Sliders
Introduction to Data Visualization with Plotly in Python

Alex Scriven
Data Scientist
What are sliders?
An interactive element to toggle between values and update a plot
Used for viewing data over time
Can be used for any group
$$
$$
$$
- 💡 Ensure it makes sense in your plot
A year slider:

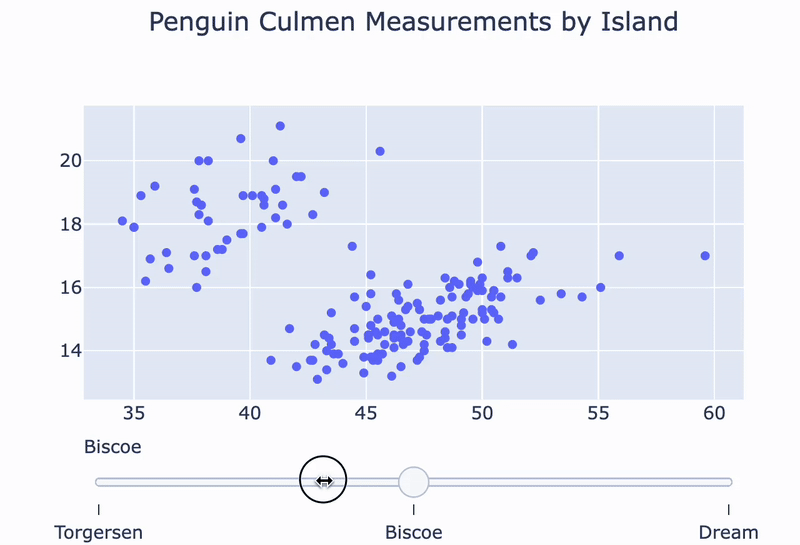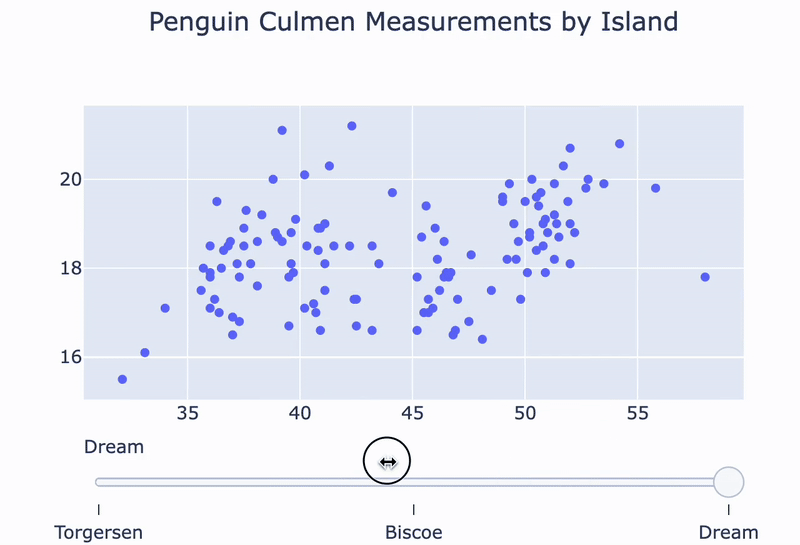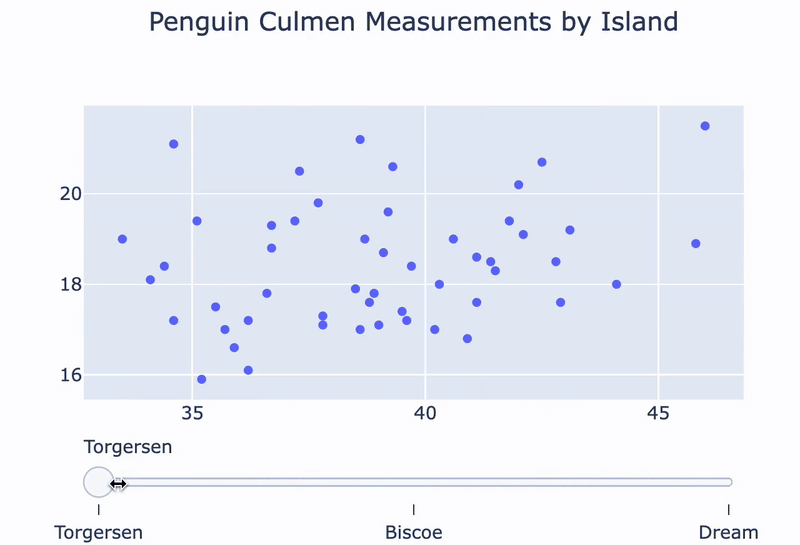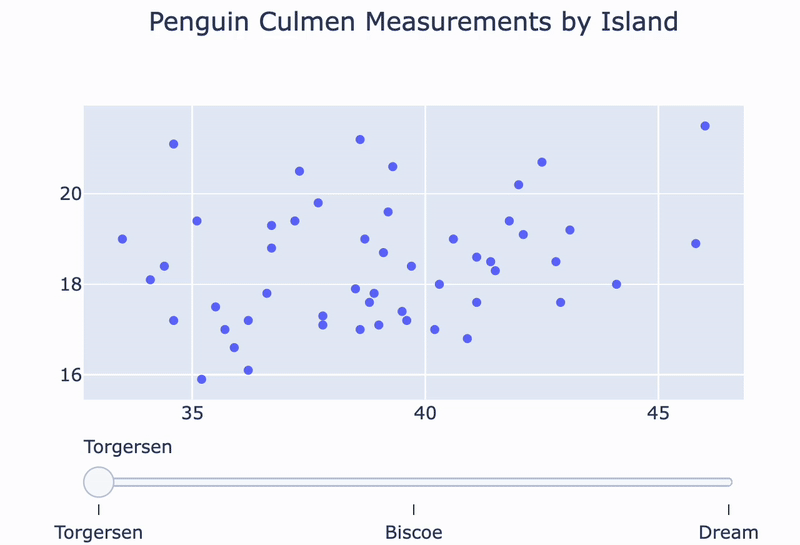
A penguin island slider:

