Sampling and point estimates
Sampling in R

Richie Cotton
Data Evangelist at DataCamp
Estimating the population of France
A census asks every household how many people live there.
There are lots of people in France
Censuses are really expensive!
Sampling households
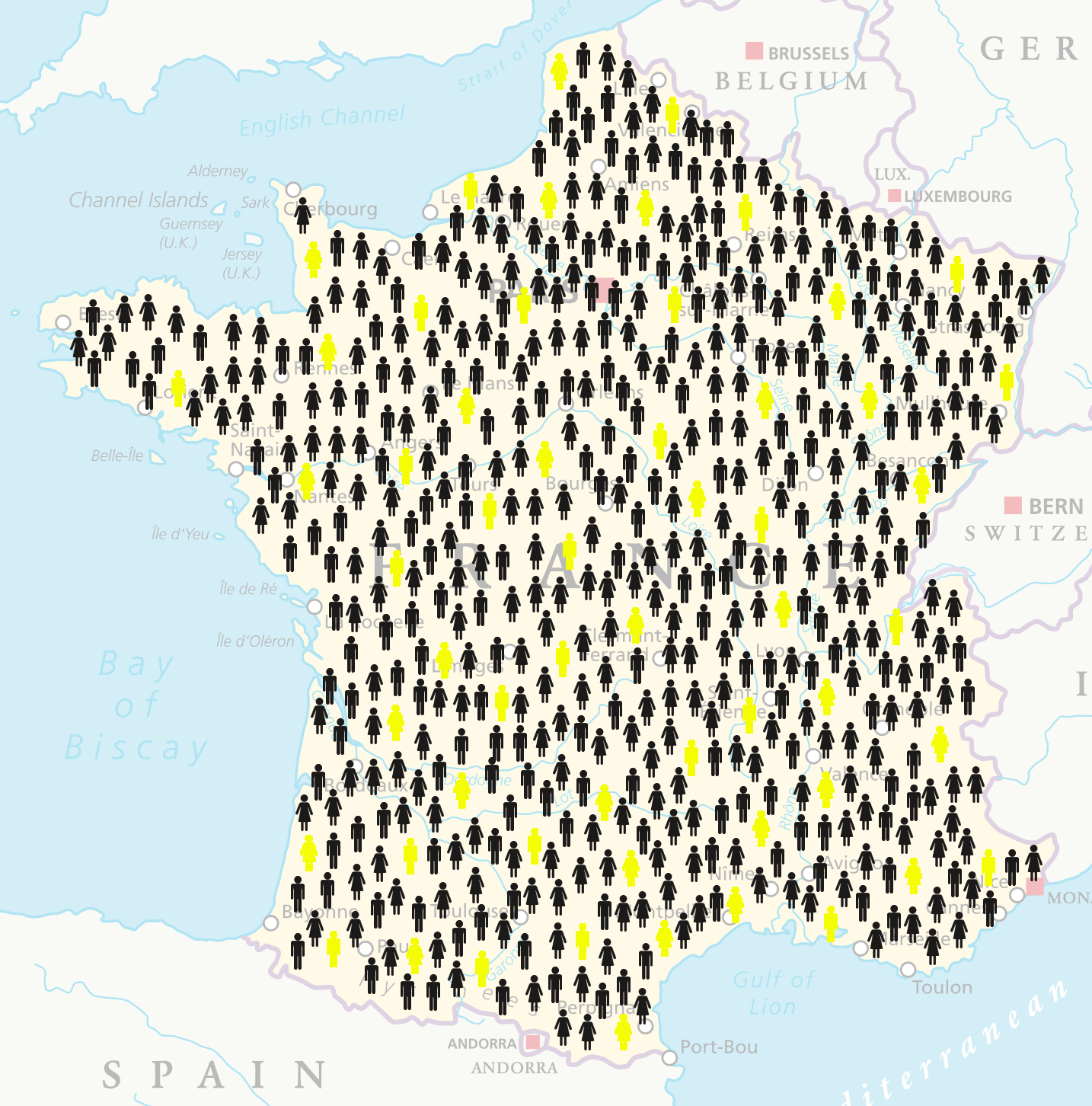
It's cheaper to ask a small number of households and use statistics to make estimates about the whole population.
Working with a subset of the whole population is called sampling.
Population vs. sample
The population is the complete dataset.
- It doesn't have to refer to people.
- You typically don't know what the whole population is.
The sample is the subset of data you calculate on.
Coffee rating dataset
| total_cup_points | variety | country_of_origin | aroma | flavor | aftertaste | body | balance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 90.58 | NA | Ethiopia | 8.67 | 8.83 | 8.67 | 8.50 | 8.42 |
| 89.92 | Other | Ethiopia | 8.75 | 8.67 | 8.50 | 8.42 | 8.42 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 73.75 | NA | Vietnam | 6.75 | 6.67 | 6.5 | 6.92 | 6.83 |
- Each row represents 1 coffee.
- 1138 rows.
- We'll treat this as the population.
Points vs. flavor: population
pts_vs_flavor_pop <- coffee_ratings %>%
select(total_cup_points, flavor)
dim(pts_vs_flavor_pop)
1338 2
total_cup_points flavor
1 90.58 8.83
2 89.92 8.67
3 89.75 8.50
4 89.00 8.58
... ... ...
1335 78.08 7.67
1336 77.17 7.33
1337 75.08 6.83
1338 73.75 6.67
Points vs. flavor: 10 row sample
pts_vs_flavor_samp <- coffee_ratings %>%
select(total_cup_points, flavor) %>%
slice_sample(n = 10)
dim(pts_vs_flavor_samp)
10 2
total_cup_points flavor
1 82.25 7.58
2 83.50 7.67
3 80.50 7.17
4 79.33 7.17
5 83.83 7.58
6 84.17 7.75
7 83.67 8.17
8 81.92 7.50
9 82.67 7.58
10 83.42 7.67
Base-R sampling
Use slice_sample() for data frames, and sample() for vectors.
cup_points_samp <- sample(coffee_ratings$total_cup_points, size = 10)
88.25 83.83 83.17 82.67 84.67 83.42 73.67 86.00 81.58 80.92
Population parameters & point estimates
A population parameter is a calculation made on the population dataset.
mean(pts_vs_flavor_pop$total_cup_points)
82.15
A point estimate or sample statistic is a calculation made on the sample dataset.
mean(cup_points_samp)
82.82
Point estimates with dplyr
pts_vs_flavor_pop %>%
summarize(mean_flavor = mean(flavor))
mean_flavor
1 7.526
pts_vs_flavor_samp %>%
summarize(mean_flavor = mean(flavor))
mean_flavor
1 7.716
Let's practice!
Sampling in R

