Reporting Bayesian results
Bayesian Data Analysis in Python

Michal Oleszak
Machine Learning Engineer
The honest way
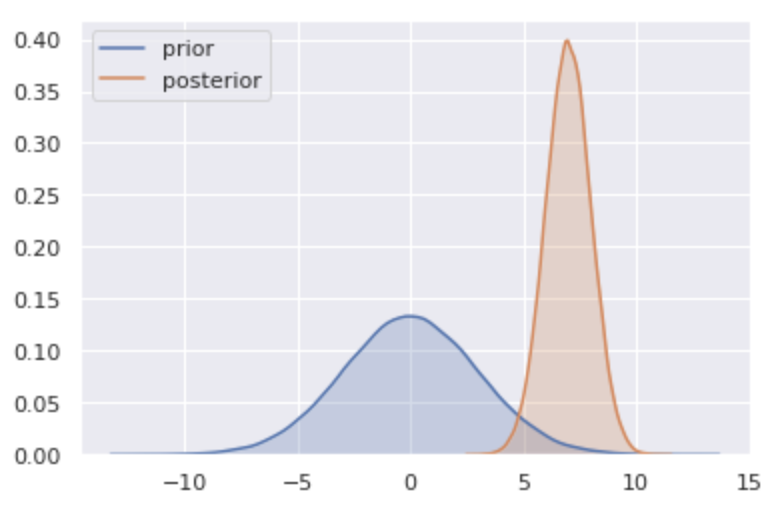
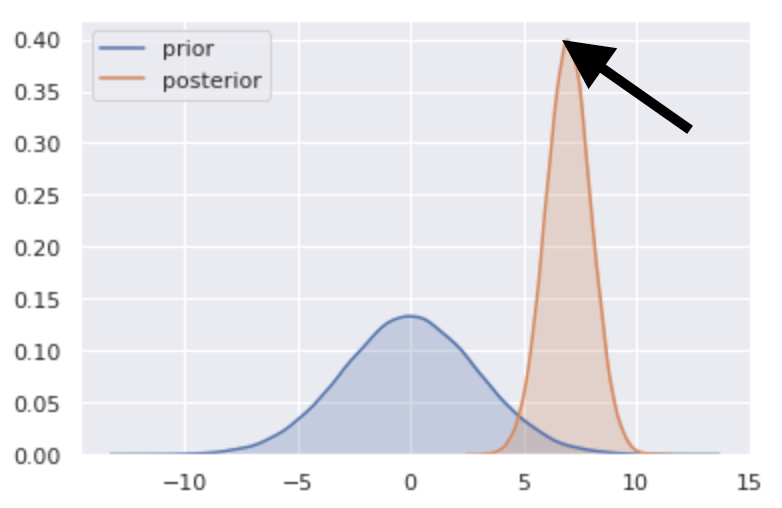
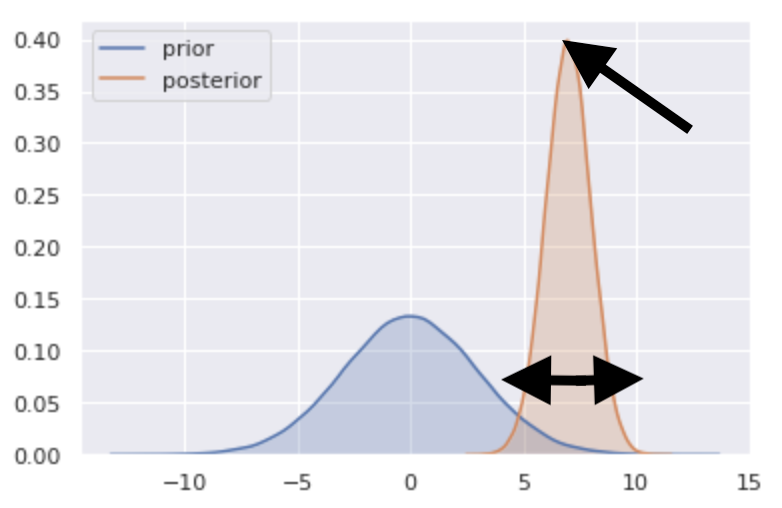
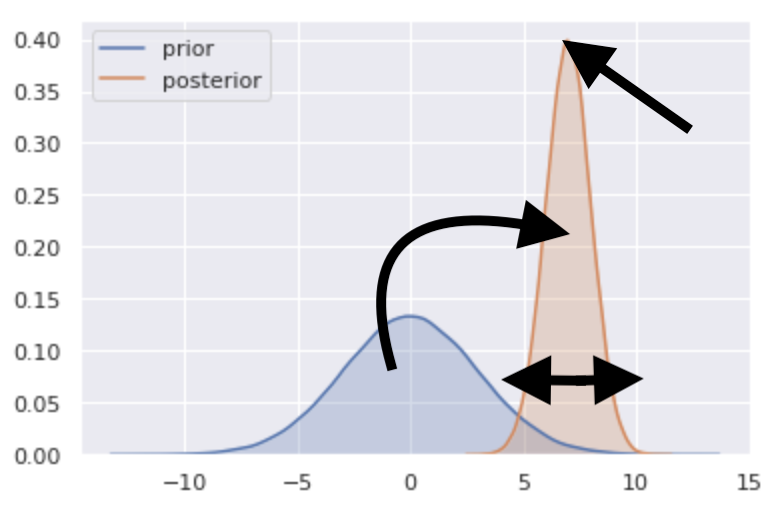
- Report the prior and the posterior of each parameter
posterior_draws
array([8.02800413, 8.97359548, 7.57437476, ..., 5.85264609, 7.92875104,
7.41463758])
- Plot prior and posterior distributions
sns.kdeplot(prior_draws, shade=True, label="prior")
sns.kdeplot(posterior_draws, shade=True, label="posterior")
The honest way
The honest way
The honest way
The honest way
Bayesian point estimates
No single number can fully convey the complete information contained in a distribution
However, sometimes a point estimate of a parameter is needed
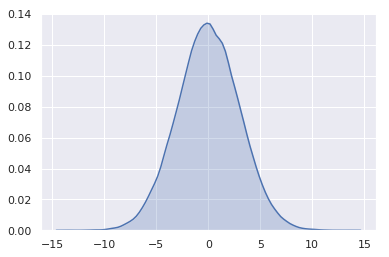
Bayesian point estimates
No single number can fully convey the complete information contained in a distribution
However, sometimes a point estimate of a parameter is needed
posterior_mean = np.mean(posterior_draws)
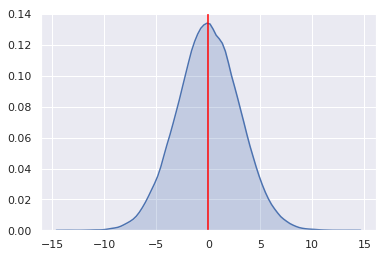
Bayesian point estimates
No single number can fully convey the complete information contained in a distribution
However, sometimes a point estimate of a parameter is needed
