Machine learning workflows
Modeling with tidymodels in R

David Svancer
Data Scientist
Classification with decision trees
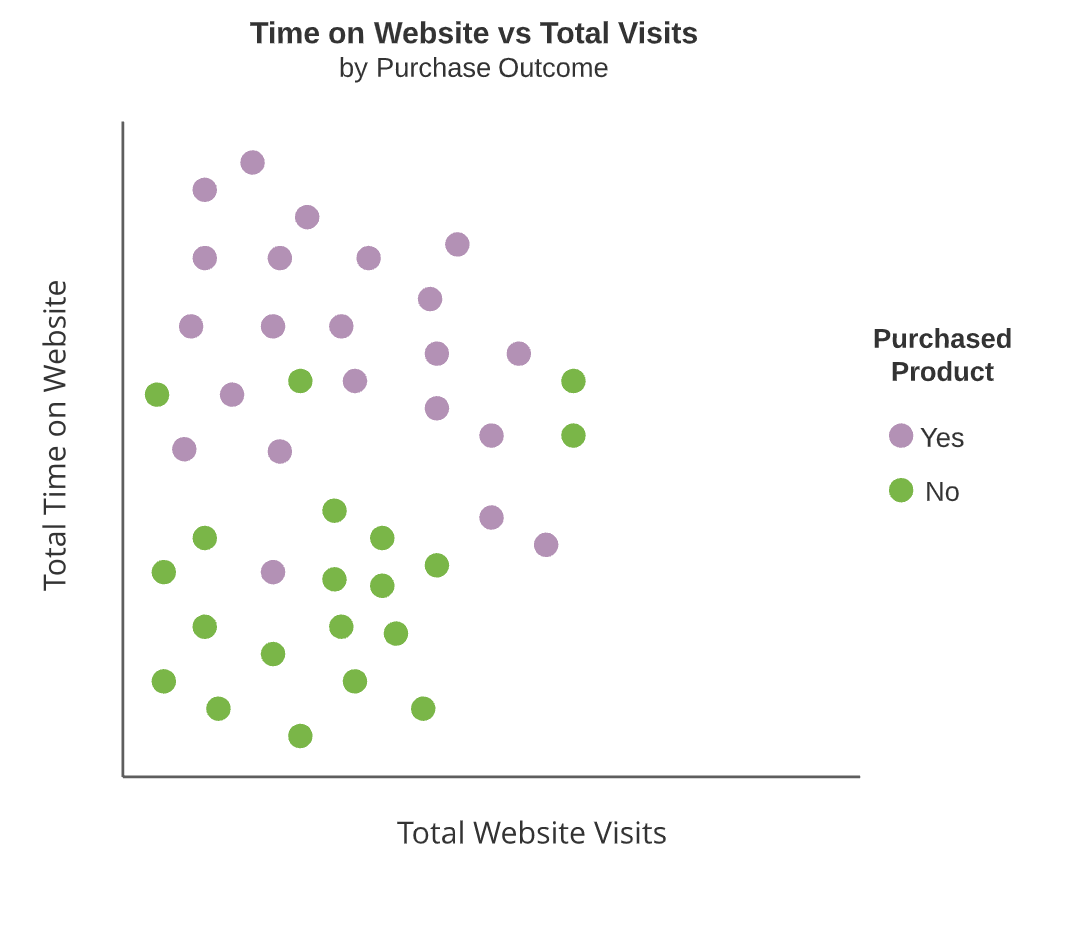
Decision trees segment the predictor space into rectangular regions
Recursive binary splitting
- Algorithm that segments predictor space into non-overlapping rectangular regions
Classification with decision trees
Decision trees segment the predictor space into rectangular regions
Recursive binary splitting
- Algorithm that segments predictor space into non-overlapping rectangular regions
- Decision splits are added iteratively
- Either horizontal or vertical cut points
Classification with decision trees
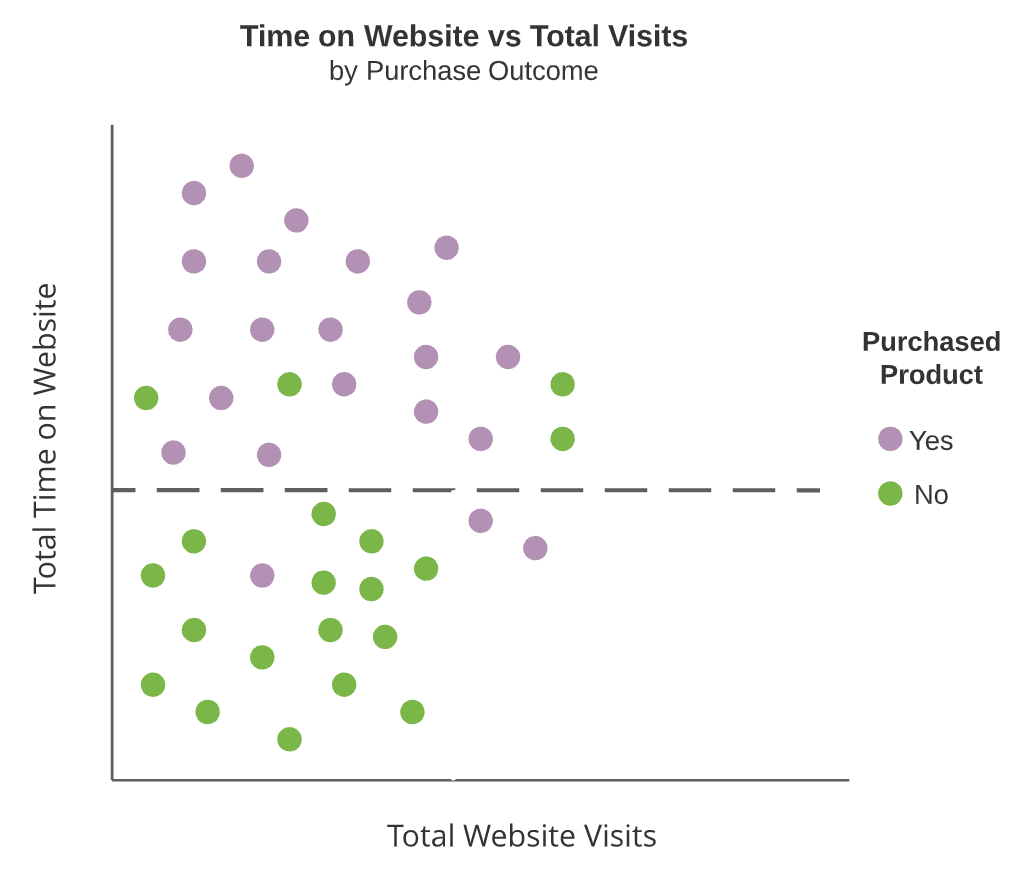
Decision trees segment the predictor space into rectangular regions
Recursive binary splitting
- Algorithm that segments predictor space into non-overlapping rectangular regions
- Decision splits are added iteratively
- Either horizontal or vertical cut points
Classification with decision trees
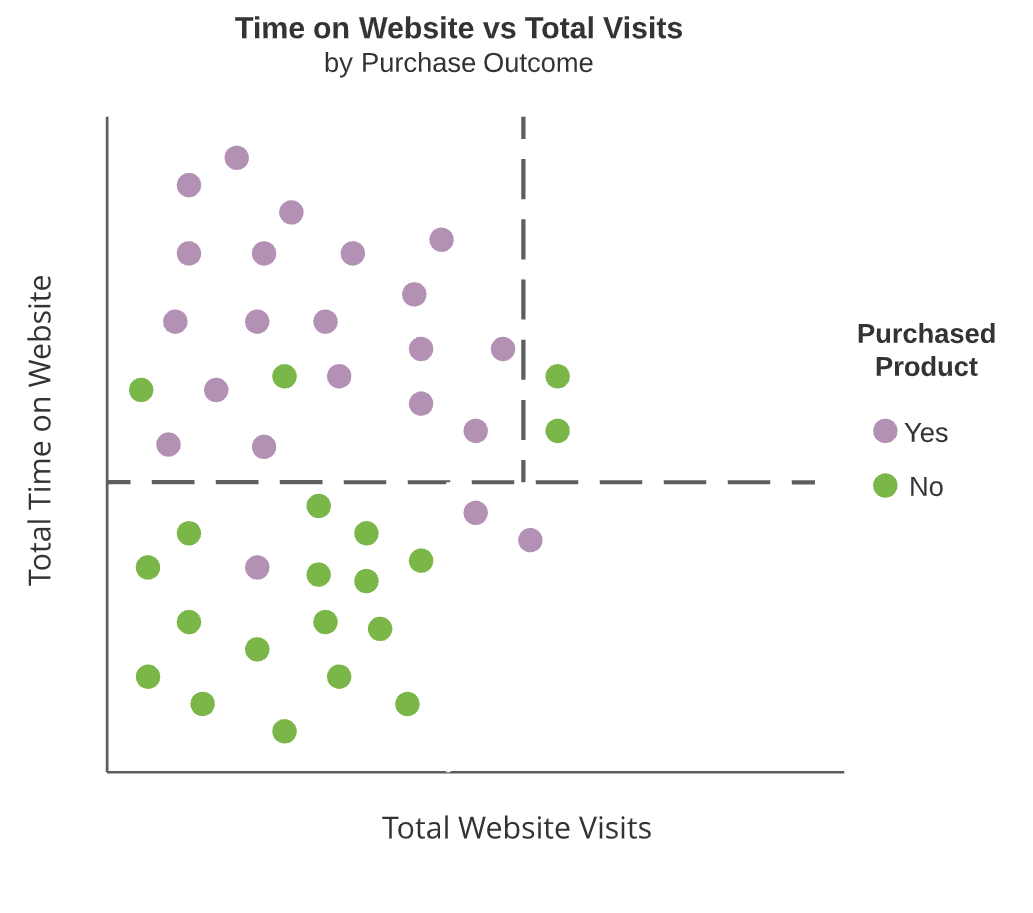
Decision trees segment the predictor space into rectangular regions
Recursive binary splitting
- Algorithm that segments predictor space into non-overlapping rectangular regions
