.estimators_[0]
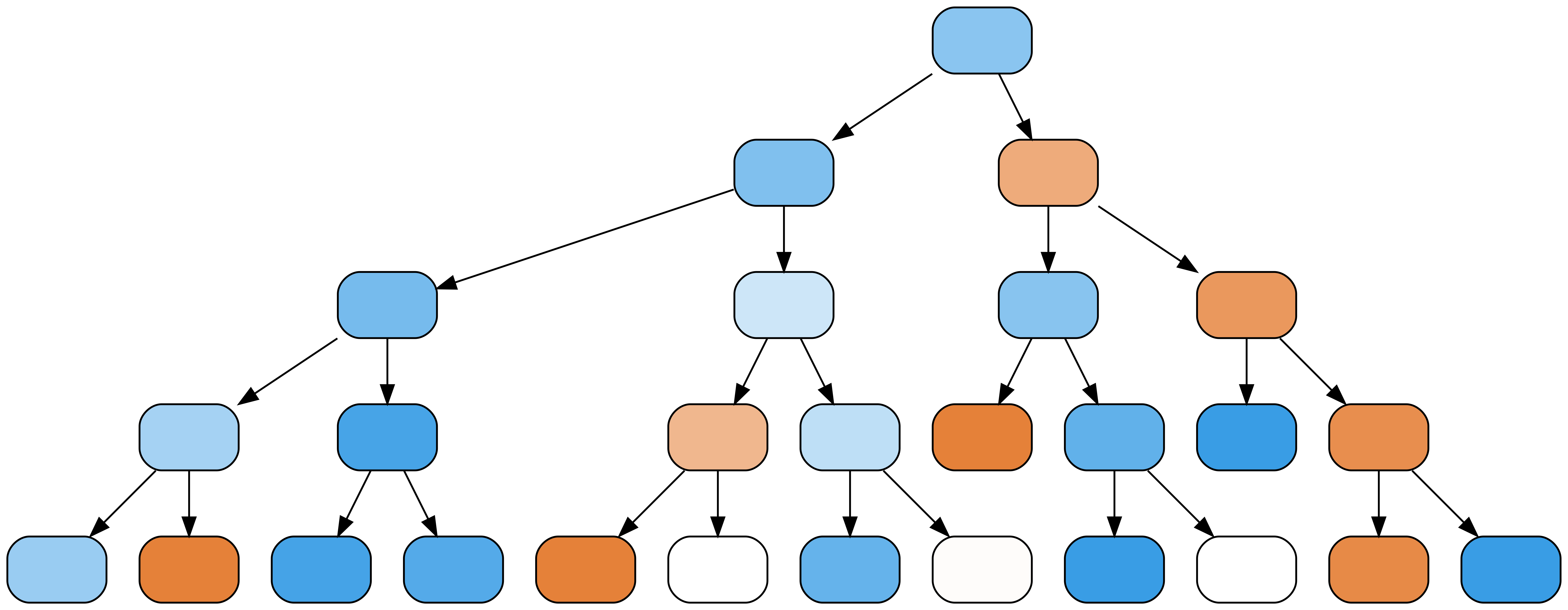
Cross-validation
Assess accuracy using cross_val_score():
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_scorecross_val_score(RandomForestClassifier(), X, y)
array([0.7218 , 0.7682, 0.7866])
numpy.mean(cross_val_score(RandomForestClassifier(), X, y))
0.7589
Tuning model complexity
Tune the tree depth using GridSearchCV():
