More probability distributions
Introduction to Statistics in R

Maggie Matsui
Content Developer, DataCamp
Exponential distribution
Probability of time between Poisson events
Examples
- Probability of > 1 day between adoptions
- Probability of < 10 minutes between restaurant arrivals
- Probability of 6-8 months between earthquakes
Also uses lambda (rate)
Continuous (time)
Customer service requests
- On average, one customer service ticket is created every 2 minutes
- $\lambda$ = 0.5 customer service tickets created each minute
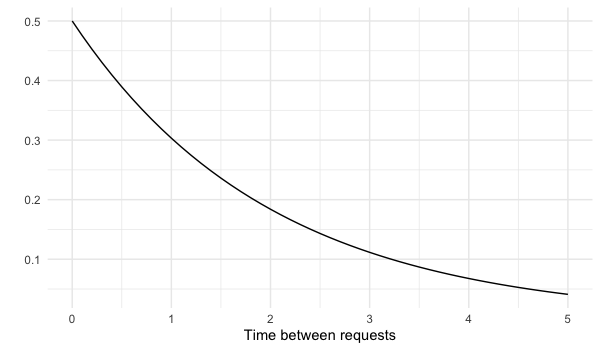
Lambda in exponential distribution
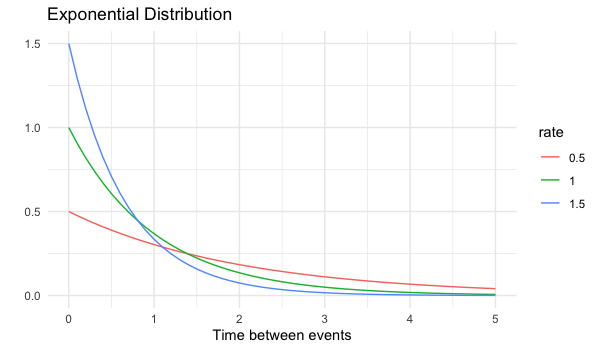
How long until a new request is created?
$P(\text{wait} < \text{1 min})$ =
pexp(1, rate = 0.5)
0.3934693
$P(\text{wait} > \text{4 min})$ =
pexp(4, rate = 0.5, lower.tail = FALSE)
0.1353353
$P(\text{1 min} < \text{wait} < \text{4 min})$ =
pexp(4, rate = 0.5) - pexp(1, rate = 0.5)
0.4711954
Expected value of exponential distribution
In terms of rate (Poisson):
- $\lambda$ = $0.5$ requests per minute
In terms of time (exponential):
- $1/\lambda$ = $1$ request per $2$ minutes
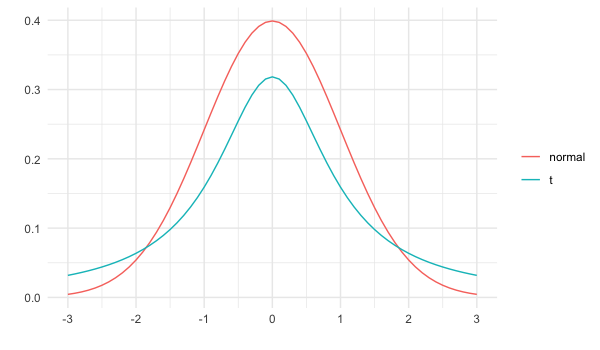
(Student's) t-distribution
- Similar shape as the normal distribution
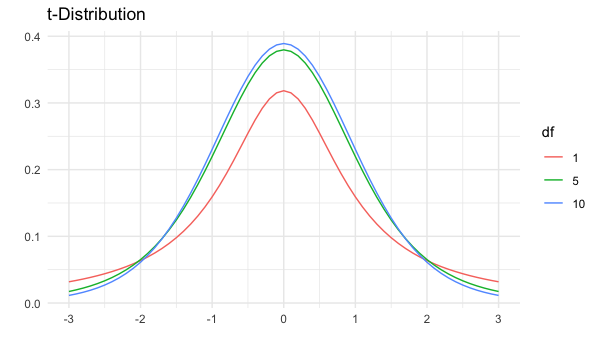
Degrees of freedom
- Has parameter degrees of freedom (df) which affects the thickness of the tails
- Lower df = thicker tails, higher standard deviation
- Higher df = closer to normal distribution
Log-normal distribution
Variable whose logarithm is normally distributed
Examples:
- Length of chess games
- Adult blood pressure
- Number of hospitalizations in the 2003 SARS outbreak
Let's practice!
Introduction to Statistics in R