- Decision splits are added iteratively
- Either horizontal or vertical cut points
Classification with decision trees
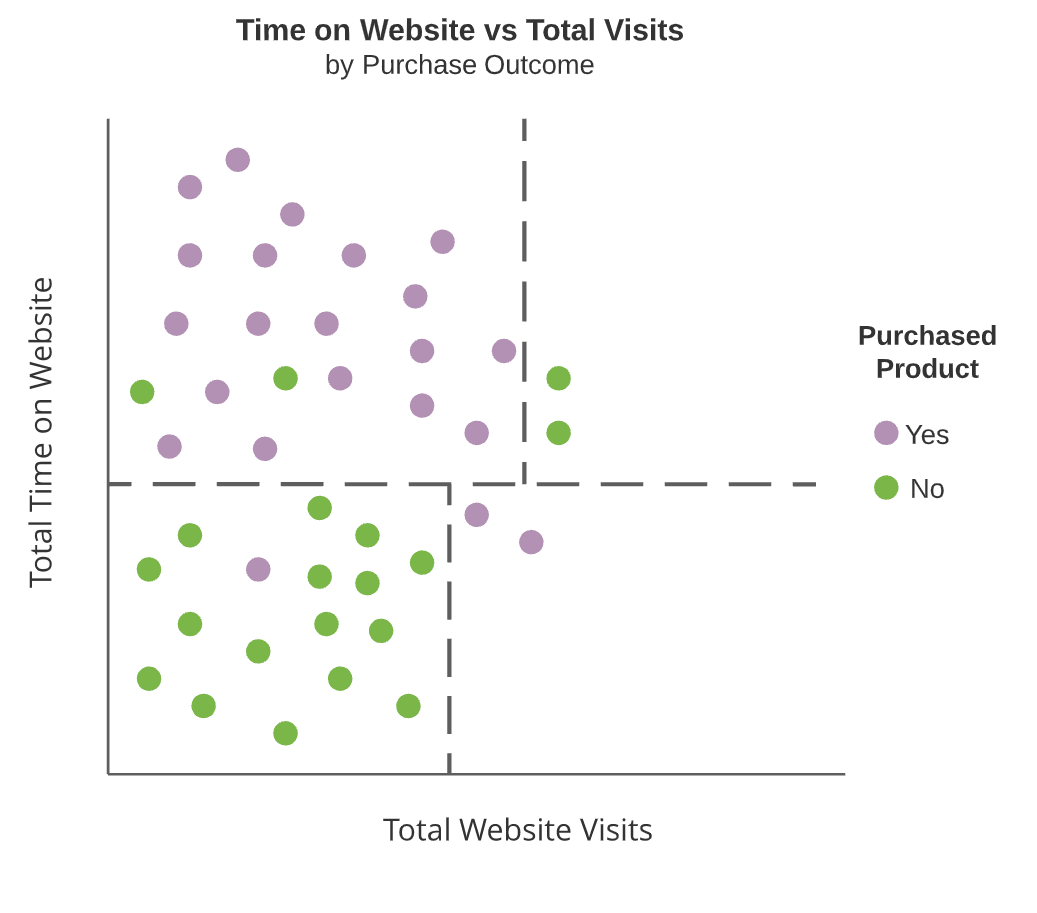
Decision trees segment the predictor space into rectangular regions
Recursive binary splitting
- Algorithm that segments predictor space into non-overlapping rectangular regions
- Decision splits are added iteratively
- Either horizontal or vertical cut points
Produces distinct rectangular regions
- For classification, majority class is predicted
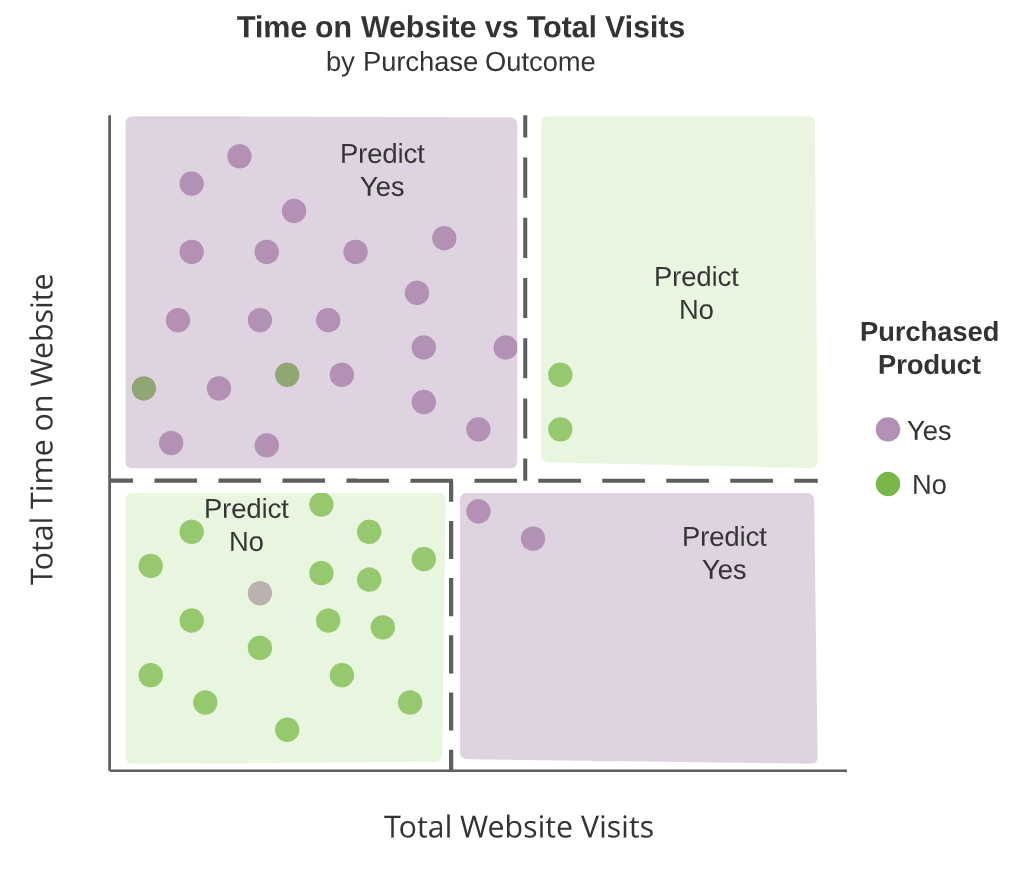
Tree diagrams
- Interior nodes
- Decision tree splits (dark boxes)
- Terminal nodes
- Regions which are not split further
- Green and purple boxes
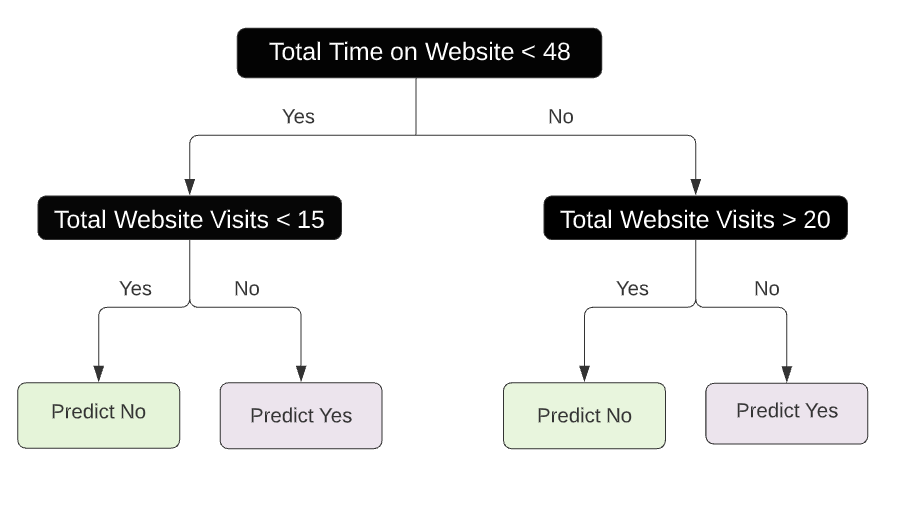
Interior nodes are dashed lines and terminal nodes are highlighted rectangular regions

Model specification
Model specification in parsnip
decision_tree()- General interface to decision tree models in
parsnip - Common engine is
'rpart' - Mode can be either
'classification'or'regression'- For lead scoring data, we need
'classification'
- For lead scoring data, we need
- General interface to decision tree models in
dt_model <- decision_tree() %>%set_engine('rpart') %>%set_mode('classification')
Feature engineering recipe
