Computing and describing predictions
Generalized Linear Models in Python

Ita Cirovic Donev
Data Science Consultant
Computing predictions
After obtaining model fit
- Fitted values for original $x$ values
Computing predictions
After obtaining model fit
fitted values for original $x$ values
New values of $x$ for predicted values
Computing predictions
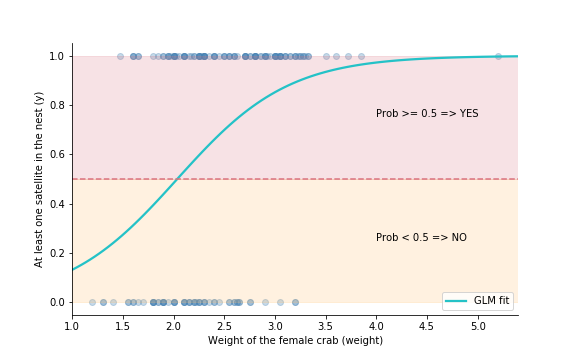
Horseshoe crab model
y ~ weight$$ \mu = \frac{\exp(-3.6947+1.8151 \times weight)}{1+\exp(-3.6947+1.8151 \times weight)} $$New measurement:
weight = 2.85
$$ \mu = \frac{\exp(-3.6947+1.8151 \times \color{blue}{2.85})}{1+\exp(-3.6947+1.8151 \times \color{blue}{2.85})} = 0.814 $$
Predictions in Python
- Compute model predictions for dataset
new_data# Compute model predictions model_GLM.predict(exog = new_data)
From probabilities to classes
Computing class predictions
# Extract fitted probabilities from model
crab['fitted'] = model.fittedvalues.values
# Define cut-off value
cut_off = 0.4
# Compute class predictions
crab['pred_class'] = np.where(crab['fitted'] > cut_off, 1, 0)
Computing class predictions
# Count occurences for each class
crab['pred_class'].value_counts()
1 151
0 22
| Cut-off | $\hat y=1$ | $\hat y=0$ |
|---|---|---|
| $\mu = 0.4$ | 151 | 22 |
| $\mu = 0.5$ | 126 | 47 |
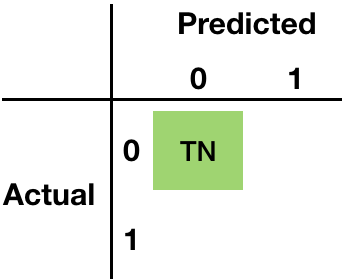
Confusion matrix
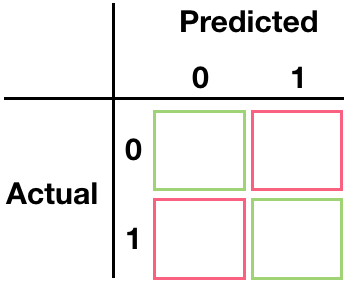
Confusion matrix - True Negatives
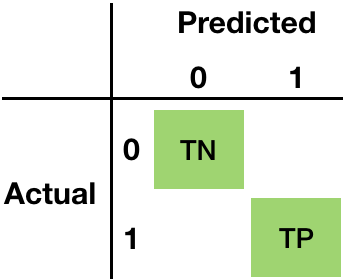
Confusion matrix - True Positives
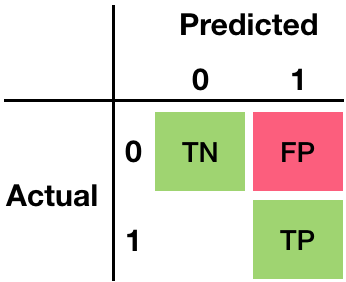
Confusion matrix - False Positives
Confusion matrix - False Negatives
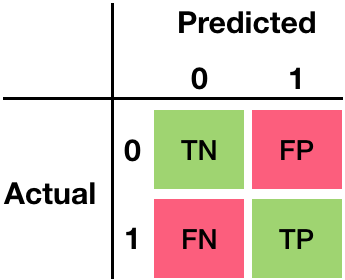
Confusion matrix in Python
print(pd.crosstab(y_actual, y_predicted,
rownames=['Actual'], colnames=['Predicted'],
margins = True))
Predicted 0 1 All
Actual
0 15 47 62
1 7 104 111
All 22 151 173
Let's practice!
Generalized Linear Models in Python

