Probability and Bayes' Theorem
Bayesian Data Analysis in Python

Michal Oleszak
Machine Learning Engineer
Probability theory
- Statement of uncertainty.
- A number between 0 and 1.
- P = 0 → impossible
- P = 1 → certain
- P = 0.5 → 50/50 chance
- P(rain tomorrow) = 0.75 → 75% chance of rain tomorrow
Probability rules
Sum rule
- Probability of A or B (independent events)
- OR = addition
- Probability of rolling 2 or 4 with a die
P(2 or 4) = 1/6 + 1/6 = 0.33333... = 33.3%
Product rule
- Probability of A and B (independent events)
- AND = multiplication
- Probability of rolling 2 and then 4 with a die
P(2 and 4) = 1/6 * 1/6 = 0.02777... = 2.8%
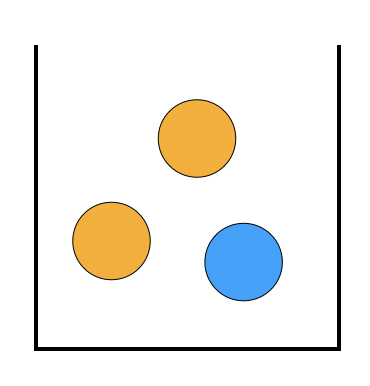
Conditional probability
- Probability of some event occurring, given that some other event has occurred.
- P(A | B)
- P(orange) = 2/3 → unconditional
- P(blue) = 1/3 → unconditional
- P(blue | orange) = 1/2 → conditional
- P(orange | blue) = 1 → conditional
Bayes' Theorem
- A way to calculate conditional probability when we know some other probabilities.
$$P(A|B) = \frac{P(B|A) * P(A)}{P(B)}$$
Bayes' Theorem
- A way to calculate conditional probability when we know some other probabilities.
$$P(\text{accident}|\text{slippery}) = \frac{P(\text{slippery}|\text{accident}) * P(\text{accident})}{P(\text{slippery})}$$
road_conditions.head()
accident slippery
0 False True
1 True True
2 False False
3 False False
4 False False
Bayes' Theorem in practice
$$P(\text{accident}|\text{slippery}) = \frac{P(\text{slippery}|\text{accident}) * P(\text{accident})}{P(\text{slippery})}$$
# Unconditional probability of an accident p_accident = road_conditions["accident"].mean() # 0.0625# Unconditional probability of the road being slippery p_slippery = road_conditions["slippery"].mean() # 0.0892# Probability of the road being slippery given there is an accident p_slippery_given_accident = road_conditions.loc[road_conditions["accident"]]["slippery"].mean() # 0.7142# Probability of an accident given the road is slippery p_accident_given_slippery = p_slippery_given_accident * p_accident / p_slippery # 0.5
Let's practice!
Bayesian Data Analysis in Python

