Vectorization over Pandas series
Writing Efficient Code with pandas

Leonidas Souliotis
PhD Candidate
DataFrames as arrays
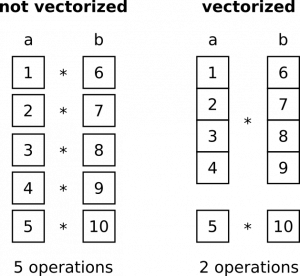
How to perform pandas vectorization
start_time = time.time()
poker[['R1', 'R2', 'R3', 'R4', 'R5']].sum(axis=1)
print("Time using pandas vectorization: {} sec".format(time.time() - start_time))
Time using pandas vectorization: 0.0026819705 sec
poker[['R1', 'R2', 'R3', 'R4', 'R5']].sum(axis=1).head()
| | |
|--------------|----|
| 0 | 47 |
| 1 | 47 |
| 2 | 47 |
| 3 | 47 |
| 4 | 47 |
| dtype: int64 | -- |
Comparison to the previous methods
data_generator = data.iterrows()
start_time = time.time()
for index, value in data_generator:
sum([value[1], value[3], value[5], value[7]])
print("Time using .iterrows(){} seconds" % (time.time() - start_time))
Results from the above operation calculated in 3.37918996 seconds
start_time = time.time()
data[['R1', 'R2', 'R3', 'R4', 'R5']].apply(lambda x: sum(x),axis=1)
print("Results from the above operation calculated in %s seconds" % (time.time() - start_time))
Results from the above operation calculated in 0.637711048 seconds
- Difference between vectorization and the `.iterows()` function: 111,800.75%
- Difference between vectorization and the `.apply()` function: 20,853%
Let's do it!
Writing Efficient Code with pandas