Data transformations for lead scoring data
- Encoded in a
recipeobject- Remove multicollinearity
- Normalize numeric predictors
- Create dummy variables for nominal predictors
Two R objects to manage
parsnipmodel andrecipespecification- Combining into one object would make life easier
leads_recipe <- recipe(purchased ~ ., data = leads_training) %>%step_corr(all_numeric(), threshold = 0.9) %>% step_normalize(all_numeric()) %>% step_dummy(all_nominal(), -all_outcomes())
leads_recipe
Data Recipe
Inputs:
role #variables
outcome 1
predictor 6
Operations:
Correlation filter on all_numeric()
Centering and scaling for all_numeric()
Dummy variables from all_nominal(), -all_outcomes()
Combining models and recipes
The workflows package is designed for streamlining the model process
- Combines a
parsnipmodel andrecipeobject into a singleworkflowobject
Initialized with the workflow() function
- Add model object with
add_model() - Add
recipeobject withadd_recipe()- Must be specification, not a trained
recipe
- Must be specification, not a trained
leads_wkfl <- workflow() %>%add_model(dt_model) %>%add_recipe(leads_recipe)leads_wkfl
== Workflow =====================
Preprocessor: Recipe
Model: decision_tree()
-- Preprocessor -----------------
3 Recipe Steps
* step_corr()
* step_normalize()
* step_dummy()
-- Model --------------------------
Decision Tree Model Specification (classification)
Computational engine: rpart
Model fitting with workflows
Training a workflow object
- Pass
workflowtolast_fit()and provide data split object - View model evaluation results with
collect_metrics()
Behind the scenes
- Training and test datasets created
recipetrained and applied- Decision tree trained with training data
- Predictions and metrics on test data
leads_wkfl_fit <- leads_wkfl %>% last_fit(split = leads_split)leads_wkfl_fit %>% collect_metrics()
# A tibble: 2 x 3
.metric .estimator .estimate
<chr> <chr> <dbl>
1 accuracy binary 0.771
2 roc_auc binary 0.775
Collecting predictions
A workflow trained with last_fit() can be passed to collect_predictions()
- Produces detailed results on the test data
- Like before, can be used with
yardstickfunctions to explore performance custom metrics
leads_wkfl_preds <- leads_wkfl_fit %>% collect_predictions()leads_wkfl_preds
# A tibble: 332 x 6
id .pred_yes .pred_no .row .pred_class purchased
<chr> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <fct> <fct>
train/test split 0.120 0.880 2 no no
train/test split 0.755 0.245 17 yes yes
