Poisson distributions
Foundations of Probability in Python

Alexander A. Ramírez M.
CEO @ Synergy Vision
Poisson modeling


Poisson distribution properties
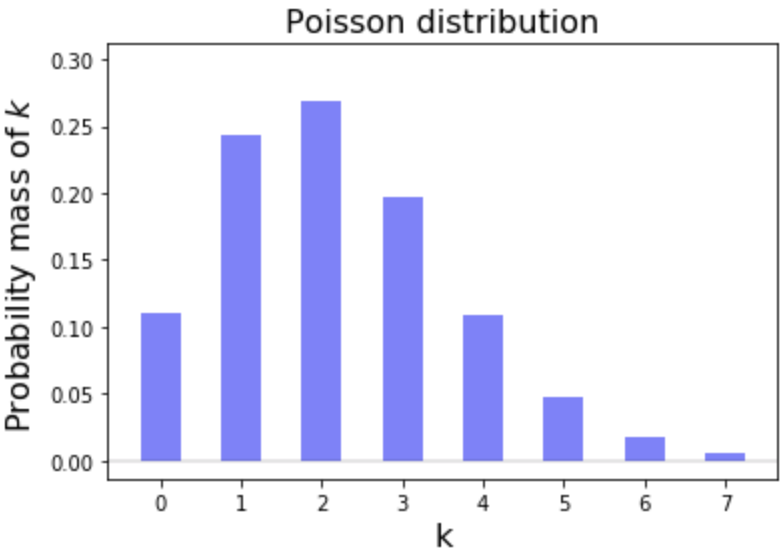
Probability mass function (pmf)

Imagine you have 2.2 calls per minute.
Probability mass function (pmf) (Cont.)
$$ $$
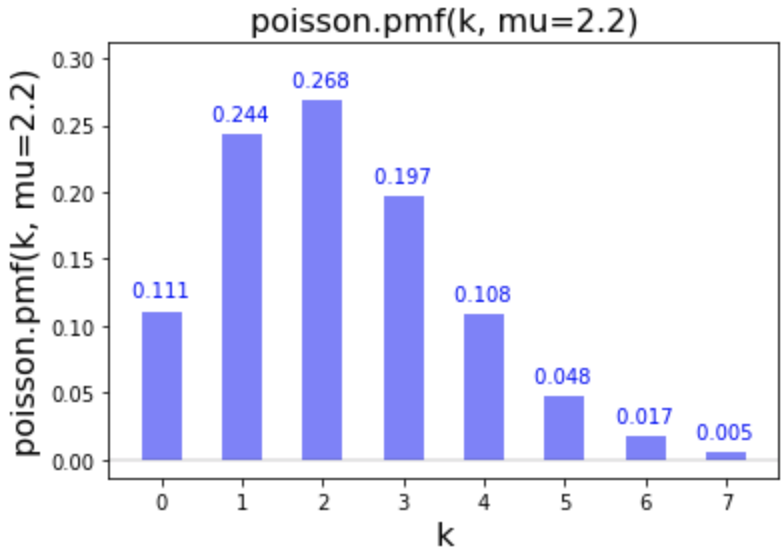
In Python we do the following:
# Import poisson
from scipy.stats import poisson
# Calculate the probability mass
# with pmf
poisson.pmf(k=3, mu=2.2)
0.19663867170702193
mu parameter specifies the mean of successful events.
