Classification models
Modeling with tidymodels in R

David Svancer
Data Scientist
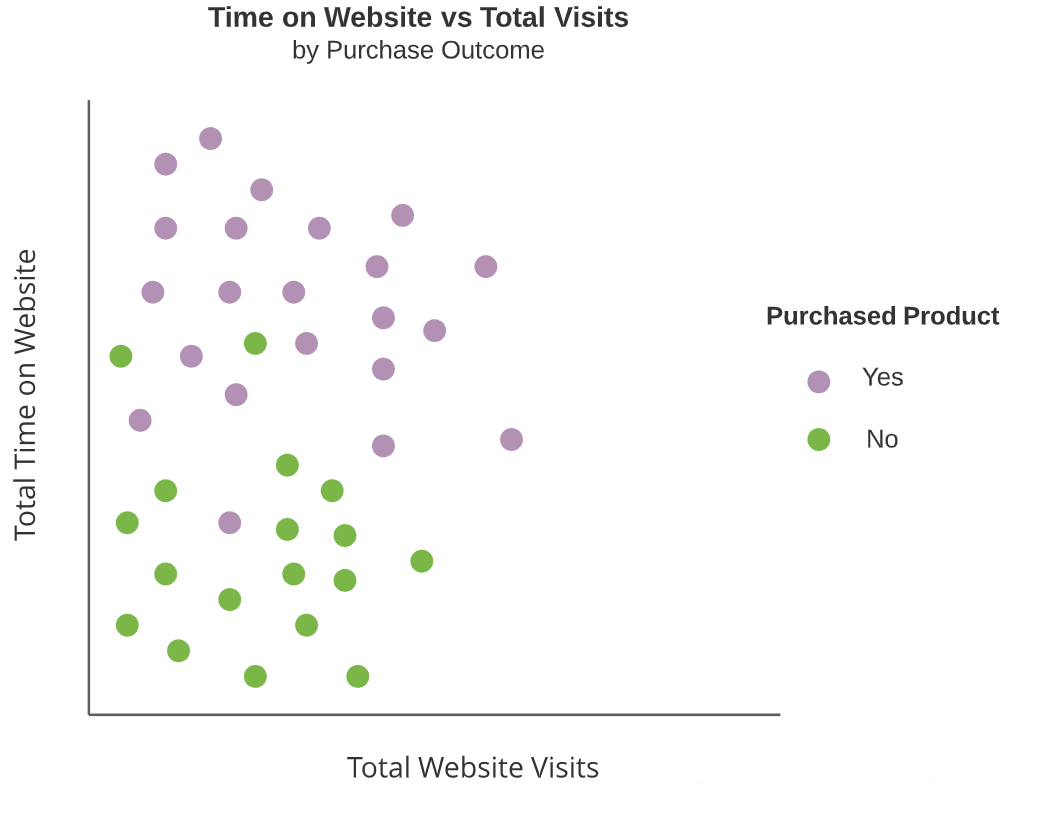
Predicting product purchases
Classification models predict categorical outcome variables
- Predicting product purchases
| purchased | total_time | total_visits |
|---|---|---|
| yes | 800 | 3 |
| yes | 978 | 7 |
| no | 220 | 4 |
| no | 124 | 5 |
| yes | 641 | 4 |
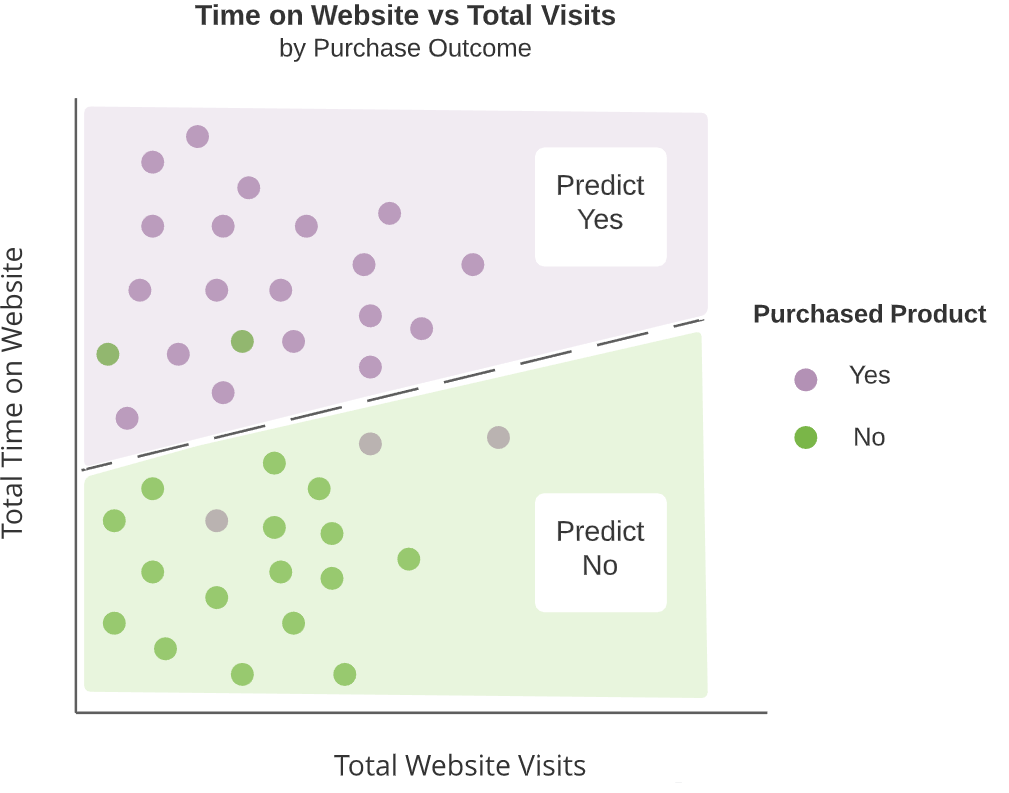
Classification algorithms
Goal: Create distinct, non-overlapping regions along set of predictor variable values
- Predict the same categorical outcome in each region
Classification algorithms
Goal: Create distinct, non-overlapping regions along set of predictor variable values
- Predict the same categorical outcome in each region
Logistic Regression
- Popular classification algorithm which creates a linear separation between outcome categories
Lead scoring data
leads_df
# A tibble: 1,328 x 7
purchased total_visits total_time pages_per_visit total_clicks lead_source us_location
<fct> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <fct> <fct>
1 yes 7 1148 7 59 direct_traffic west
2 no 8 100 2.67 24 direct_traffic west
3 no 5 228 2.5 25 email southeast
4 no 7 481 2.33 21 organic_search west
5 no 4 177 4 37 direct_traffic west
6 no 2 1273 2 26 email midwest
7 no 3 711 3 28 organic_search west
8 no 3 166 3 32 direct_traffic southeast
9 no 3 7 3 23 organic_search west
10 no 6 562 6 48 organic_search southeast
# ... with 1,318 more rows
Data resampling
First step in fitting a model
- Create data split object with
initial_split() - Create training and test datasets with
training()andtesting()
leads_split <- initial_split(leads_df, prop = 0.75, strata = purchased)leads_training <- leads_split %>% training()leads_test <- leads_split %>% testing()
Logistic regression model specification
Model specification in parsnip
logistic_reg()- General interface to logistic regression models in
parsnip - Common engine is 'glm'
- Mode is 'classification'
- General interface to logistic regression models in
logistic_model <- logistic_reg() %>%set_engine('glm') %>%set_mode('classification')
Model fitting
Once model is specified, the fit() function is used for model training
- Pass model object to
fit() - Specify model formula
- Provide training data,
data
logistic_fit <- logistic_model %>%fit(purchased ~ total_visits + total_time,data = leads_training)
Predicting outcome categories
The predict() function
new_dataspecifies dataset on which to predict new valuestype'class'provides categorical predictions
Standardized output from predict()
- Returns a tibble
- When
typeis'class', returns a factor column named.pred_class
class_preds <- logistic_fit %>%predict(new_data = leads_test,type = 'class')class_preds
# A tibble: 332 x 1
.pred_class
<fct>
1 no
2 yes
3 no
4 no
5 yes
# ... with 327 more rows
Estimated probabilities
Setting type to 'prob' provides estimated probabilities for each outcome category
The predict() function will return a tibble with multiple columns
- One for each category of the outcome variable
- Naming convention is
.pred_{outcome_category}
prob_preds <- logistic_fit %>%
predict(new_data = leads_test,
type = 'prob')
prob_preds
# A tibble: 332 x 2
.pred_yes .pred_no
<dbl> <dbl>
1 0.134 0.866
2 0.729 0.271
3 0.133 0.867
4 0.0916 0.908
5 0.598 0.402
# ... with 327 more rows
Combining results
For model evaluation with the yardstick package, a results tibble will be needed
The outcome variable from the test dataset and prediction tibbles can be combined with bind_cols()
leads_results <- leads_test %>%
select(purchased) %>%
bind_cols(class_preds, prob_preds)
leads_results
# A tibble: 332 x 4
purchased .pred_class .pred_yes .pred_no
<fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl>
1 no no 0.134 0.866
2 yes yes 0.729 0.271
3 no no 0.133 0.867
4 no no 0.0916 0.908
5 yes yes 0.598 0.402
# ... with 327 more rows
Telecommunications data
telecom_df
# A tibble: 975 x 9
canceled_service cellular_service avg_data_gb avg_call_mins avg_intl_mins internet_service contract months_with_company monthly_charges
<fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl>
1 yes single_line 7.78 497 127 fiber_optic month_to_month 7 76.4
2 yes single_line 9.04 336 88 fiber_optic month_to_month 10 94.9
3 no single_line 10.3 262 55 fiber_optic one_year 50 103.
4 yes multiple_lines 5.08 250 107 digital one_year 53 60.0
5 no multiple_lines 8.05 328 122 digital two_year 50 75.2
6 no single_line 9.3 326 114 fiber_optic month_to_month 25 95.7
7 yes multiple_lines 8.01 525 97 fiber_optic month_to_month 19 83.6
8 no multiple_lines 9.4 312 147 fiber_optic one_year 50 99.4
9 yes single_line 5.29 417 96 digital month_to_month 8 49.8
10 no multiple_lines 9.96 340 136 fiber_optic month_to_month 61 106.
# ... with 965 more rows
Let's practice!
Modeling with tidymodels in R