Sliders in plotly.express
animation_frameWhat will be on the slider (YearorIslandon the previous slide)
$$
animation_group: Identifies which samples stay consistent across frames
Revenue vs. Employees with slider
fig = px.scatter( data_frame=revenues, y='Revenue', x='Employees', color='Industry',animation_frame='Year', animation_group='Company')fig.update_layout({ 'yaxis': {'range': [0, 500000]}, 'xaxis': {'range': [-100000, 2500000]} })fig['layout'].pop('updatemenus') fig.show()
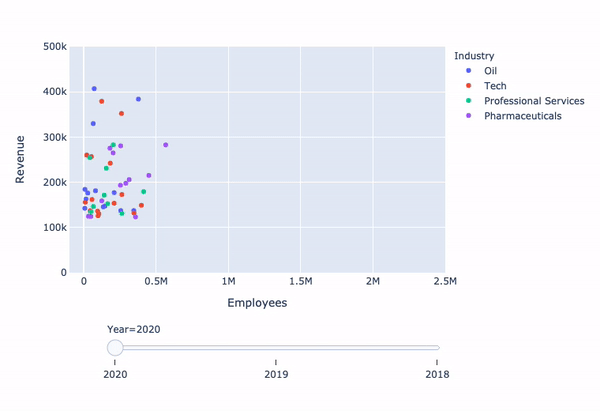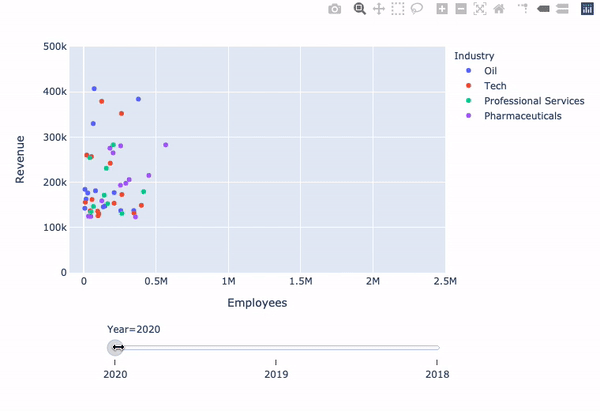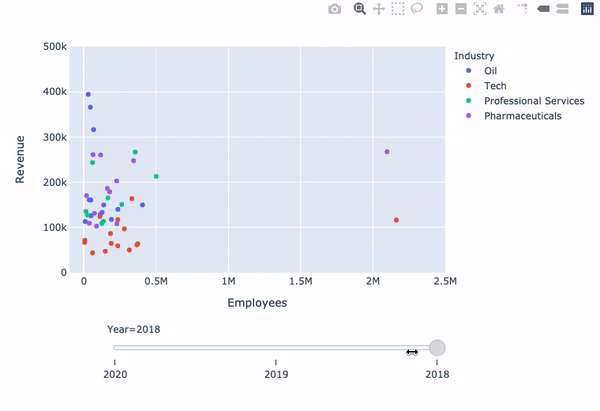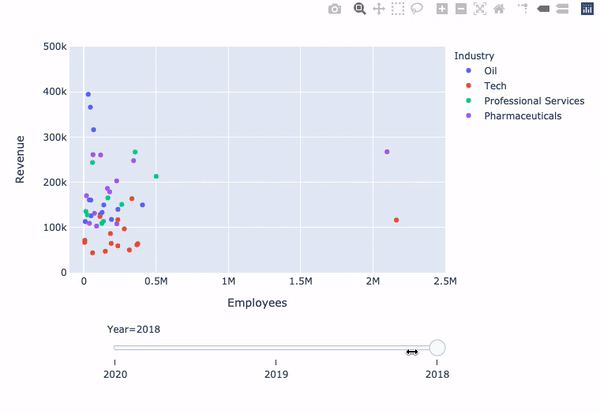
Limitation: animate method
plotly.express implements sliders using animate method
$$
fig['layout']['sliders'][0].steps[0]['method']
animate
$$
- Only animates the same data point over time
- Build the slider using traces
Our plan
- Create a figure object with necessary traces
- Define a sliders object to show/hide traces
- Update the layout to add the slider to the figure
Creating the figure
fig = go.Figure()for island in ['Torgersen', 'Biscoe', 'Dream']: df = penguins[penguins.Island == island]temp_trace = px.scatter(df, x="Culmen Length (mm)", y="Culmen Depth (mm)") fig.add_trace(temp_trace.data[0])
Creating the slider
sliders = [ {'steps':[{'method': 'update', 'label': 'Torgersen','args': [{'visible': [True, False, False]}]},{'method': 'update', 'label': 'Bisco','args': [{'visible': [False, True, False]}]},{'method': 'update', 'label': 'Dream','args': [{'visible': [False, False, True]}]}]} ]
$$
More formatting options available in the documentation
Adding the slider
$$
fig.update_layout({'sliders': sliders})
fig.show()
Let's practice!
Introduction to Data Visualization with Plotly in Python

