Standard errors and the Central Limit Theorem
Sampling in R

Richie Cotton
Data Evangelist at DataCamp
Sampling distribution of mean cup points
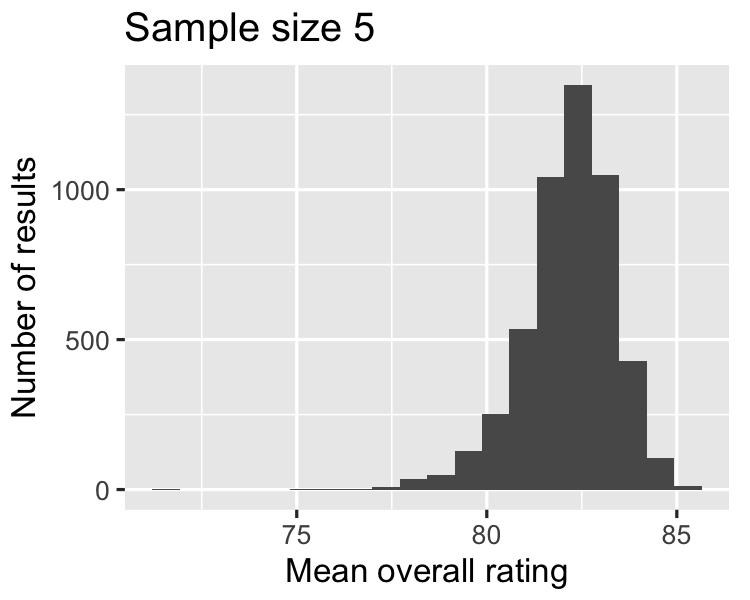
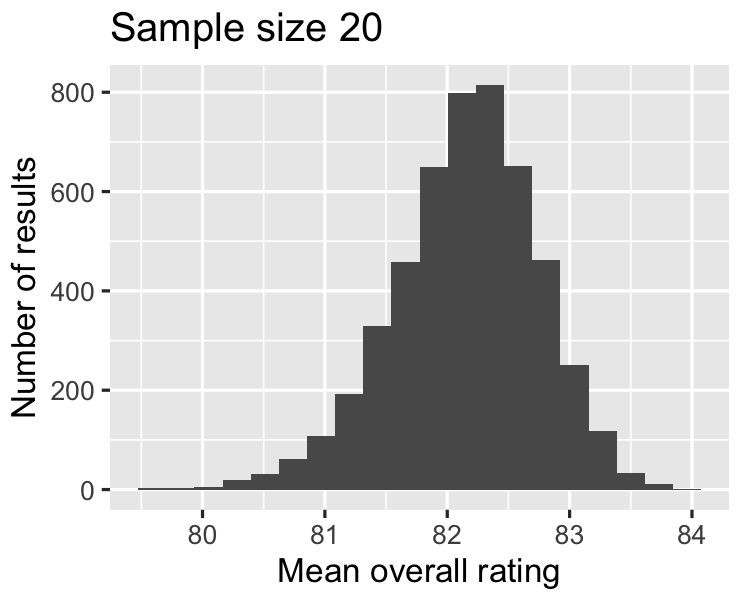
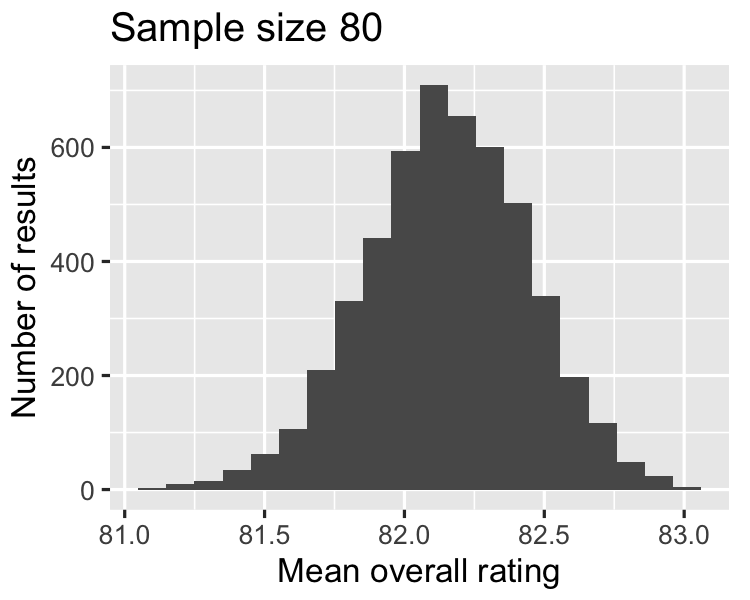
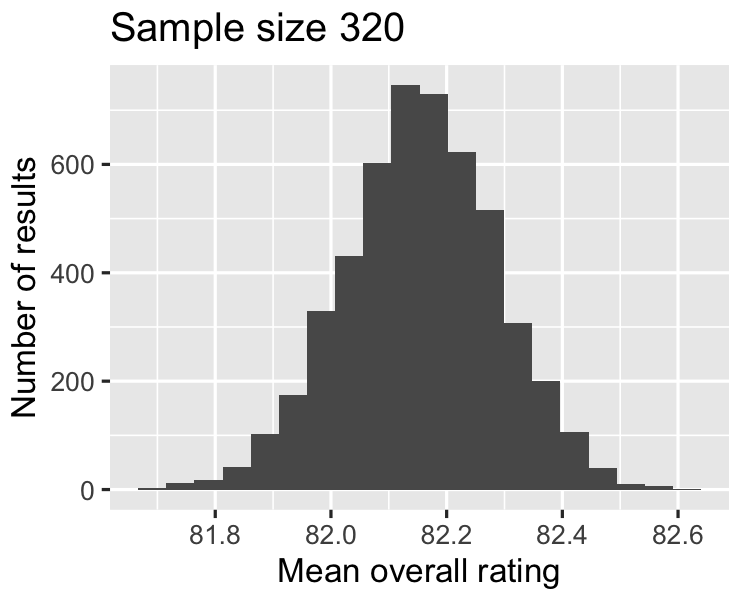
Consequences of the central limit theorem
- Averages of independent samples have approximately normal distributions.
As the sample size increases,
the distribution of the averages gets closer to being normally distributed, and
the width of the sampling distribution gets narrower.
Population & sampling distribution means
coffee_ratings %>%
summarize(
mean_cup_points = mean(total_cup_points)
) %>%
pull(mean_cup_points)
82.1512
| Sample size | Mean sample mean |
|---|---|
| 5 | 82.1496 |
| 20 | 82.1610 |
| 80 | 82.1496 |
| 320 | 82.1521 |
Population & sampling distribution standard deviations
coffee_ratings %>%
summarize(
sd_cup_points = sd(total_cup_points)
) %>%
pull(sd_cup_points)
2.68686
| Sample size | Std dev sample mean |
|---|---|
| 5 | 1.1929 |
| 20 | 0.6028 |
| 80 | 0.2865 |
| 320 | 0.1304 |
Population mean over square root sample size
| Sample size | Std dev sample mean | Calculation | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 1.1929 |
2.68686 / sqrt(5) |
1.2016 |
| 20 | 0.6028 |
2.68686 / sqrt(20) |
0.6008 |
| 80 | 0.2865 |
2.68686 / sqrt(80) |
0.3004 |
| 320 | 0.1304 |
2.68686 / sqrt(320) |
0.1502 |
Let's practice!
Sampling in R

