Word Count Representation
Feature Engineering for Machine Learning in Python

Robert O'Callaghan
Director of Data Science, Ordergroove
Text to columns
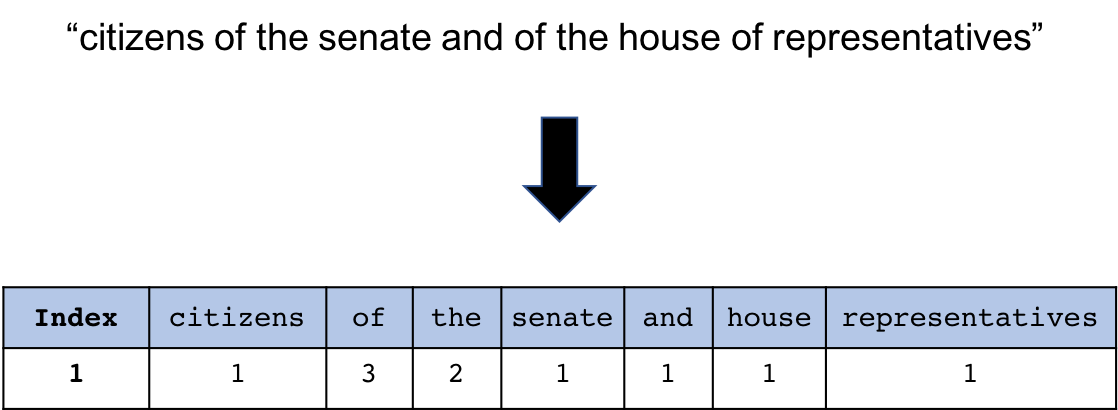
Initializing the vectorizer
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
cv = CountVectorizer()
print(cv)
CountVectorizer(analyzer=u'word', binary=False,
decode_error=u'strict',
dtype=<type 'numpy.int64'>,
encoding=u'utf-8', input=u'content',
lowercase=True, max_df=1.0, max_features=None,
min_df=1,ngram_range=(1, 1), preprocessor=None,
stop_words=None, strip_accents=None,
token_pattern=u'(?u)\\b\\w\\w+\\b',
tokenizer=None, vocabulary=None
Specifying the vectorizer
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
cv = CountVectorizer(min_df=0.1, max_df=0.9)
min_df: minimum fraction of documents the word must occur in
max_df: maximum fraction of documents the word can occur in
Fit the vectorizer
cv.fit(speech_df['text_clean'])
Transforming your text
cv_transformed = cv.transform(speech_df['text_clean'])
print(cv_transformed)
<58x8839 sparse matrix of type '<type 'numpy.int64'>'
Transforming your text
cv_transformed.toarray()
Getting the features
feature_names = cv.get_feature_names()
print(feature_names)
[u'abandon', u'abandoned', u'abandonment', u'abate',
u'abdicated', u'abeyance', u'abhorring', u'abide',
u'abiding', u'abilities', u'ability', u'abject'...
Fitting and transforming
cv_transformed = cv.fit_transform(speech_df['text_clean'])
print(cv_transformed)
<58x8839 sparse matrix of type '<type 'numpy.int64'>'
Putting it all together
cv_df = pd.DataFrame(cv_transformed.toarray(),
columns=cv.get_feature_names())\
.add_prefix('Counts_')
print(cv_df.head())
Counts_aback Counts_abandoned Counts_a...
0 1 0 ...
1 0 0 ...
2 0 1 ...
3 0 1 ...
4 0 0 ...
1 ```out Counts_aback Counts_abandon Counts_abandonment 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 2 0 1 0 3 0 1 0 4 0 0 0 ```
Updating your DataFrame
speech_df = pd.concat([speech_df, cv_df],
axis=1, sort=False)
print(speech_df.shape)
(58, 8845)
Let's practice!
Feature Engineering for Machine Learning in Python