posterior_mean = np.mean(posterior_draws)
posterior_median = np.median(posterior_draws)
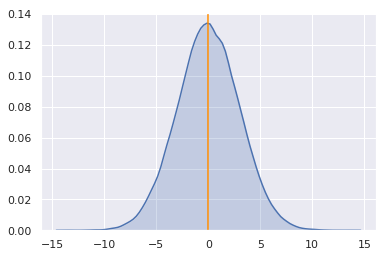
Bayesian point estimates
No single number can fully convey the complete information contained in a distribution
However, sometimes a point estimate of a parameter is needed
posterior_mean = np.mean(posterior_draws)
posterior_median = np.median(posterior_draws)
posterior_p75 = np.percentile(posterior_draws, 75)
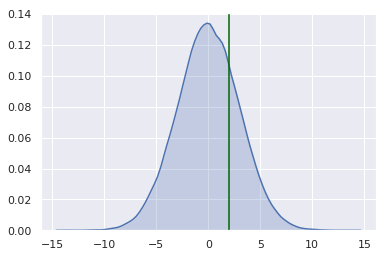
Credible intervals
- Such an interval that the probability that the parameter falls inside it is x%
- The wider the credible interval, the more uncertainty in parameter estimate
- Parameter is random, so it can fall into an interval with some probability
- In the frequentist world, the (confidence) interval is random while the parameter is fixed
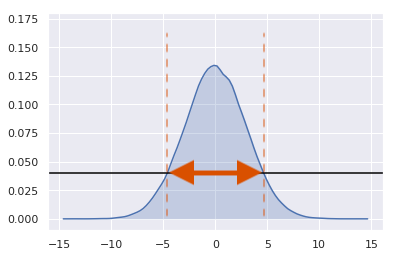
Highest Posterior Density (HPD)
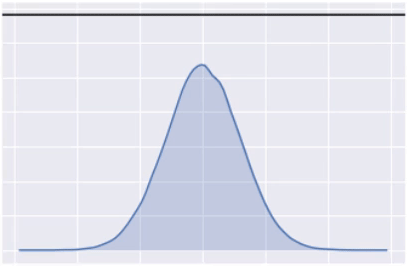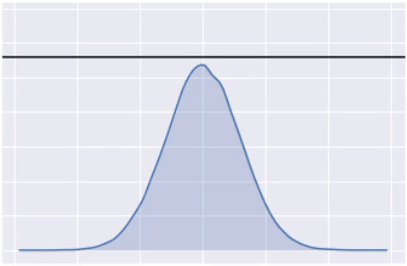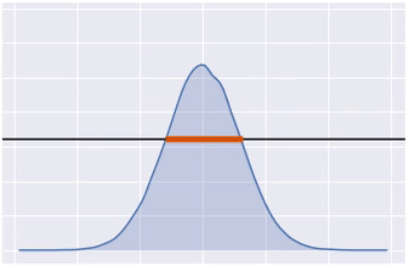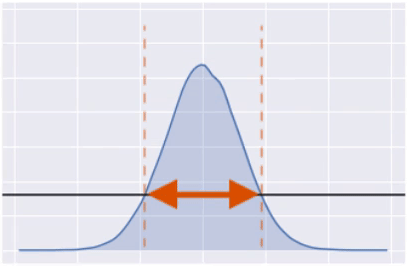
import arviz as az
hpd = az.hdi(posterior_draws,
hdi_prob=0.9)
print(hpd)
[-4.86840193 4.96075498]
Let's practice reporting Bayesian results!
Bayesian Data Analysis in Python

