Interpreting results and comparing models
Bayesian Data Analysis in Python

Michal Oleszak
Machine Learning Engineer
Running the model revisited
formula = "num_clicks ~ clothes_banners_shown + sneakers_banners_shown"
with pm.Model() as model_1:
pm.GLM.from_formula(formula, data=ads_aggregated)
trace_1 = pm.sample(draws=1000, tune=500)
Running the model revisited
formula = "num_clicks ~ clothes_banners_shown + sneakers_banners_shown"
with pm.Model() as model_1:
pm.GLM.from_formula(formula, data=ads_aggregated)
trace_1 = pm.sample(draws=1000, tune=500, chains=4)
- Number of parameters: 4
- Number of draws for each parameter: 1000 $\times$ 4 = 4000
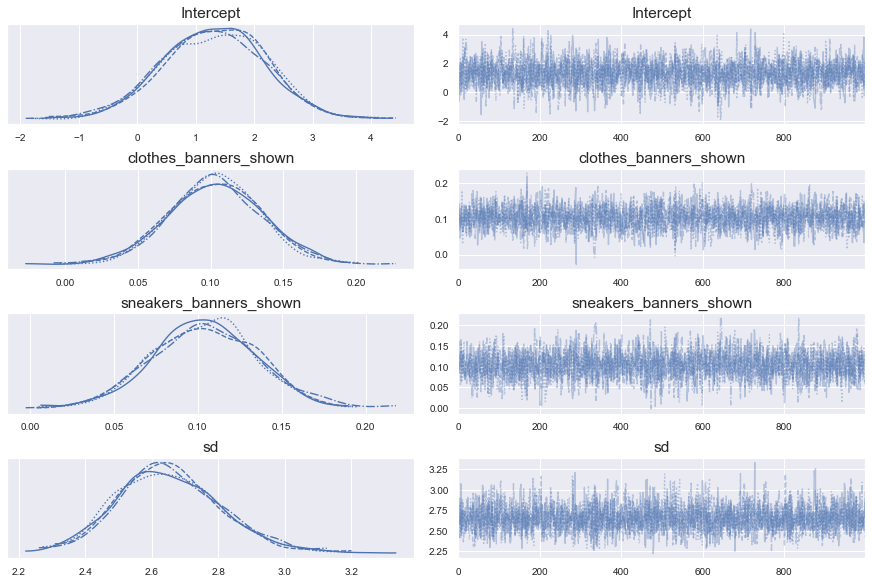
Trace plot
pm.traceplot(trace_1)
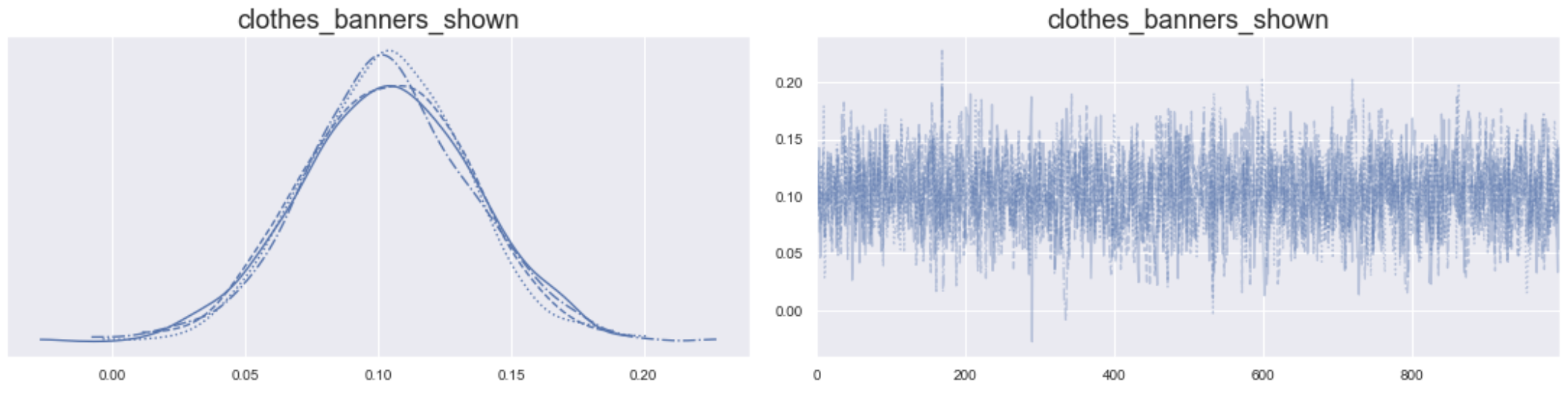
Trace plot: zoom in on one parameter
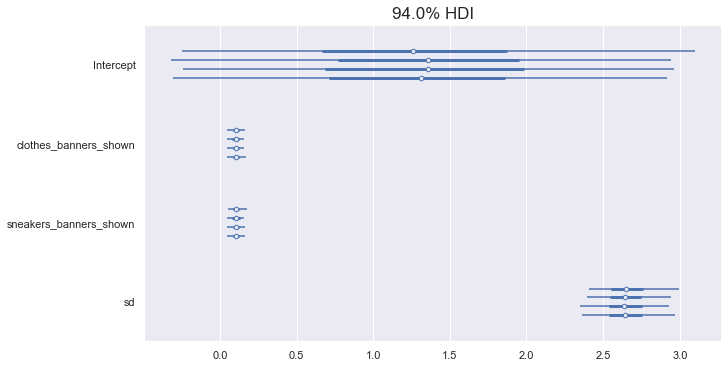
Forest plot
pm.forestplot(trace_1)
Trace summary
pm.summary(trace_1)
mean sd hdi_3% hdi_97% mcse_mean mcse_sd \
Intercept 1.307 0.886 -0.305 2.962 0.018 0.013
clothes_banners_shown 0.103 0.031 0.043 0.160 0.001 0.000
