Row-oriented storage and partitions
Improving Query Performance in PostgreSQL

Amy McCarty
Instructor
Database storage types
Row oriented storage
- Relation between columns retained
Column-oriented storage
- Relation between rows retained
| id | name | species | age | habitat | received |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | Bob | panda | 2 | Asia | 2018 |
| 02 | Sunny | zebra | 3 | Africa | 2018 |
| 03 | Beco | zebra | 10 | Africa | 2017 |
| 04 | Coco | koala | 5 | Australia | 2016 |
Row-oriented
Row-oriented storage
- Relation between columns retained
| id | name | species | age | habitat | received |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | Bob | panda | 2 | Asia | 2018 |
Column-oriented
Column-oriented storage
- Relation between rows retained
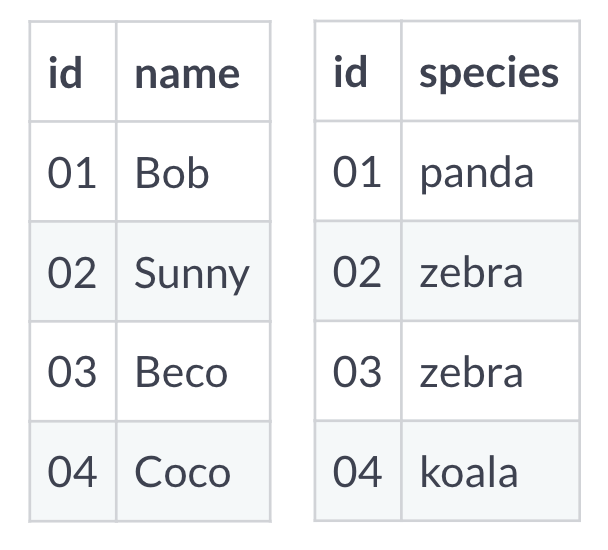
Row-oriented storage
- One row stored in same location
- Fast to append or delete whole records
- Quick to return all columns
- Slow to return all rows
Reducing the rows
Reduce the number of rows
WHEREfilterINNER JOINDISTINCTLIMIT
Row-oriented database methods
Partitions
- Method of splitting one (parent) table into many, smaller (children) tables
Indexes
- Method of creating sorted column keys to improve search
Using partitions and indexes
- Require set up and maintenance
- Existence known from database administrator or documentation
Partition structure
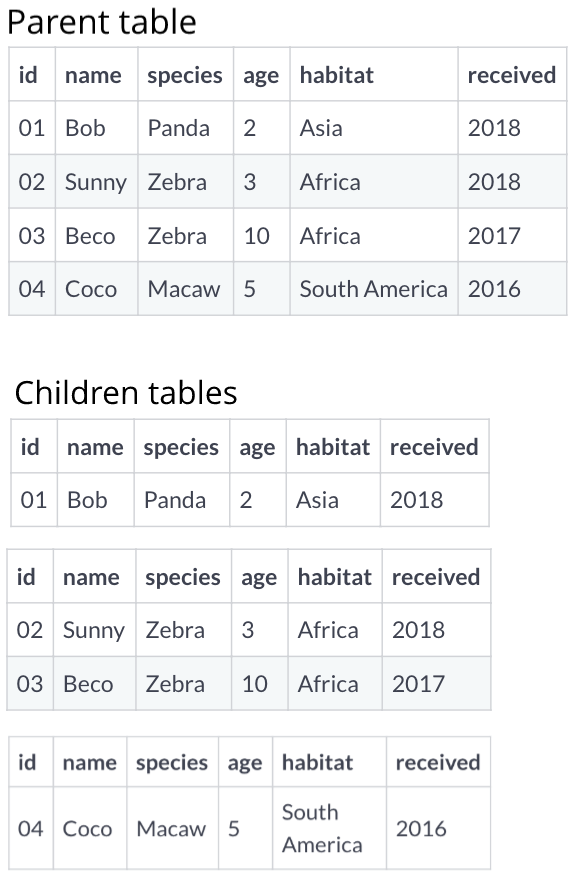
- Parent table
- Visible in database front end
- Write queries
- Children tables
- Not visible in database front end
- Queries search
Partition structure
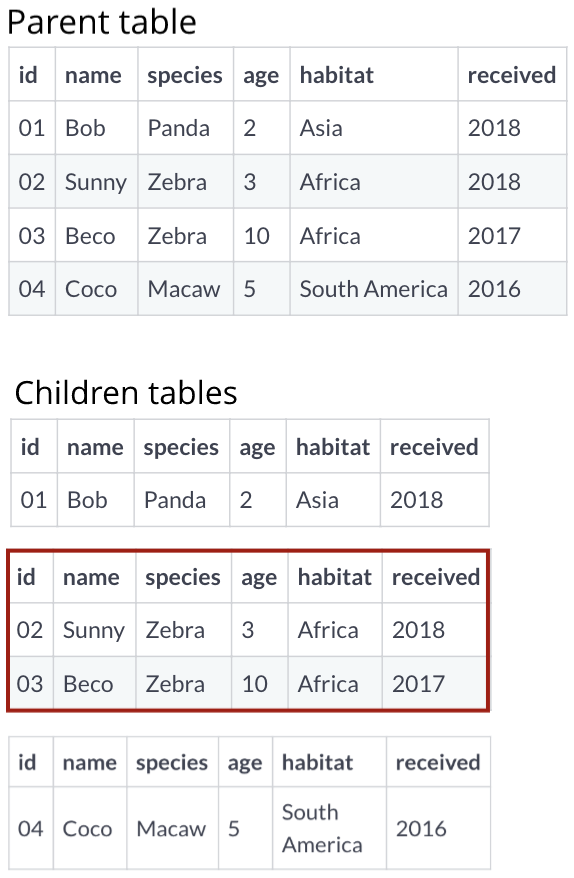
SELECT species
FROM zoo_animals
WHERE habitat = 'Africa'
Partition overview
What
- Splitting of one table into many smaller tables
Why
- Storage flexibility
- Faster queries
Where
- Common filter columns
- Date, location
Partition query assessment
Query planner

EXPLAIN
SELECT species
FROM zoo_animals
WHERE habitat = 'Africa'
Query Plan
Seq Scan on zoo_animals (cost=0.00..
17.70 rows=2 width=182)
Filter: (state_code = 15)
- Cost (time) estimates
Let's practice!
Improving Query Performance in PostgreSQL

