Heatmaps
Market Basket Analysis in Python

Isaiah Hull
Visiting Associate Professor of Finance, BI Norwegian Business School
MovieLens dataset
import pandas as pd
# Load ratings data.
ratings = pd.read_csv('datasets/movie_ratings.csv')
print(ratings.head())
userId movieId title
0 3149 54286 Bourne Ultimatum, The (2007)
1 3149 1220 Blues Brothers, The (1980)
2 3149 4007 Wall Street (1987)
3 3149 7156 Fog of War: Eleven...
4 3149 97304 Argo (2012)
Creating "transactions" from ratings
# Recover unique user IDs.
user_id = movies['userId'].unique()
# Create library of highly rated movies for each user.
libraries = [list(ratings[ratings['userId'] == u].title) for u in user_id]
# Print example library.
print(library[0])
['Battlestar Galactica (2003)',
'Gorgon, The (1964)',
'Under the Skin (2013)',
'Upstream Color (2013)',
'Destry Rides Again (1939)',
'Dr. Phibes Rises Again (1972)']
One-hot encoding transactions
from mlxtend.preprocessing import TransactionEncoder
# Instantiate transaction encoder.
encoder = TransactionEncoder()
# One-hot encode libraries.
onehot = encoder.fit(libraries).transform(libraries)
# Use movie titles as column headers.
onehot = pd.DataFrame(onehot, columns = encoder.columns_)
# Print onehot header.
print(onehot.head())
One-hot encoding transactions
(500) Days of Summer (2009) .45 (2006) 10 Things I Hate About You (1999)
0 False False False
1 False False False
2 False False False
3 False False False
4 False False False
What is a heatmap?
Preparing the data
- Generate the rules.
- Use Apriori algorithm and association rules.
- Convert antecedents and consequents into strings.
- Stored as frozen sets by default in mlxtend.
- Convert rules into matrix format.
- Suitable for use in heatmaps.
Preparing the data
from mlxtend.frequent_patterns import association_rules, apriori
import seaborn as sns
# Apply the apriori algorithm
frequent_itemsets = apriori(onehot, min_support=0.10,
use_colnames=True, max_len=2)
# Recover the association rules
rules = association_rules(frequent_itemsets)
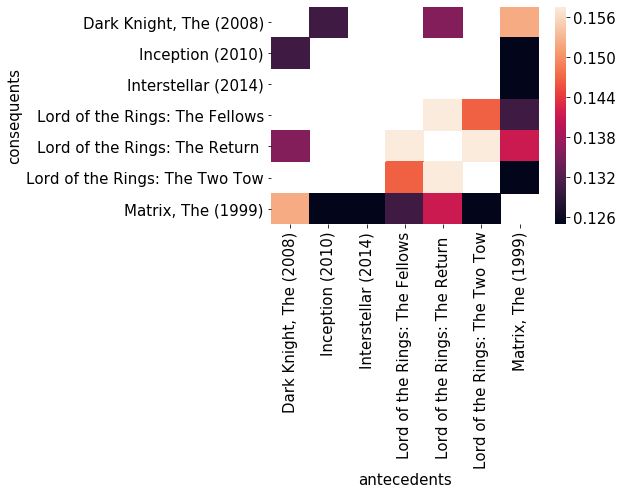
Generating a heatmap
# Convert antecedents and consequents into strings
rules['antecedents'] = rules['antecedents'].apply(lambda a: ','.join(list(a)))
rules['consequents'] = rules['consequents'].apply(lambda a: ','.join(list(a)))
# Print example.
print(rules[['antecedents','consequents']])
antecedents consequents
0 Batman Begins (2005) Dark Knight Rises, The (2012)
Generating a heatmap
# Transform antecedent, consequent, and support columns into matrix
support_table = rules.pivot(index='consequents', columns='antecedents',
values='support')
# Generate heatmap
sns.heatmap(support_table)
Generating a heatmap
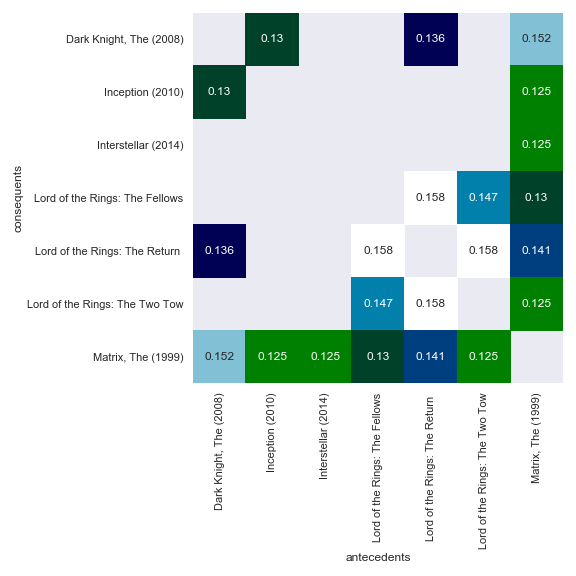
Customizing heatmaps
sns.heatmap(pivot, annot=True, cbar=False, cmap='ocean')
Let's practice!
Market Basket Analysis in Python

