Model diagnostics
ARIMA Models in Python

James Fulton
Climate informatics researcher
Introduction to model diagnostics
- How good is the final model?
Residuals
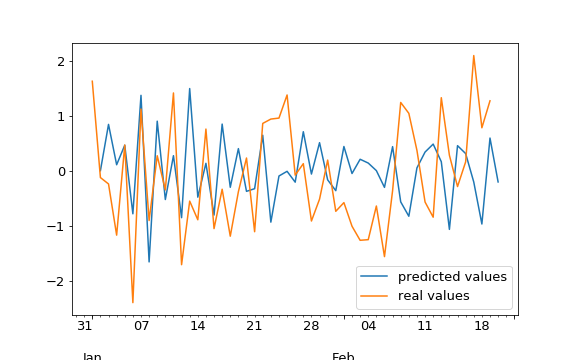
Residuals
# Fit model model = ARIMA(df, order=(p,d,q)) results = model.fit()# Assign residuals to variable residuals = results.resid
2013-01-23 1.013129
2013-01-24 0.114055
2013-01-25 0.430698
2013-01-26 -1.247046
2013-01-27 -0.499565
... ...
Mean absolute error
How far our the predictions from the real values?
mae = np.mean(np.abs(residuals))
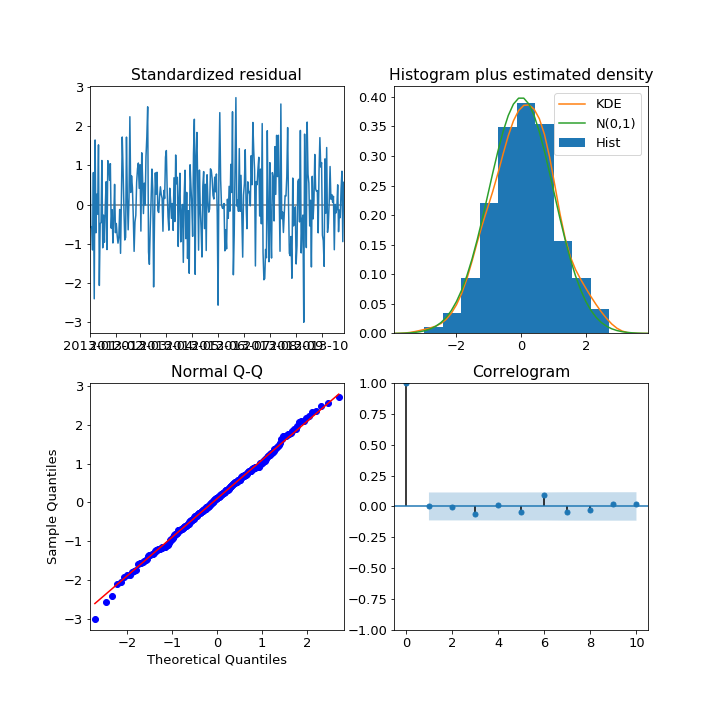
Plot diagnostics
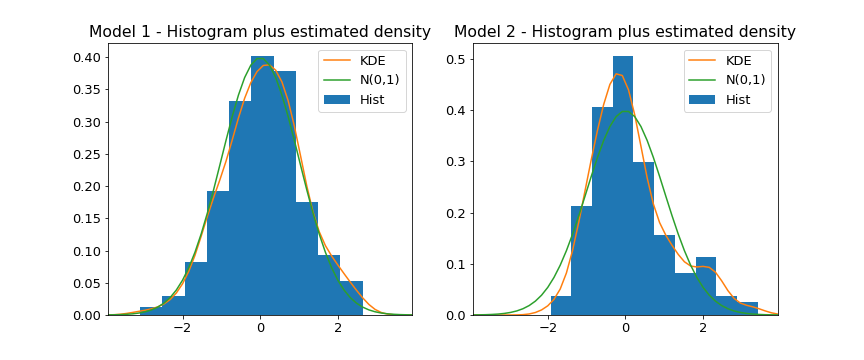
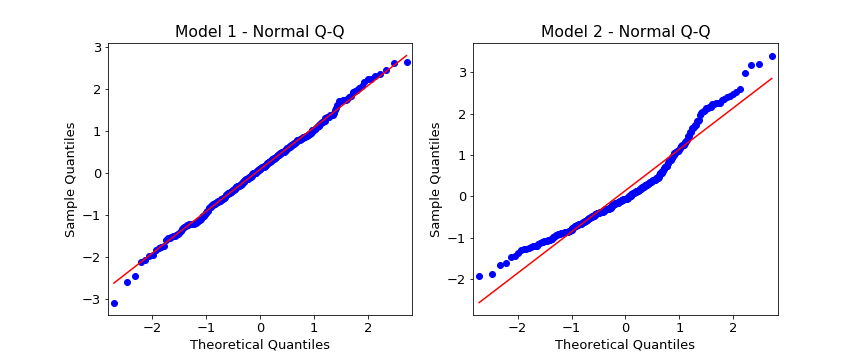
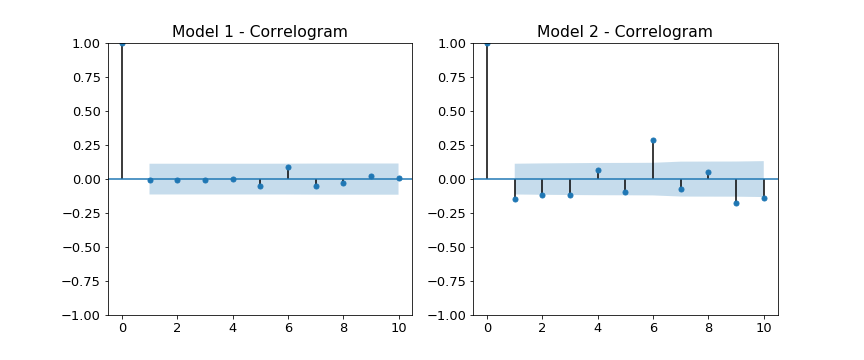
If the model fits well the residuals will be white Gaussian noise
# Create the 4 diagostics plots
results.plot_diagnostics()
plt.show()
Residuals plot
Residuals plot
Histogram plus estimated density
Normal Q-Q
Correlogram
Summary statistics
print(results.summary())
...
===================================================================================
Ljung-Box (Q): 32.10 Jarque-Bera (JB): 0.02
Prob(Q): 0.81 Prob(JB): 0.99
Heteroskedasticity (H): 1.28 Skew: -0.02
Prob(H) (two-sided): 0.21 Kurtosis: 2.98
===================================================================================
Prob(Q)- p-value for null hypothesis that residuals are uncorrelatedProb(JB)- p-value for null hypothesis that residuals are normal
Let's practice!
ARIMA Models in Python

