Multivariable logistic regression
Generalized Linear Models in Python

Ita Cirovic Donev
Data Science Consultant
Multivariable setting
- Model formula $$ \text{logit}(y) = \beta_0+\beta_1\color{red}{x_1} $$
Multivariable setting
- Model formula $$ \text{logit}(y) = \color{blue}{\beta_0}+\color{blue}{\beta_1}\color{red}{x_1} $$
Multivariable setting
- Model formula $$ \text{logit}(y) = \beta_0+\beta_1x_1 + \beta_2\color{red}{x_2} + ... + \beta_p \color{red}{x_p} $$
Multivariable setting
Model formula $$ \text{logit}(y) = \beta_0+\beta_1x_1 + \color{blue}{\beta_2}\color{red}{x_2} + ... + \color{blue}{\beta_p}\color{red}{x_p} $$
In Python
model = glm('y ~ x1 + x2 + x3 + x4', data = my_data, family = sm.families.Binomial()).fit()
Example - well switching
formula = 'switch ~ distance100 + arsenic'
wells_fit = glm(formula = formula, data = wells,
family = sm.families.Binomial()).fit()
===============================================================================
coef std err z P>|z| [0.025 0.975]
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Intercept 0.0027 0.079 0.035 0.972 -0.153 0.158
distance100 -0.8966 0.104 -8.593 0.000 -1.101 -0.692
arsenic 0.4608 0.041 11.134 0.000 0.380 0.542
===============================================================================
Example - well switching
coef std err z P>|z| [0.025 0.975]
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Intercept 0.0027 0.079 0.035 0.972 -0.153 0.158
distance100 -0.8966 0.104 -8.593 0.000 -1.101 -0.692
arsenic 0.4608 0.041 11.134 0.000 0.380 0.542
- Both coefficients are statistically significant
- Sign of coefficients logical
- A unit-change in
distance100corresponds to a negative difference of 0.89 in the logit - A unit-change in
arseniccorresponds to a positive difference of 0.46 in the logit
Impact of adding a variable
- Impact of
arsenicvariable distance100changes from -0.62 to -0.89- Further away from the safe well
- More likely to have higher arsenic levels
coef std err
---------------------------------
Intercept 0.0027 0.079
distance100 -0.8966 0.104
arsenic 0.4608 0.041
coef std err
---------------------------------
Intercept 0.6060 0.060
distance100 -0.6291 0.097
Multicollinearity
- Variables that are correlated with other model variables
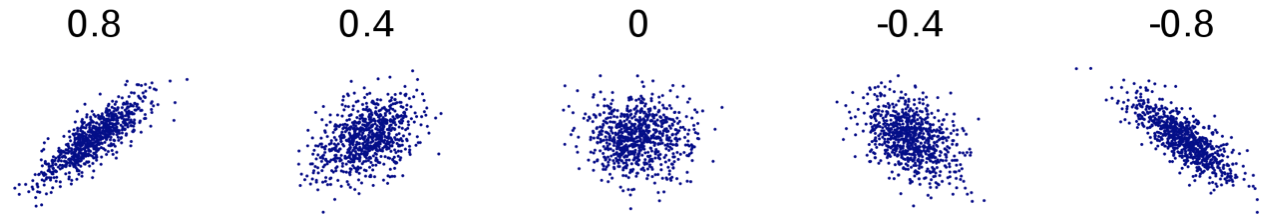
- Increase in standard errors of coefficients
- Coefficients may not be statistically significant
1 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Correlation_and_dependence
Presence of multicollinearity?
What to look for?
- Coefficient is not significant, but variable is highly correlated with $y$
- Adding/removing a variable significantly changes coefficients
- Not logical sign of the coefficient
- Variables have high pairwise correlation
Variance inflation factor (VIF)
- Most widely used diagnostic for multicollinearity
- Computed for each explanatory variable
- How inflated the variance of the coefficient is
- Suggested threshold VIF > 2.5
- In Python
from statsmodels.stats.outliers_influence import variance_inflation_factor
Let's practice!
Generalized Linear Models in Python

