Introduction to the Normal distribution
Statistical Thinking in Python (Part 1)

Justin Bois
Teaching Professor at the California Institute of Technology
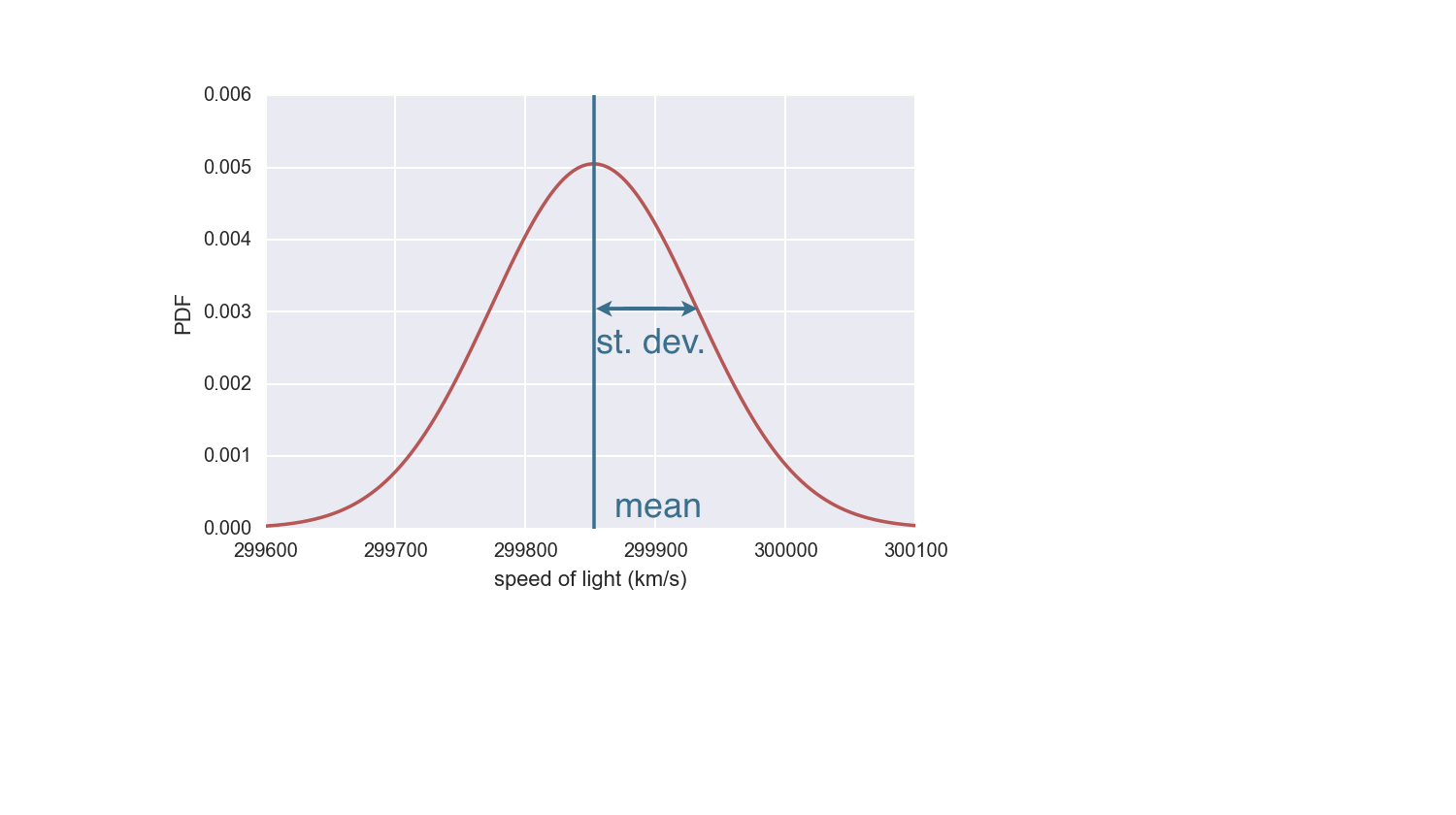
Normal distribution
- Describes a continuous variable whose PDF has a single symmetric peak.