pmf examples
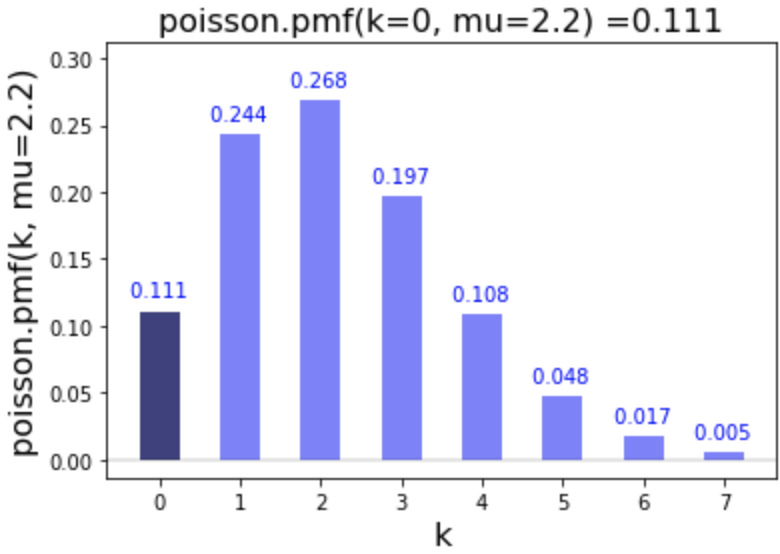
# Calculate pmf of 0
poisson.pmf(k=0, mu=2.2)
0.11080315836233387
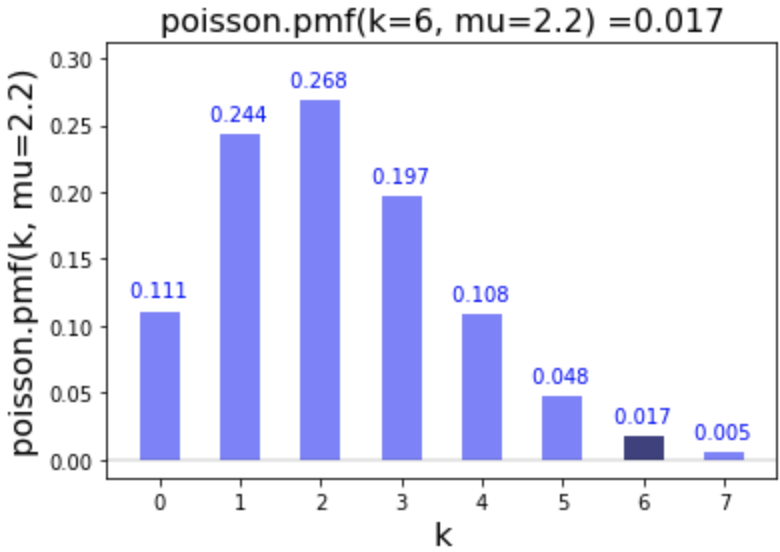
# Calculate pmf of 6
poisson.pmf(k=6, mu=2.2)
0.01744840480280308
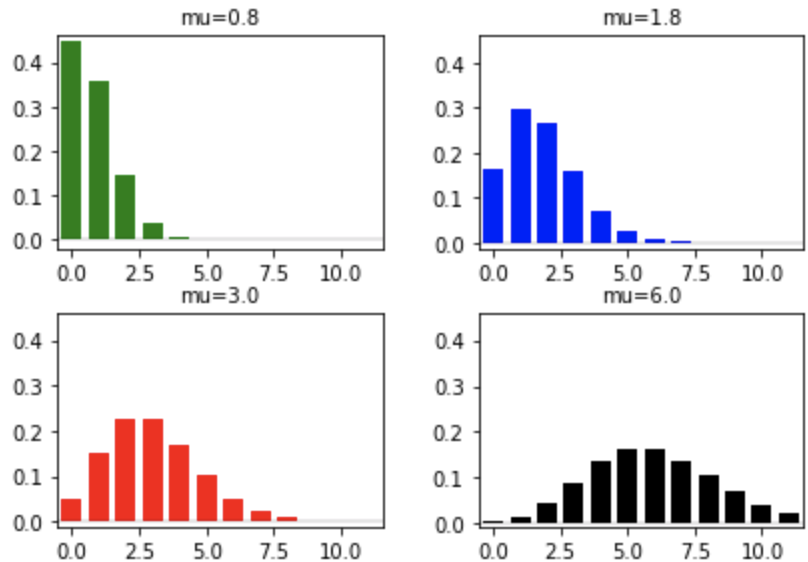
Different means
Cumulative distribution function (cdf)
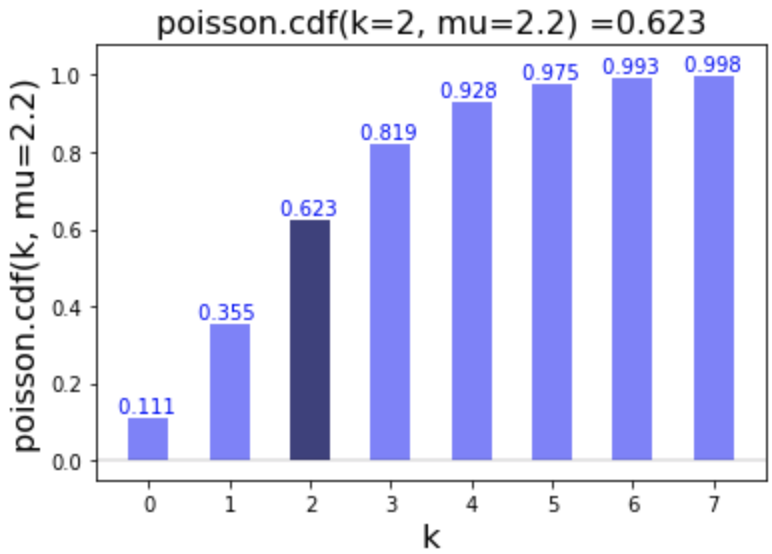
# Calculate cdf of 2
poisson.cdf(k=2, mu=2.2)
