Momentum indicator: RSI
Financial Trading in Python

Chelsea Yang
Data Science Instructor
What is RSI?
- Stands for "Relative Strength Index"
- Developed by J. Welles Wilder
- "New Concepts in Technical Systems" (1987)
- Measures the momentum of a trend
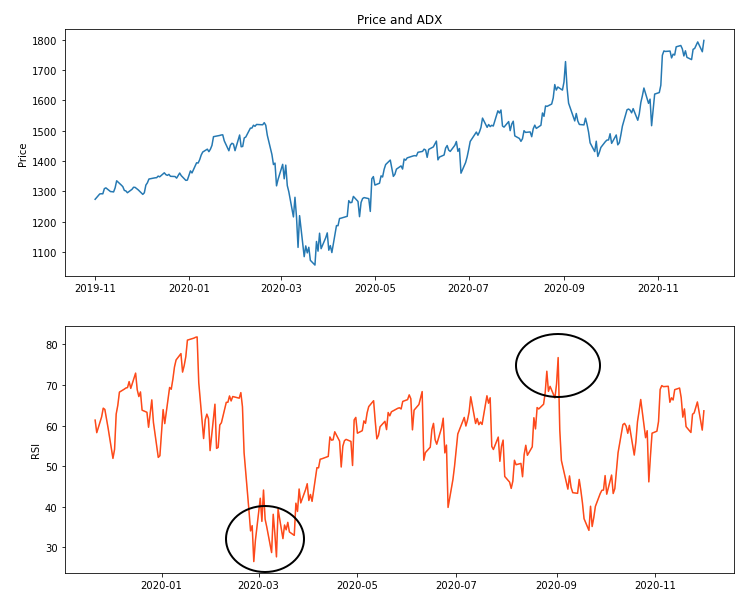
- Oscillates between 0 and 100
- RSI > 70: Overbought
- RSI < 30: Oversold
How is RSI calculated?
$ RSI = 100 - 100/(1+RS) $
Where:
- RS: relative strength
- RS = average of upward price changes / average of downward price changes
Implementing RSI in Python
# Calculate RSI stock_data['RSI'] = talib.RSI(stock_data['Close'], timeperiod=14)# Print the last five rows print(stock_data.tail())
Open High Low Close RSI
Date
2020-11-24 1730.50 1771.60 1727.69 1768.88 62.78
2020-11-25 1772.89 1778.54 1756.54 1771.43 63.10
2020-11-27 1773.09 1804.00 1772.44 1793.19 65.81
2020-11-30 1781.18 1788.06 1755.00 1760.74 58.87
2020-12-01 1774.37 1824.83 1769.37 1798.10 63.63
Plotting RSI
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # Create subplots fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(2)# Plot RSI with the price ax1.set_ylabel('Price') ax1.plot(stock_data['Close']) ax2.set_ylabel('RSI') ax2.plot(stock_data['RSI']) ax1.set_title('Price and RSI') plt.show()
Let's practice!
Financial Trading in Python

