Alternative measures of risk
Introduction to Portfolio Analysis in Python

Charlotte Werger
Data Scientist
Looking at downside risk
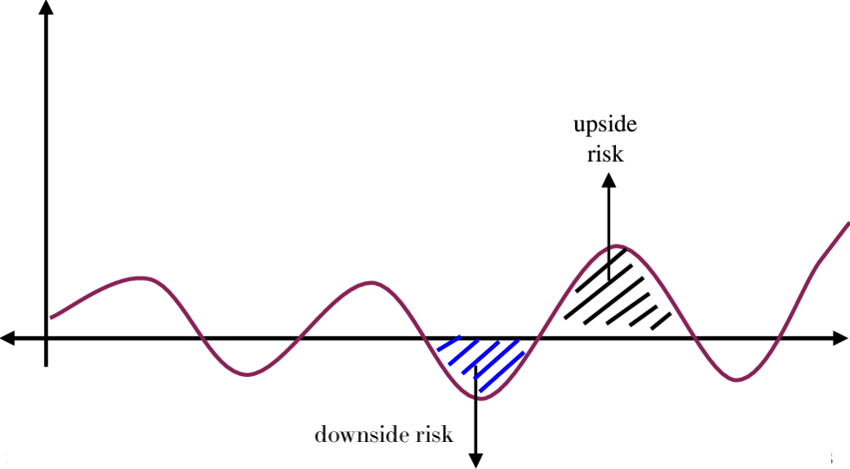
- A good risk measure should focus on potential losses i.e. downside risk
Sortino ratio
$$
- Similar to the Sharpe ratio, just with a different standard deviation
- $ Sortino \; Ratio = \frac{R_p - R_f}{\sigma_d}$
- $\sigma_d$ is the standard deviation of the downside.
$$
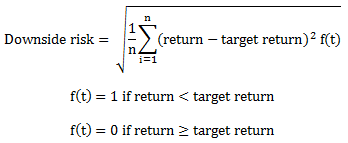
Sortino ratio in python
# Define risk free rate and target return of 0
rfr = 0
target_return = 0
# Calcualte the daily returns from price data
apple_returns=pd.DataFrame(apple_price.pct_change())
# Select the negative returns only
negative_returns = apple_returns.loc[apple_returns['AAPL'] < target]
# Calculate expected return and std dev of downside returns
expected_return = apple_returns['AAPL'].mean()
down_stdev = negative_returns.std()
# Calculate the sortino ratio
sortino_ratio = (expected_return - rfr)/down_stdev
print(sortino_ratio)
0.07887683763760528
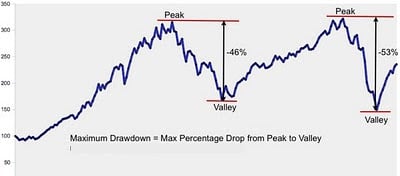
Maximum draw-down
- The largest percentage loss from a market peak to trough
- Dependent on the chosen time window
- The recovery time: time it takes to get back to break-even
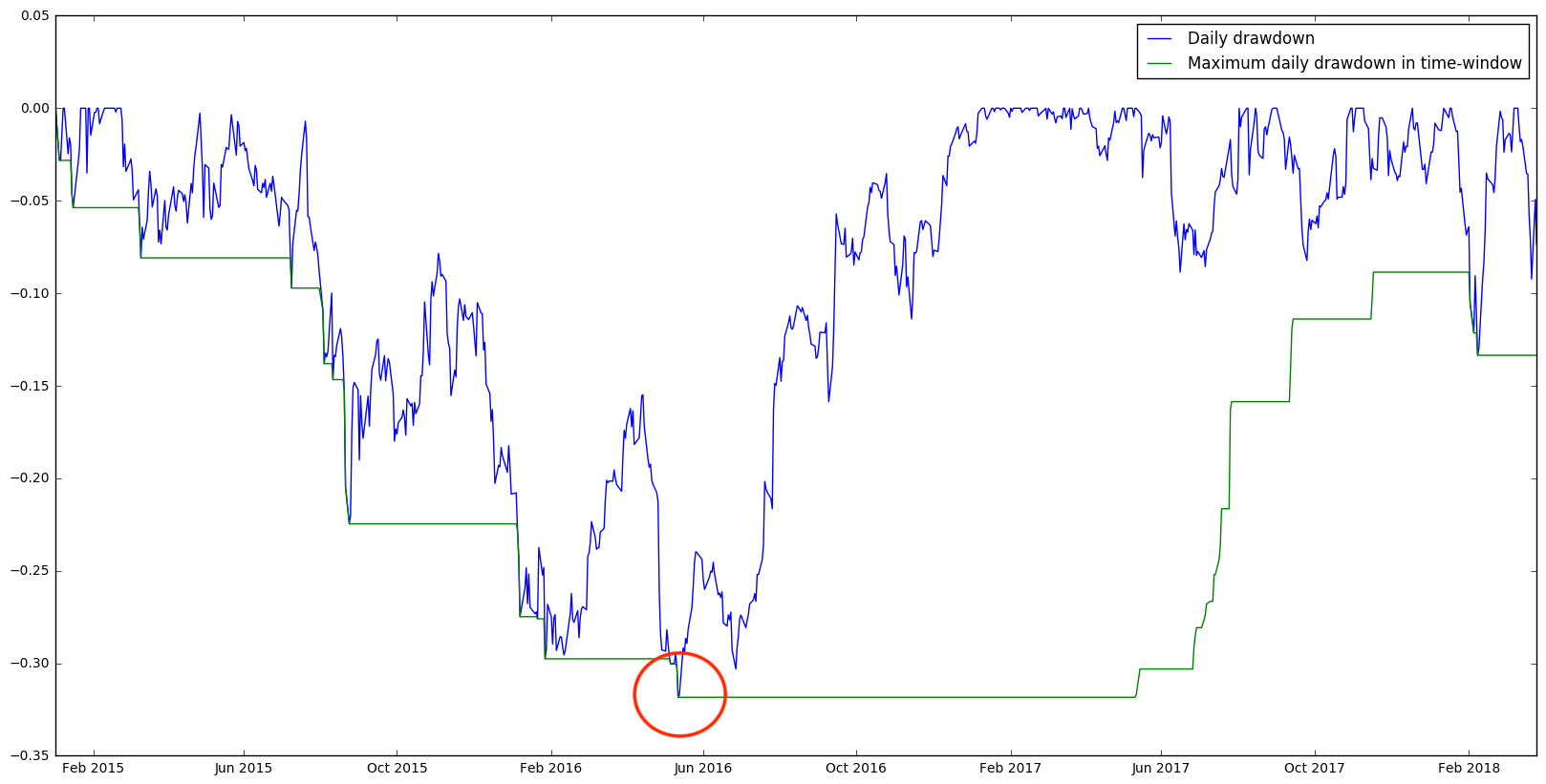
Maximum daily draw-down in Python
# Calculate the maximum value of returns using rolling().max() roll_max = apple_price.rolling(min_periods=1,window=250).max()# Calculate daily draw-down from rolling max daily_drawdown = apple_price/roll_max - 1.0# Calculate maximum daily draw-down max_daily_drawdown = daily_drawdown.rolling(min_periods=1,window=250).min()# Plot the results daily_drawdown.plot() max_daily_drawdown.plot() plt.show()
Maximum draw-down of Apple
Let's practice!
Introduction to Portfolio Analysis in Python