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
param_grid = {'max_depth':[5,10,20]}
grid = GridSearchCV(RandomForestClassifier(), param_grid)
grid.fit(X,y)
grid._best_params
{'max_depth': 10}
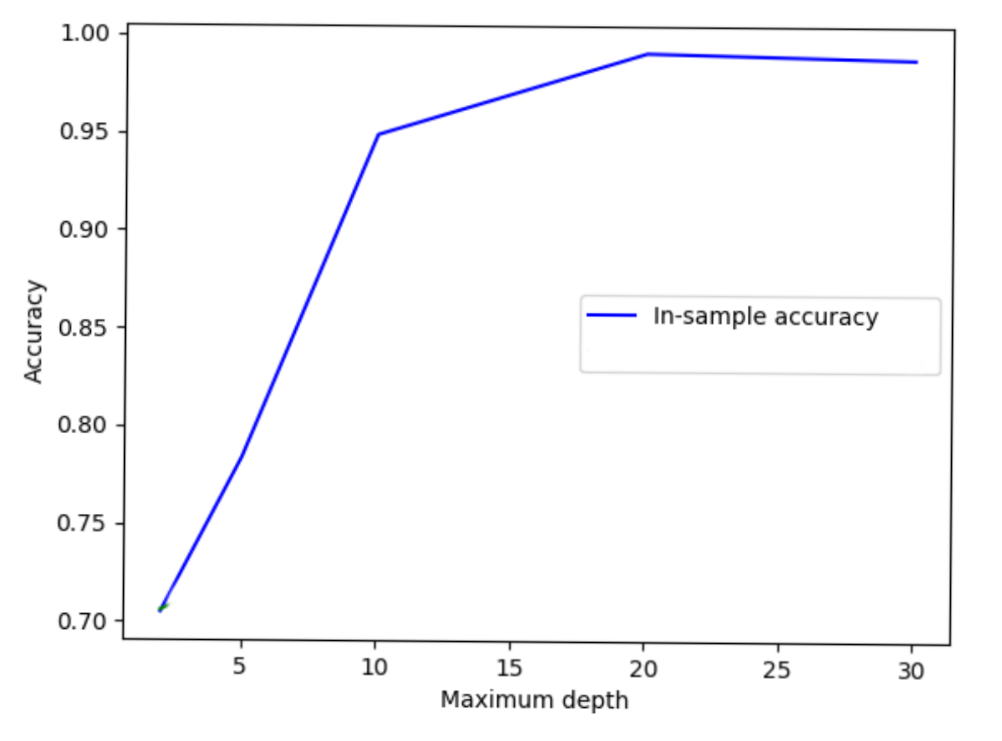
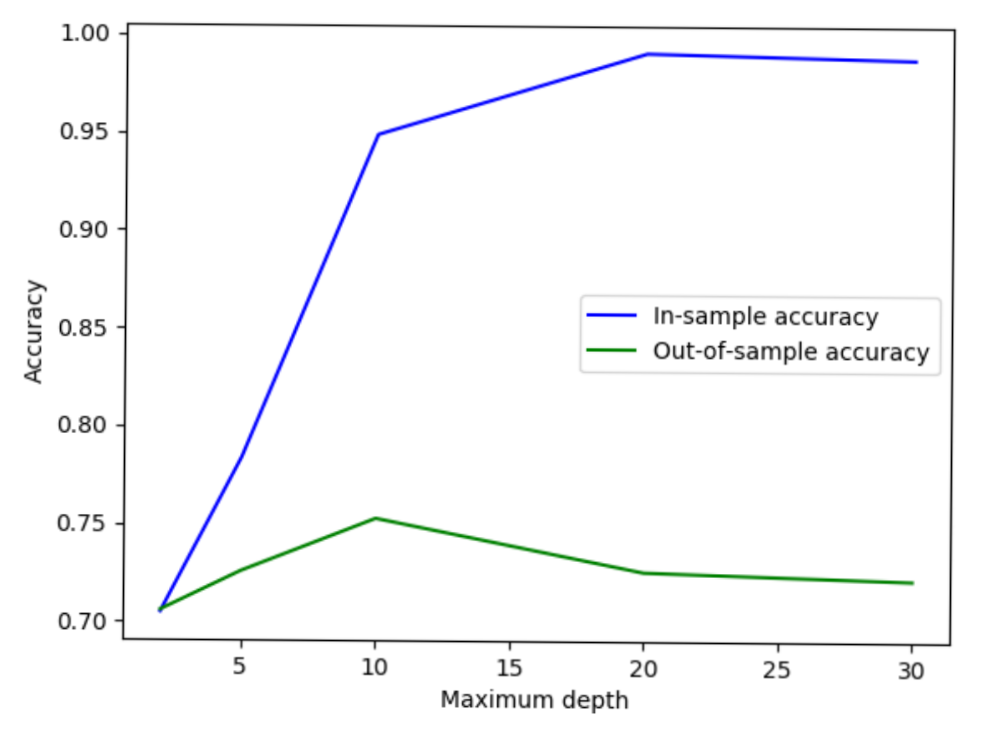
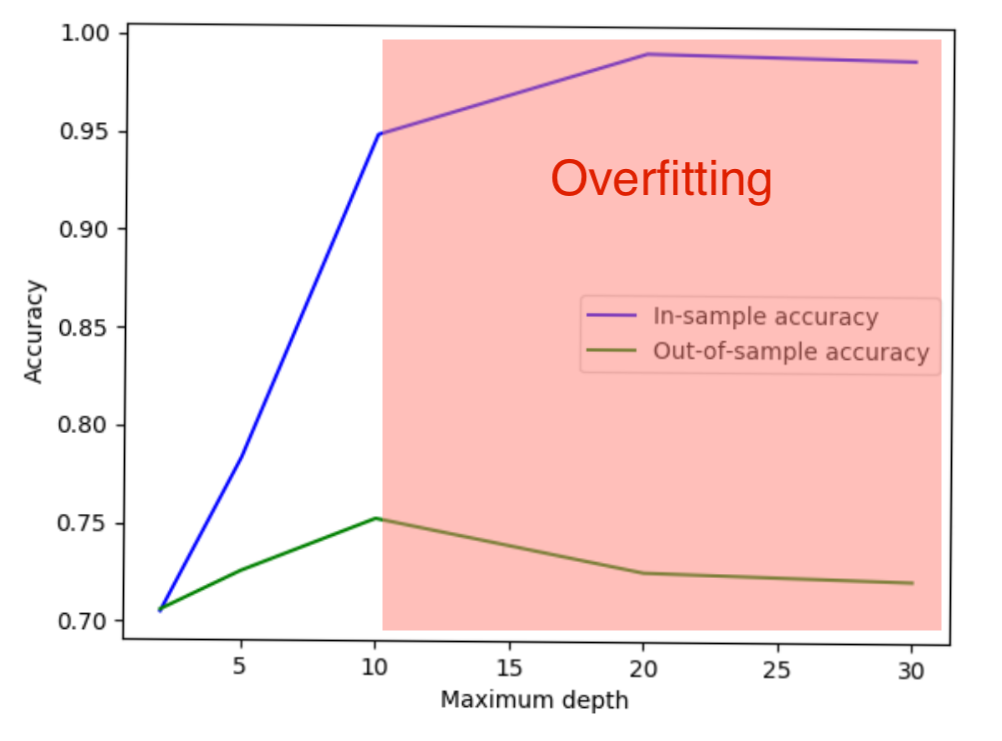
More complex is not always better!
Designing Machine Learning Workflows in Python