sneakers_banners_shown 0.104 0.032 0.045 0.163 0.001 0.001
sd 2.654 0.157 2.382 2.970 0.003 0.002
ess_mean ess_sd ess_bulk ess_tail r_hat
Intercept 2346.0 2318.0 2351.0 2083.0 1.0
clothes_banners_shown 2085.0 2085.0 2089.0 1868.0 1.0
sneakers_banners_shown 2105.0 1953.0 2122.0 1869.0 1.0
sd 2615.0 2590.0 2646.0 1834.0 1.0
Fitting another model
formula = "num_clicks ~ clothes_banners_shown + sneakers_banners_shown + weekend"
with pm.Model() as model_2:
pm.GLM.from_formula(formula, data=ads_aggregated)
trace_2 = pm.sample(draws=1000, tune=500)
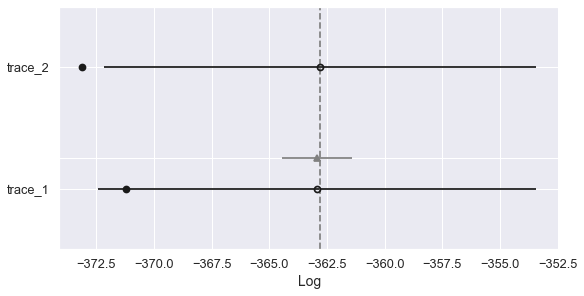
Widely Applicable Information Criterion (WAIC)
comparison = pm.compare({"trace_1": trace_1, "trace_2": trace_2},
ic="waic", scale="deviance")
print(comparison)
rank waic p_waic d_waic weight se dse warning \
trace_2 0 -362.8 5.1576 0 0.513792 9.37269 0 True
trace_1 1 -362.926 4.13318 0.126236 0.486208 9.48352 1.50682 True
waic_scale
trace_2 log
trace_1 log
Compare plot
pm.compareplot(comparison)
Let's practice comparing models!
Bayesian Data Analysis in Python

