Inference (causal) models
Machine Learning for Business

Karolis Urbonas
Head of Machine Learning & Science, Amazon
What is causality?
- Identify causal relationship of how much certain actions affect an outcome of interest
- Answers the "why?" questions
- Optimizes for model interpretability vs. performance
- Models try to detect patterns in observed data (observational) and draw causal conclusions
Experiments vs. observations
- Experiments are designed and causal conclusions are guaranteed e.g. in A/B tests
- When experiments are impossible (unethical, too expensive, both) - the models are used (also called observational studies) to calculate effect of certain inputs on desired outcomes
- Experiments are always preferred over observational studies whenever possible
Best practices
- Do experiments wherever you can
- If running experiments all the time is too expensive, run them periodically (quarterly, annually) and use it as benchmark
- If there are no way to run any experiments, build a causal model. This will require an advanced methodology
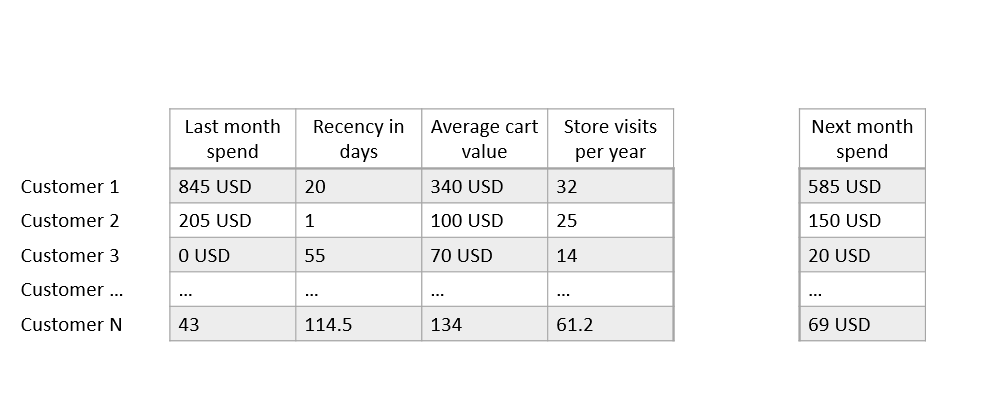
Inference model example
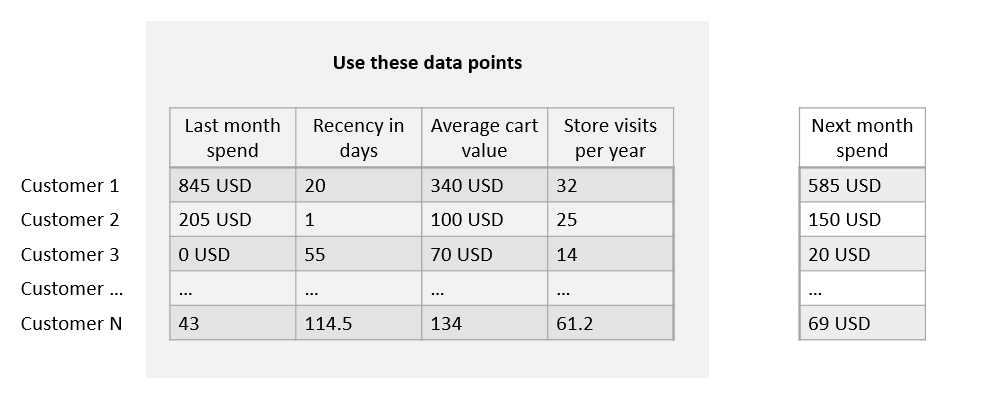
Inference - training
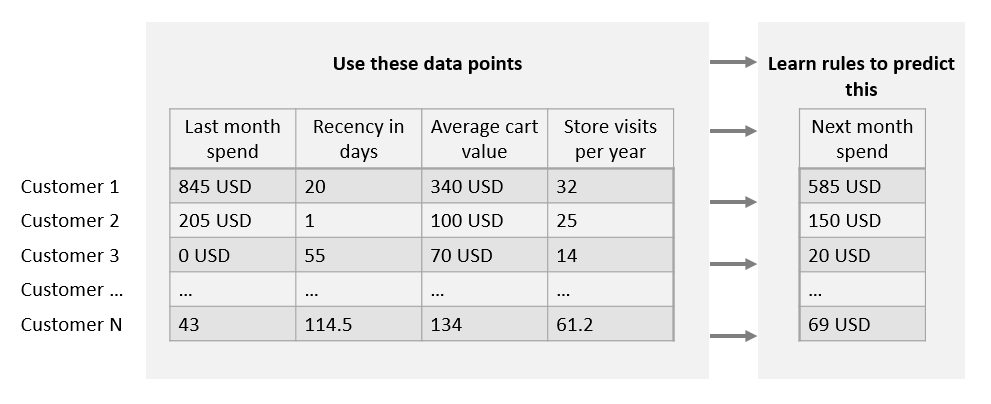
Inference - learning
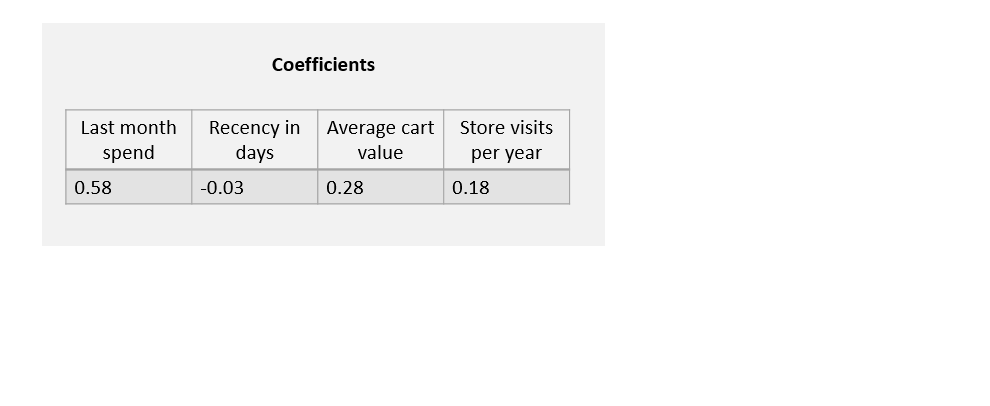
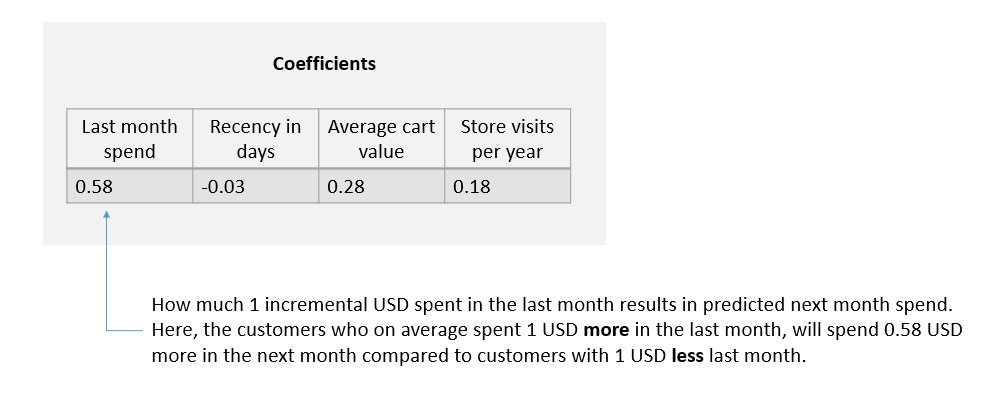
Inference - regression coefficients
Inference - interpretation
Let's practice!
Machine Learning for Business