Categorical and interaction terms
Generalized Linear Models in Python

Ita Cirovic Donev
Data Science Consultant
Categorical variables
- Simple binary variable
Yes, No
- Nominal variables
- Color:
red, green, blue
- Color:
- Ordinal variables
- Levels of education:
Education1, Education2,...,Education4
- Levels of education:
Analysis of covariance
Explanatory variables
- $x_1$: categorical (binary)
- $x_2$: continuous
Logistic model $$ \text{logit}(y=1|X)=\beta_0 + \beta_1x_1 + \beta_2x_2 $$
Analysis of covariance
- Explanatory variables
- $x_1$: categorical (binary)
- $x_2$: continuous
- Logistic model $$ \text{logit}(y=1|\color{red}{X})=\beta_0 + \beta_1\color{red}{x_1} + \beta_2\color{red}{x_2} $$
Analysis of covariance
- Explanatory variables
- $x_1$: categorical (binary)
- $x_2$: continuous
Logistic model $$ \text{logit}(y=1|X)=\beta_0 + \beta_1\color{red}{x_1} + \beta_2x_2 $$
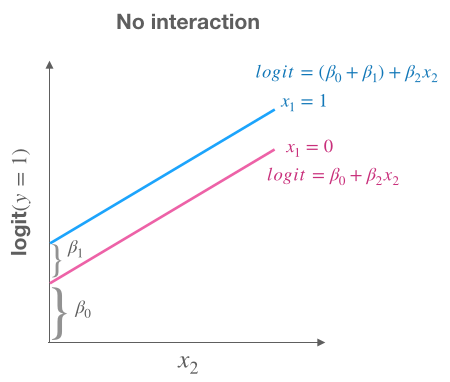
If $x_1=0$ then $$ \text{logit}(y=1|\color{red}{x_1=0},x_2)=\beta_0 + \color{red}{0} + \beta_2x_2 $$
Analysis of covariance
- Explanatory variables
- $x_1$: categorical (binary)
- $x_2$: continuous
Logistic model $$ \text{logit}(y=1|X)=\beta_0 + \beta_1\color{red}{x_1} + \beta_2x_2 $$
If $x_1=0$ then $$ \text{logit}(y=1|x_1=0,x_2)=\beta_0 + 0 + \beta_2x_2 $$
If $x_1 = 1$ then $$ \text{logit}(y=1|\color{red}{x_1=1},x_2)=\beta_0 + \color{red}{\beta_1} + \beta_2x_2 $$ $$ \text{logit}(y=1|\color{red}{x_1=1},x_2)=(\beta_0 + \color{red}{\beta_1}) + \beta_2x_2 $$
Assumptions
Assumptions
Assumptions

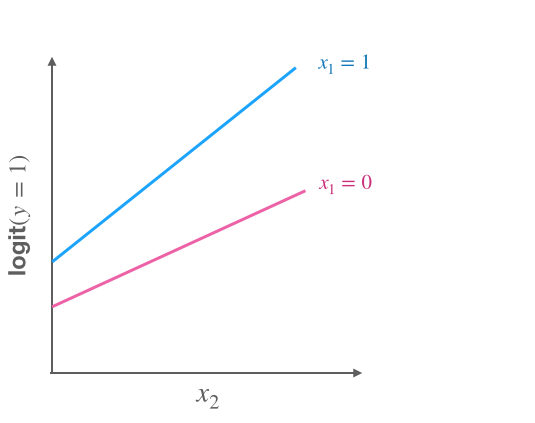
Interactions
- Not equal slopes $\rightarrow$ presence of interaction
- The effect of $x_1$ on $y$ depends on the level of $x_2$ and vice versa
- Logistic model allowing for interactions $$ \text{logit}(y=1|X)=\beta_0 + \beta_1x_1 + \beta_2x_2 + \color{red}{\beta_3x_1x_2} $$
Interactions
- Not equal slopes $\rightarrow$ presence of interaction
- The effect of $x_1$ on $y$ depends on the level of $x_2$ and vice versa
Logistic model allowing for interactions $$ \text{logit}(y=1|X)=\beta_0 + \beta_1x_1 + \beta_2x_2 + \beta_3x_1x_2 $$
If $x_1=0$ then $$ \text{logit}(y=1|\color{red}{x_1=0},x_2)=\beta_0 + \color{red}{0} + \beta_2x_2 + \color{red}{0} $$
Interactions
- Not equal slopes $\rightarrow$ presence of interaction
- The effect of $x_1$ on $y$ depends on the level of $x_2$ and vice versa
Logistic model allowing for interactions $$ \text{logit}(y=1|X)=\beta_0 + \beta_1x_1 + \beta_2x_2 + \beta_3x_1x_2 $$
If $x_1=0$ then $$ \text{logit}(y=1|x_1=0,x_2)=\beta_0 + \beta_2x_2 $$
If $x_1 = 1$ then $$ \text{logit}(y=1|\color{red}{x_1=1},x_2)=\beta_0 + \color{red}{\beta_1} + \beta_2x_2 + \color{red}{\beta_3}x_2 $$ $$ \text{logit}(y=1|\color{red}{x_1=1},x_2)=(\beta_0 + \color{red}{\beta_1}) + (\beta_2 + \color{red}{\beta_3})x_2 $$
Interactions
- Not equal slopes $\rightarrow$ presence of interaction
- The effect of $x_1$ on $y$ depends on the level of $x_2$ and vice versa
Logistic model allowing for interactions $$ \text{logit}(y=1|X)=\beta_0 + \beta_1x_1 + \beta_2x_2 + \beta_3x_1x_2 $$
If $x_1=0$ then $$ \text{logit}(y=1|x_1=0,x_2)=\color{red}{\beta_0} + \color{red}{\beta_2}x_2 $$
If $x_1 = 1$ then $$ \text{logit}(y=1|x_1=1,x_2)=\beta_0 + \beta_1 + \beta_2x_2 + \beta_3x_2 $$ $$ \text{logit}(y=1|x_1=1,x_2)=\color{red}{(\beta_0 + \beta_1)} + \color{red}{(\beta_2 + \beta_3)}x_2 $$
Visualizing interactions
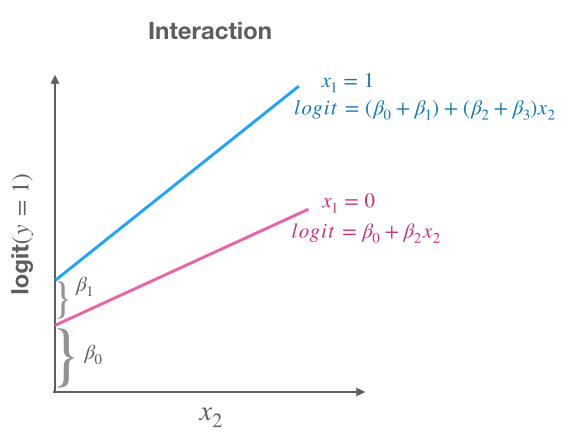
Interactions allow for:
- intercept and slope different for $x_1$
- $\beta_1$: difference between the two intercepts
- $\beta_3$: difference between the two slopes
Interaction types
- binary $\times$ binary
- binary $\times$ categorical
- binary $\times$ continuous
- continuous $\times$ categorical
- continuous $\times$ continuous
- categorical $\times$ categorical
- more than 2 variable interactions
Let's practice!
Generalized Linear Models in Python