train/test split 0.120 0.880 21 no no
train/test split 0.120 0.880 22 no no
train/test split 0.755 0.245 24 yes yes
# ... with 327 more rows
Exploring custom metrics
Create a custom metric set with metric_set()
- Area under the ROC curve, sensitivity, and specificity
Pass predictions datasets to leads_metrics() to calculate metrics
leads_metrics <- metric_set(roc_auc, sens, spec)leads_wkfl_preds %>% leads_metrics(truth = purchased, estimate = .pred_class, .pred_yes)
# A tibble: 3 x 3
.metric .estimator .estimate
<chr> <chr> <dbl>
1 sens binary 0.75
2 spec binary 0.783
3 roc_auc binary 0.775
Loan default dataset
Financial data for consumer loans at a bank
- Outcome variable is
loan_default
loans_df
# A tibble: 872 x 8
loan_default loan_purpose missed_payment_2_yr loan_amount interest_rate installment annual_income debt_to_income
<fct> <fct> <fct> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
no debt_consolidation no 25000 5.47 855. 62823 39.4
yes medical no 10000 10.2 364. 40000 24.1
no small_business no 13000 6.22 442. 65000 14.0
no small_business no 36000 5.97 1152. 125000 8.09
yes small_business yes 12000 11.8 308. 65000 20.1
# ... with 867 more rows
Let's practice building workflows!
Modeling with tidymodels in R