Normal distribution
Normal distribution
Normal distribution
Normal distribution
Normal distribution

Comparing data to a Normal PDF
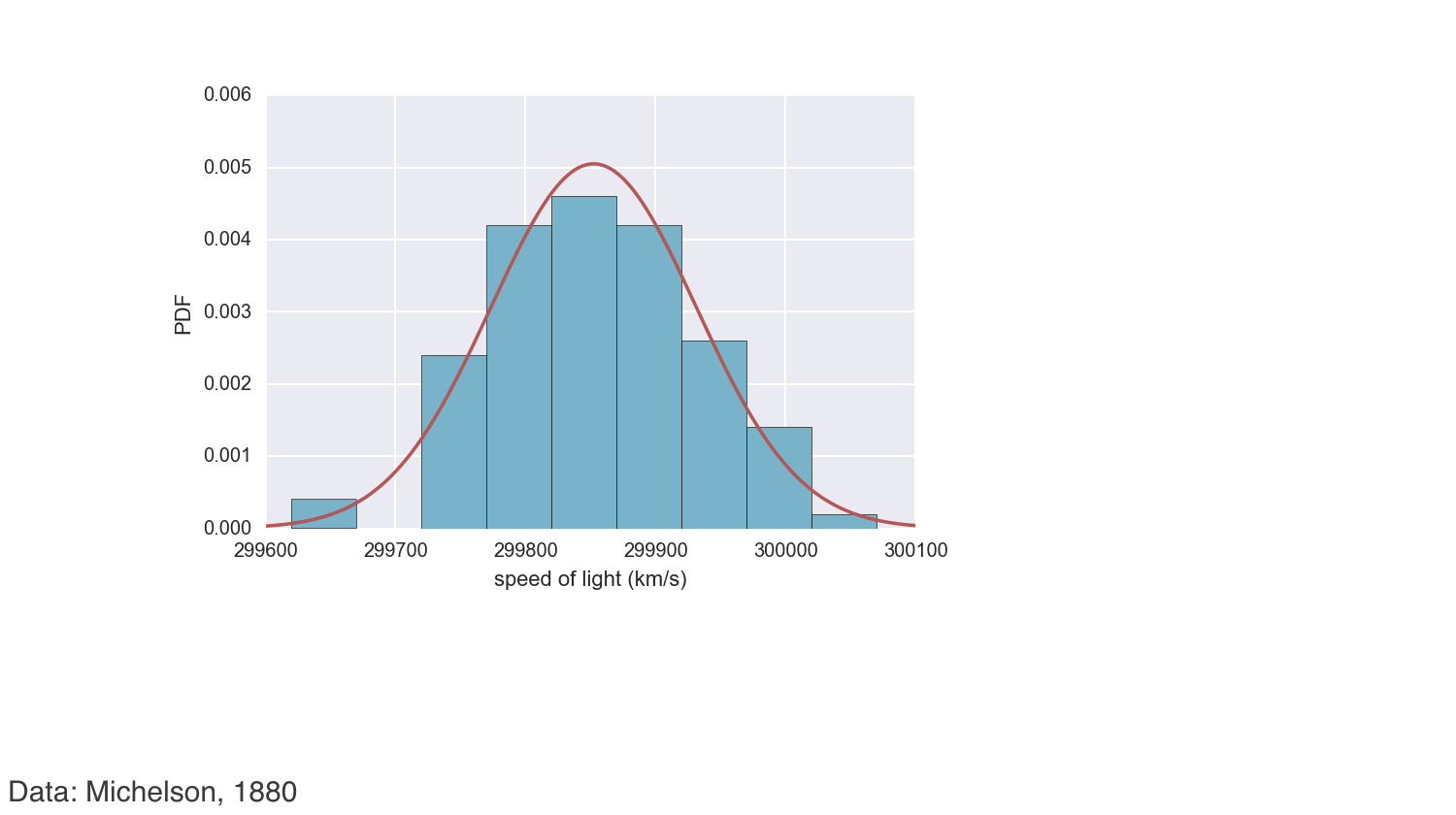
Checking Normality of Michelson data
import numpy as np
rng = np.random.default_rng()
mean = np.mean(michelson_speed_of_light)
std = np.std(michelson_speed_of_light)
samples = rng.normal(mean, std, size=10000)
x, y = ecdf(michelson_speed_of_light)
x_theor, y_theor = ecdf(samples)
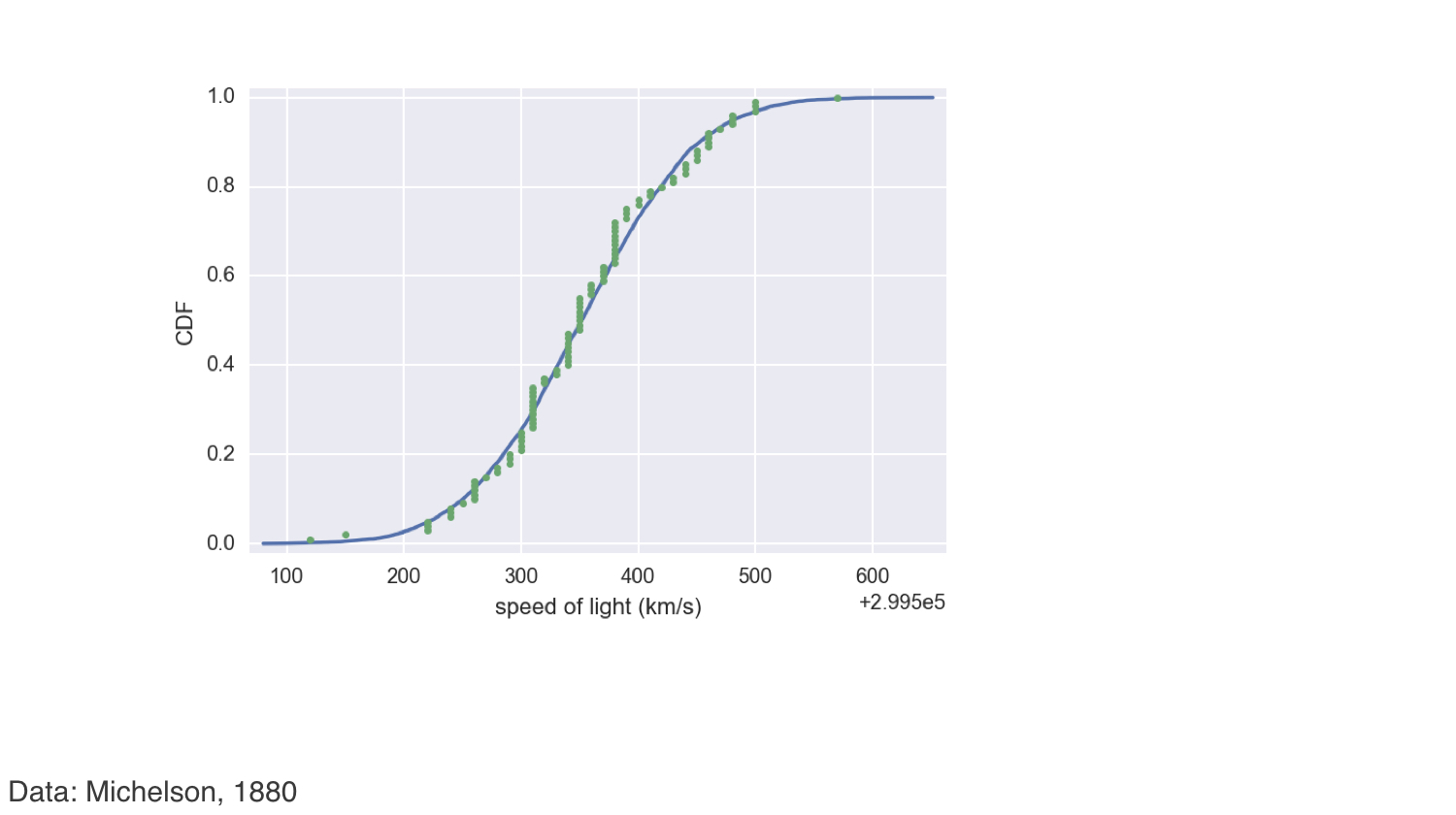
Checking Normality of Michelson data
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
sns.set()
_ = plt.plot(x_theor, y_theor)
_ = plt.plot(x, y, marker='.', linestyle='none')
_ = plt.xlabel('speed of light (km/s)')
_ = plt.ylabel('CDF')
plt.show()
Checking Normality of Michelson data
Let's practice!
Statistical Thinking in Python (Part 1)