0.6227137499963162
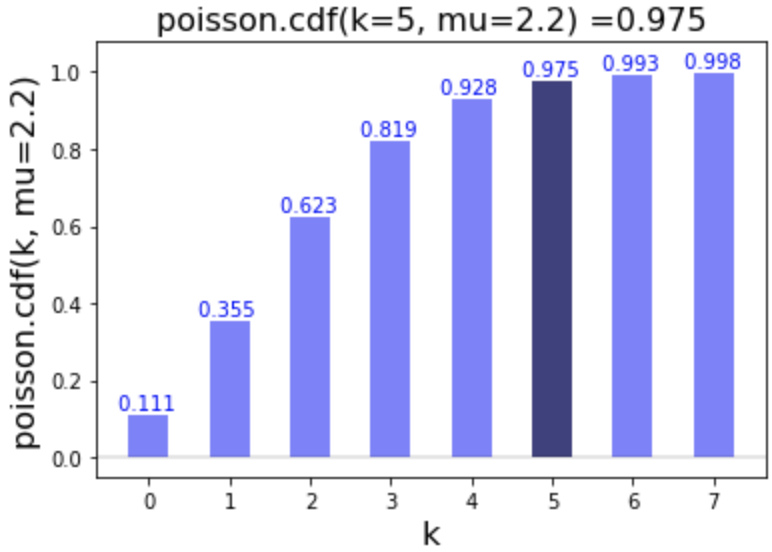
# Calculate cdf of 5
poisson.cdf(k=5, mu=2.2)
0.9750902496952996
Survival function and percent point function (ppf)
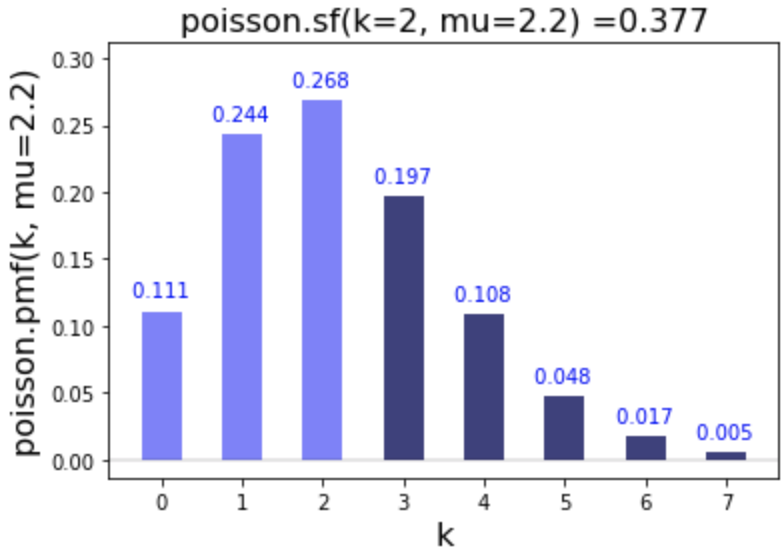
# Calculate sf of 2
poisson.sf(k=2, mu=2.2)
0.3772862500036838
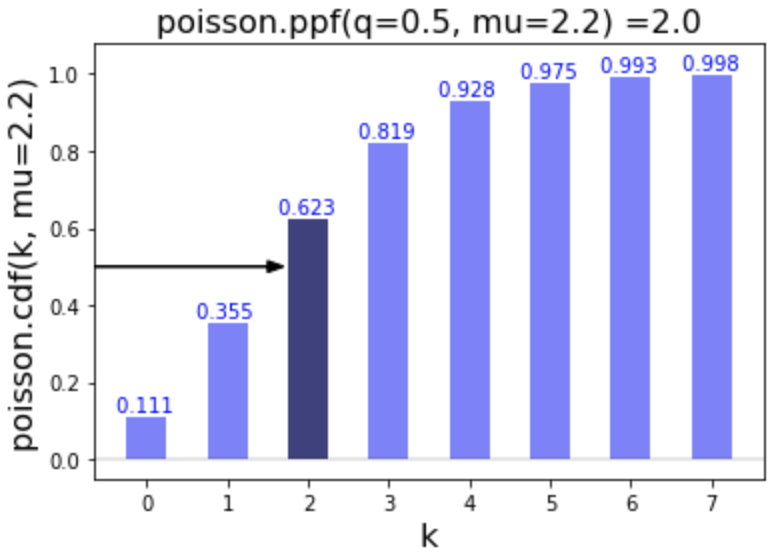
# Calculate ppf of 0.5
poisson.ppf(q=0.5, mu=2.2)
2.0
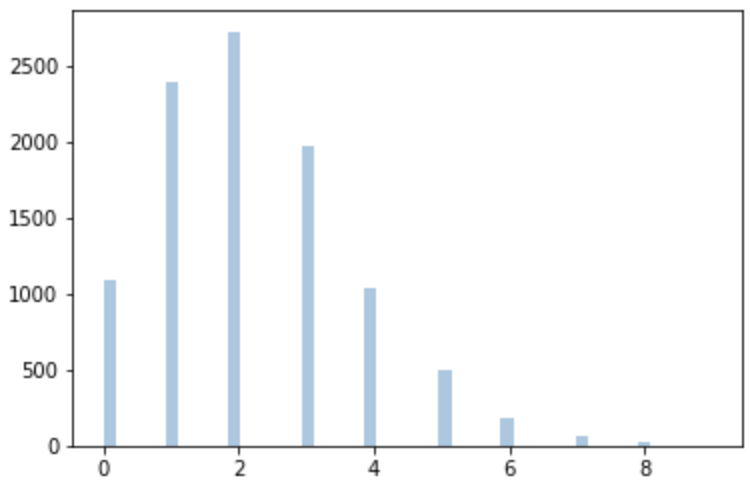
Sample generation (rvs)
# Import poisson, matplotlib.pyplot, and seaborn
from scipy.stats import poisson
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
# Create the sample using poisson.rvs()
sample = poisson.rvs(mu=2.2, size=10000, random_state=13)
# Plot the sample
sns.distplot(sample, kde=False)
plt.show()
Sample generation (Cont.)
Let's practice with Poisson
Foundations of Probability in Python

