The central limit theorem
Introduction to Statistics in Python

Maggie Matsui
Content Developer, DataCamp
Rolling the dice 5 times
die = pd.Series([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])# Roll 5 times samp_5 = die.sample(5, replace=True) print(samp_5)
array([3, 1, 4, 1, 1])
np.mean(samp_5)
2.0

Rolling the dice 5 times
# Roll 5 times and take mean
samp_5 = die.sample(5, replace=True)
np.mean(samp_5)
4.4
samp_5 = die.sample(5, replace=True)
np.mean(samp_5)
3.8
Rolling the dice 5 times 10 times
Repeat 10 times:
- Roll 5 times
- Take the mean
sample_means = []for i in range(10):samp_5 = die.sample(5, replace=True) sample_means.append(np.mean(samp_5))print(sample_means)
[3.8, 4.0, 3.8, 3.6, 3.2, 4.8, 2.6,
3.0, 2.6, 2.0]
Sampling distributions
Sampling distribution of the sample mean
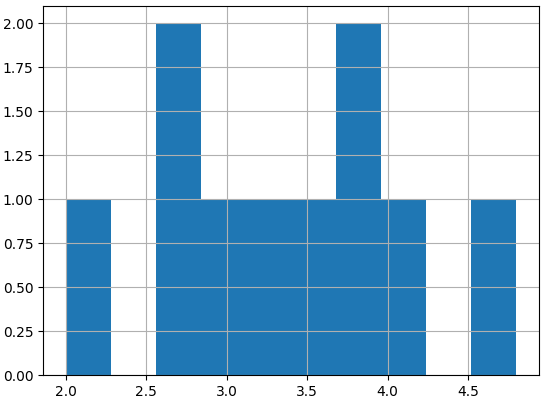
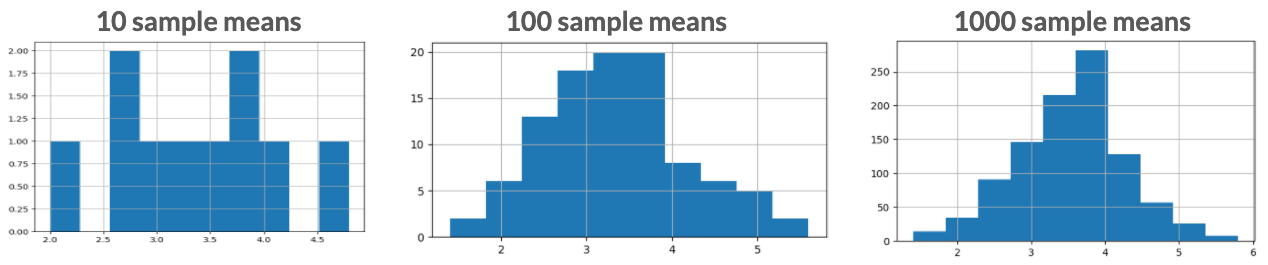
100 sample means
sample_means = []
for i in range(100):
sample_means.append(np.mean(die.sample(5, replace=True)))
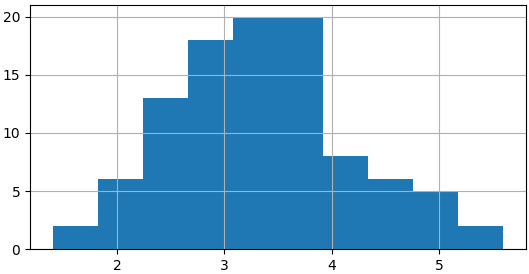
1000 sample means
sample_means = []
for i in range(1000):
sample_means.append(np.mean(die.sample(5, replace=True)))
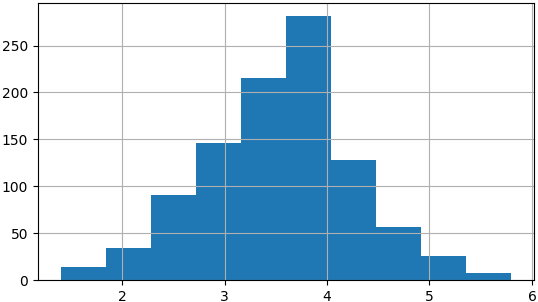
Central limit theorem
The sampling distribution of a statistic becomes closer to the normal distribution as the number of trials increases.
* Samples should be random and independent
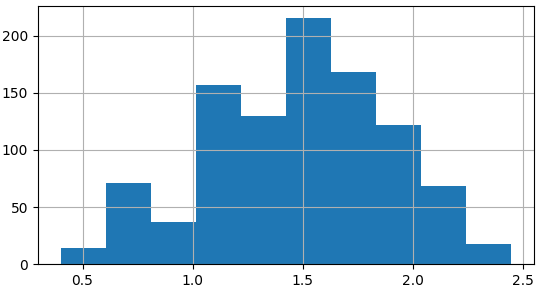
Standard deviation and the CLT
sample_sds = []
for i in range(1000):
sample_sds.append(np.std(die.sample(5, replace=True)))
Proportions and the CLT
sales_team = pd.Series(["Amir", "Brian", "Claire", "Damian"])sales_team.sample(10, replace=True)
array(['Claire', 'Damian', 'Brian', 'Damian', 'Damian', 'Amir', 'Amir', 'Amir',
'Amir', 'Damian'], dtype=object)
sales_team.sample(10, replace=True)
array(['Brian', 'Amir', 'Brian', 'Claire', 'Brian', 'Damian', 'Claire', 'Brian',
'Claire', 'Claire'], dtype=object)
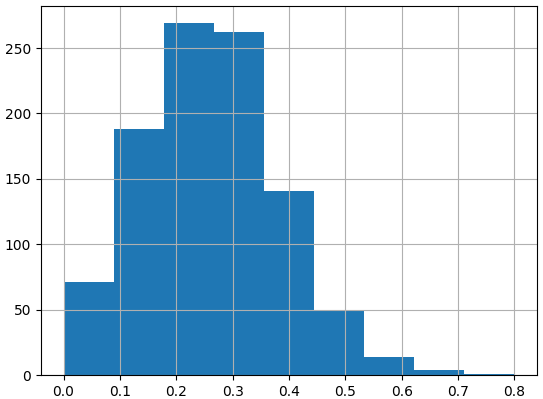
Sampling distribution of proportion
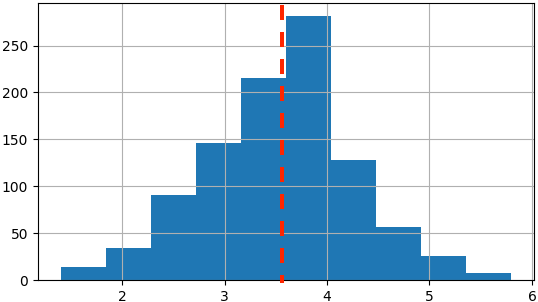
Mean of sampling distribution
# Estimate expected value of die
np.mean(sample_means)
3.48
# Estimate proportion of "Claire"s
np.mean(sample_props)
0.26
- Estimate characteristics of unknown underlying distribution
- More easily estimate characteristics of large populations
Let's practice!
Introduction to Statistics in Python

