Performance metrics for regression trees
Machine Learning with Tree-Based Models in R

Sandro Raabe
Data Scientist
How to measure performance?
- Classification problems: accuracy (confusion matrix)
- Regression problems: "correct" is relative, no binary correctness
$\Rightarrow$ Measure how far predictions are away from truth
Common metrics for regression
- Mean Absolute Error (MAE)
- Root Mean Square Error (RMSE)
MAE intuition:
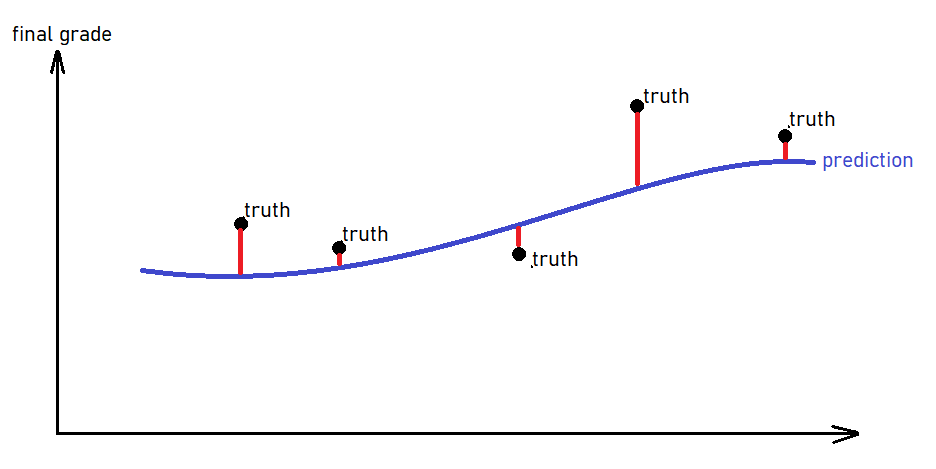
MAE = average length of the red bars
Formulas and intuition
$$MAE = \frac{1}{n} \sum_{i=1}^n\left| actual_i - predicted_i \right|$$
- "Sum of absolute deviations divided by the number of predictions"
$$\quad MSE = \quad \frac{1}{n} \sum_{i=1}^n\left( actual_i - predicted_i \right)^2$$
- "Mean squared error"
Formulas and intuition
$$MAE = \frac{1}{n} \sum_{i=1}^n\left| actual_i - predicted_i \right|$$
- "Sum of absolute deviations divided by the number of predictions"
$$RMSE = \sqrt{\frac{1}{n} \sum_{i=1}^n\left( actual - predicted \right)^2}$$
- "Root of the mean squared error"
- Large errors get higher weight
Coding: predictions
# parsnip and yardstick are included in tidymodels
library(tidymodels)
# Make predictions and add to test data predictions <- predict(model, new_data = chocolate_test) %>%bind_cols(chocolate_test)
# A tibble: 358 x 7
.pred final_grade review_date cocoa_percent company_location
<dbl> <dbl> <int> <dbl> <fct>
1 2.5 2.75 2013 0.7 France
2 3.64 3.25 2014 0.8 France
3 3.3 3.5 2012 0.7 France
4 3.25 3.5 2011 0.72 Fiji
# ... with 354 more rows, and 2 more variables: bean_type <fct>, broad_bean_origin <fct>
Coding: mae() and rmse()
# Evaluate using mae() mae(predictions,estimate = .pred,truth = final_grade)
# A tibble: 1 x 2
.metric .estimate
<chr> <dbl>
1 mae 0.363
# Evaluate using rmse()
rmse(predictions,
estimate = .pred,
truth = final_grade)
# A tibble: 1 x 2
.metric .estimate
<chr> <dbl>
1 rmse 0.457
Let's evaluate!
Machine Learning with Tree-Based Models in R

