Visulize your results using Tidyverse
Scalable Data Processing in R

Michael Kane
Assistant Professor, Yale University
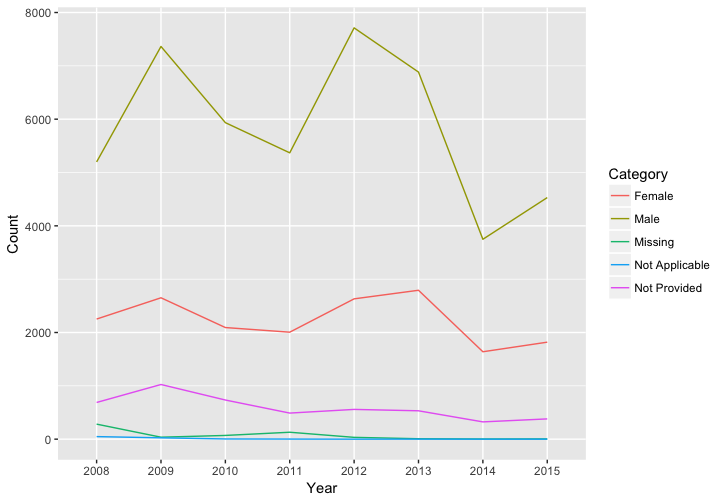
Missingness by Year
library(ggplot2) library(tidyr) library(dplyr)mort %>% bigtable(c("borrower_gender", "year")) %>% as.data.frame()
Missingness by Year
library(ggplot2)
library(tidyr)
library(dplyr)
mort %>%
bigtable(c("borrower_gender", "year")) %>%
as.data.frame() %>%
mutate(Category = c("Male", "Female", "Not Provided",
"Not Applicable", "Missing"))
Missingness by Year
library(ggplot2)
library(tidyr)
library(dplyr)
mort %>%
bigtable(c("borrower_gender", "year")) %>%
as.data.frame() %>%
mutate(Category = c("Male", "Female", "Not Provided",
"Not Applicable", "Missing")) %>%
pivot_longer(-Category, names_to = "Year", values_to = "Count") %>%
arrange(Year)
Missingness by Year
library(ggplot2)
library(tidyr)
library(dplyr)
mort %>%
bigtable(c("borrower_gender", "year")) %>%
as.data.frame() %>%
mutate(Category = c("Male", "Female", "Not Provided",
"Not Applicable", "Missing")) %>%
pivot_longer(-Category, names_to = "Year", values_to = "Count") %>%
arrange(Year) %>%
ggplot(aes(x = Year, y = Count, group = Category,
color = Category)) +
geom_line()
Let's practice!
Scalable Data Processing in R

