Count data and Poisson distribution
Generalized Linear Models in Python

Ita Cirovic Donev
Data Science Consultant
Count data
- Count the number of occurrences in a specified unit of time, distance, area or volume
Examples:
- Goals in a soccer match
- Number of earthquakes
- Number of crab satellites
- Number of awards won by a person
- Number of bike crossings over the bridge
Poisson random variable
- Events occur independently and randomly
- Poisson distribution
$$ P(y)=\frac{\lambda^ye^{-\lambda}}{y!} $$
- $\lambda$ : mean and variance
- $y=0,1,2,3, ...$
- $\text{\color{#E80C7A}{Always positive}}$
- Discrete (not continuous)
- $\text{\color{#E80C7A}{Lower bound at zero}}$, but no upper bound
Understanding the parameter of the Poisson distribution
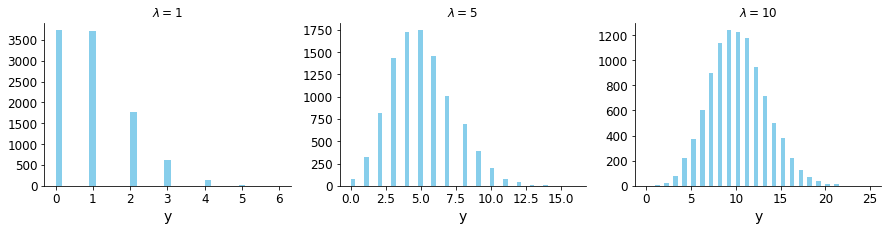
Visualizing the response
import seaborn as sns
sns.distplot('y')
Poisson regression
Response variable $$ y \sim Poisson(\lambda) $$
Mean of the response $$ E(y)=\lambda $$
Poisson regression model $$ log(\lambda)=\beta_0+\beta_1x_1 $$
Explanatory variables
- Continuous and/or categorical $\rightarrow$ Poisson regression model
- Categorical $\rightarrow$ log-linear model
GLM with Poisson in Python
import statsmodels.api as sm
from statsmodels.formula.api import glm
glm('y ~ x',
data = my_data,
family = sm.families.Poisson())
Let's practice!
Generalized Linear Models in Python

