Tuning hyperparameters
Machine Learning with Tree-Based Models in R

Sandro Raabe
Data Scientist
Hyperparameters
- Influence shape and complexity of trees
- Model parameters whose values control model complexity and are set prior to model training
Hyperparameters in parsnip decision trees:
min_n: Minimum number of samples required to split a nodetree_depth: maximum allowed depth of the treecost_complexity: penalty for tree complexity
Why tuning?
Default values set by parsnip:
decision_tree(min_n = 20, tree_depth = 30, cost_complexity = 0.01)
- Work well in many cases, but may not be the best values for all datasets
Goal of hyperparameter tuning is finding the optimal set of hyperparameter values.
Tuning with tidymodels using the tune package
Tuning with tidymodels
Tuning with tidymodels
Tuning with tidymodels
Step 1: Create placeholders: tune()
spec_untuned <- decision_tree(min_n = tune(), tree_depth = tune()) %>% set_engine("rpart") %>% set_mode("classification")
Decision Tree Model Specification (classification)Main Arguments: tree_depth = tune() min_n = tune()
tune()labels parameters for tuning- Rest of the specification as usual
Step 2: Create a tuning grid: grid_regular()
tree_grid <- grid_regular(parameters(spec_untuned),levels = 3 )
# A tibble: 9 x 2
min_n tree_depth
1 2 1
2 21 1
3 40 1
4 2 8
5 21 8
6 40 8
7 2 15
8 21 15
9 40 15
- Helper function
parameters() levels: number of grid points for each hyperparameter
Step 3: Tune the grid: tune_grid()
- Builds a model for every grid point
- Evaluates every model out-of-sample (CV)
Usage and arguments:
- Untuned tree spec
- Model formula
- CV folds
- Tuning grid
- List of metrics wrapped in
metric_set()
tune_results <- tune_grid(spec_untuned,outcome ~ .,resamples = my_folds,grid = tree_grid,metrics = metric_set(accuracy))
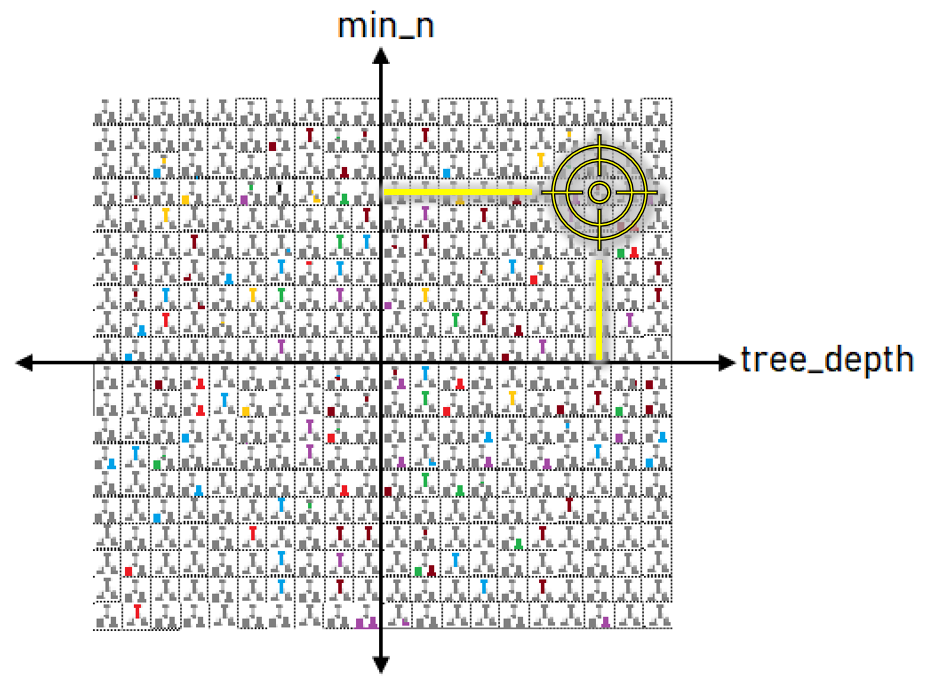
Visualize the tuning results
autoplot(tune_results)
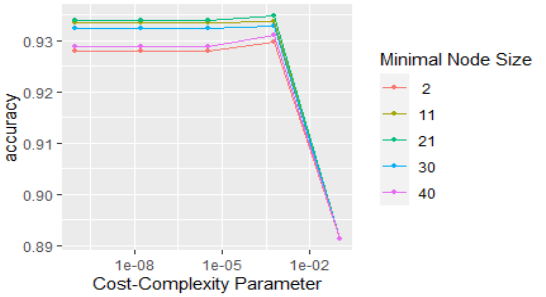
Step 4: Use the best parameters: finalize_model()
# Select the best performing parameters final_params <- select_best(tune_results)final_params
# A tibble: 1 x 3
min_n tree_depth .config
<int> <int> <chr>
1 2 8 Model4
# Plug them into the specification best_spec <- finalize_model(spec_untuned, final_params)best_spec
Decision Tree Model Specification
(classification)
Main Arguments:
tree_depth = 8
min_n = 2
Computational engine: rpart
Let's tune!
Machine Learning with Tree-Based Models in R

