Cross-validation
Model Validation in Python

Kasey Jones
Data Scientist
Cross-validation
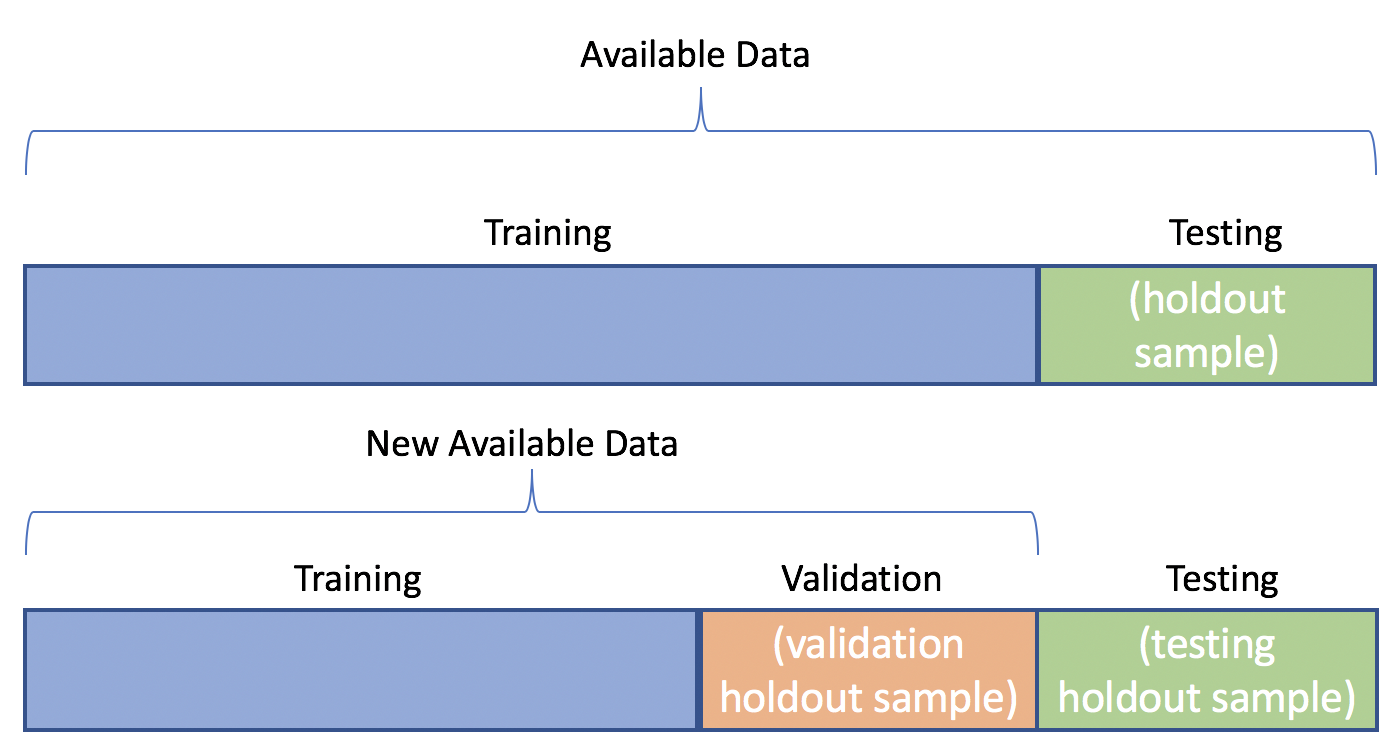
Cross-validation
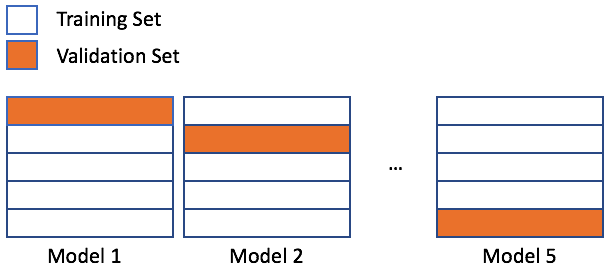
n_splits: number of cross-validation splits
shuffle: boolean indicating to shuffle data before splitting
random_state: random seed
from sklearn.model_selection import KFold X = np.array(range(40)) y = np.array([0] * 20 + [1] * 20) kf = KFold(n_splits=5)splits = kf.split(X)
kf = KFold(n_splits=5) splits = kf.split(X)for train_index, test_index in splits: print(len(train_index), len(test_index))
32 8 32 8 32 8 32 8 32 8
# Print one of the index sets:
print(train_index, test_index)
[ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 ...]
[32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39]
rfr = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=25, random_state=1111)errors = [] for train_index, val_index in splits: X_train, y_train = X[train_index], y[train_index] X_val, y_val = X[val_index], y[val_index] rfr.fit(X_train, y_train) predictions = rfr.predict(X_val) errors.append(<some_accuracy_metric>)print(np.mean(errors))
4.25
Practice time
Model Validation in Python

