Using and creating indexes
Improving Query Performance in PostgreSQL

Amy McCarty
Instructor
Index overview
What
- Method of creating sorted column keys to improve search
- Similar to book index
- Reference to data location
Why
- Faster queries
Where
- Common filter columns
- Primary key
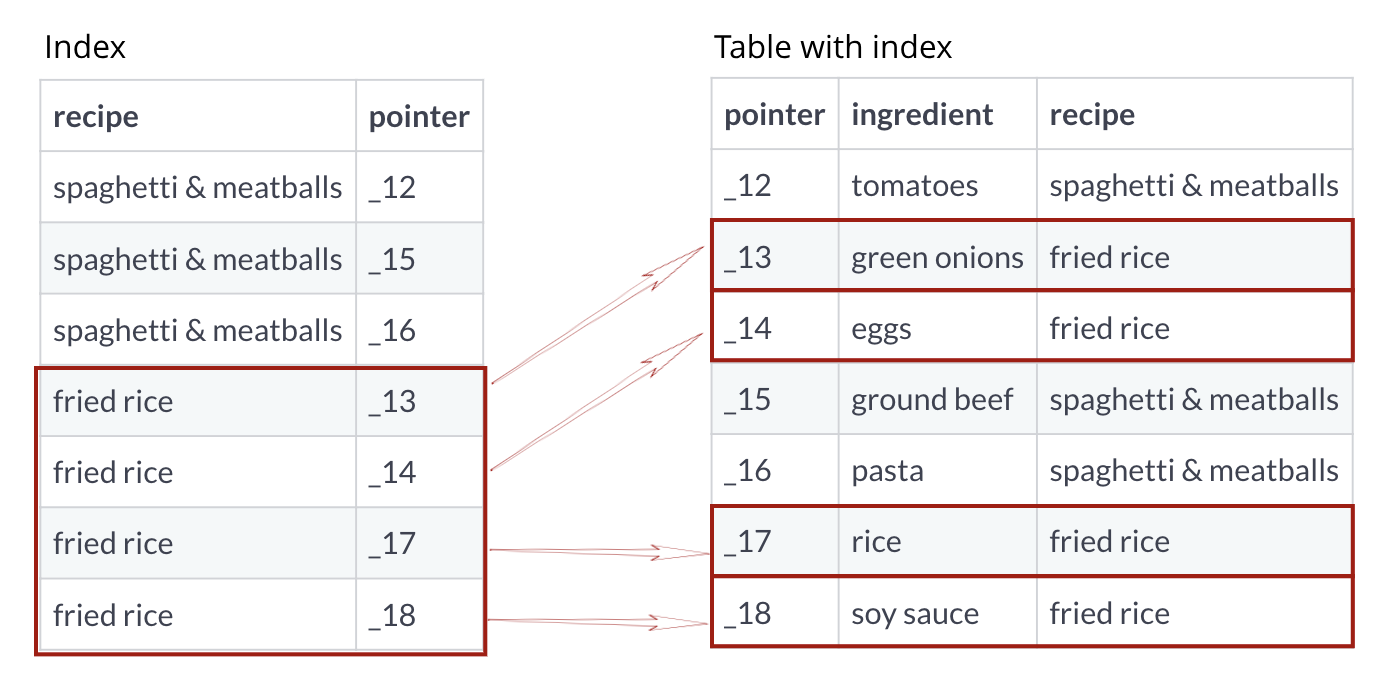
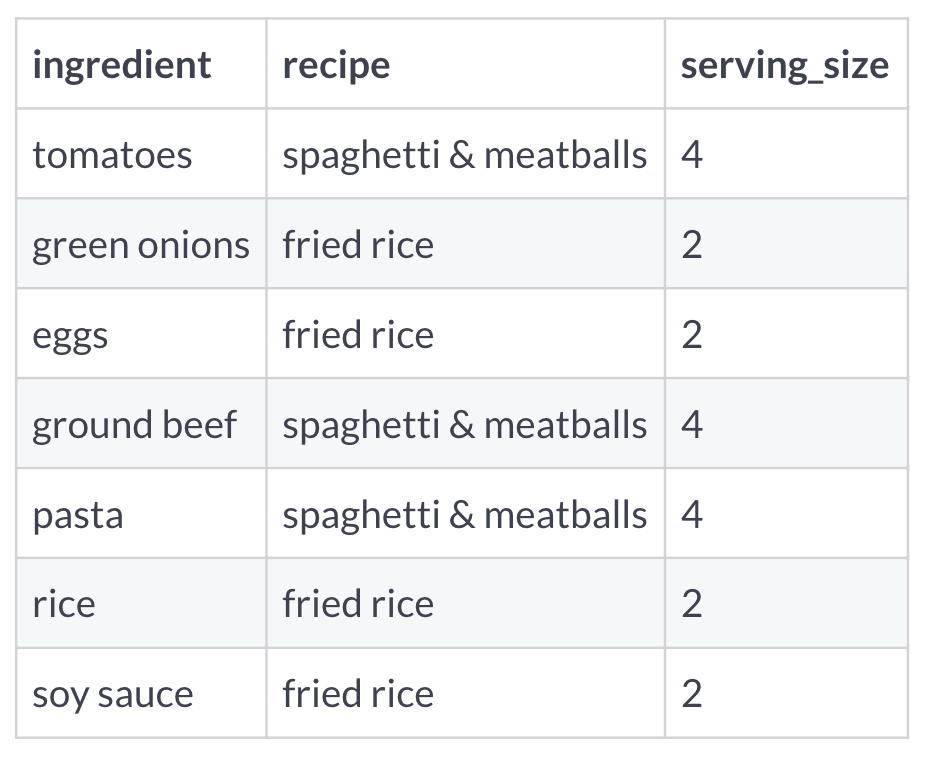
Index example
| ingredient | recipe |
|---|---|
| tomatoes | spaghetti & meatballs |
| green onions | fried rice |
| eggs | fried rice |
| ground beef | spaghetti & meatballs |
| pasta | spaghetti & meatballs |
| rice | fried rice |
| soy sauce | fried rice |
SELECT *
FROM cookbook
WHERE recipe = 'fried rice'
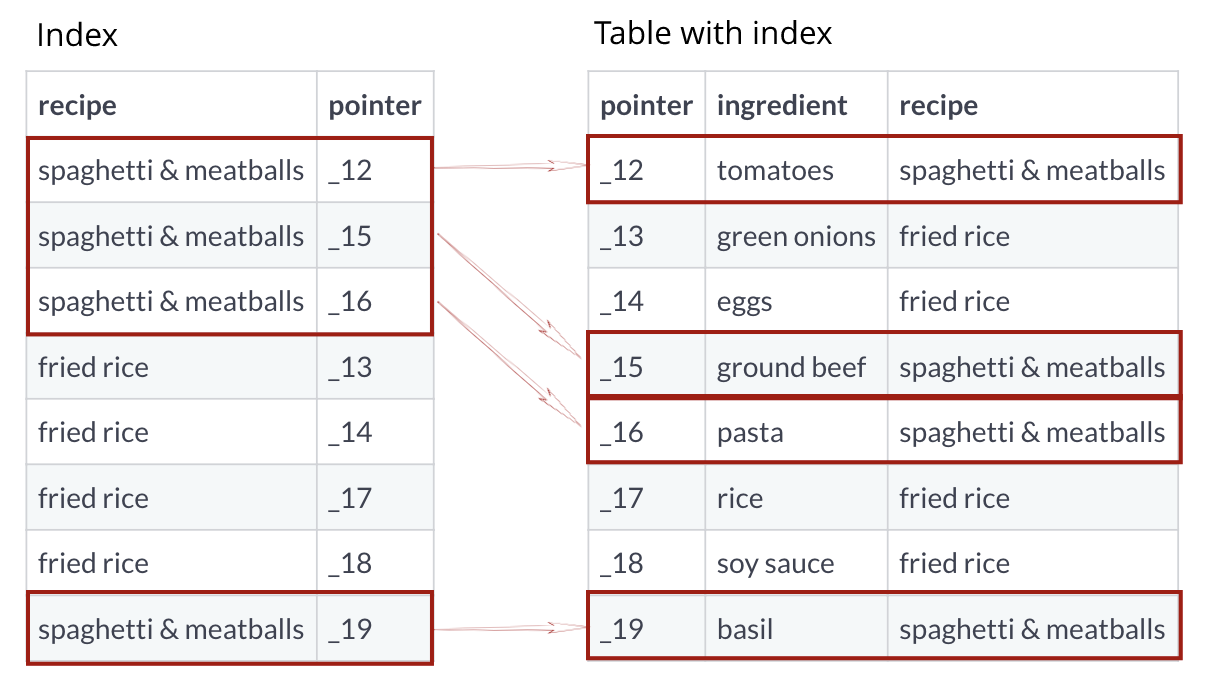
Index as a key and pointer
Finding existing indexes
pg_tables
- Similar to information_schema
- specific to Postgres
- Metadata about database
Finding existing indexes
pg_tables
- Similar to information_schema
- specific to Postgres
- Metadata about database
SELECT * FROM pg_indexes
| schemaname | tablename | indexname | tablespace | indexdef |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| food | dinner | recipe_index | null | CREATE INDEX recipe_index ... |
Creating an index
CREATE INDEX recipe_index
ON cookbook (recipe);
CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY recipe_index
ON cookbook (recipe, serving_size);
To use or not to use
Use an index
- Large tables
- Common filter conditions
- Primary key
Avoid an index
- Small tables
- Columns with many nulls
- Frequently updated tables
- Index will become fragmented
- Writes data in two places
Frequently updated tables
Index query assessment
Query planner

EXPLAIN
SELECT *
FROM cookbook
Query Plan
Seq scan on cookbook (cost=0.00...22.70
rows = 1270 width = 36)
- Cost (time) estimates
Let's practice!
Improving Query Performance in PostgreSQL

