Forecasting
Statistical Techniques in Tableau

Maarten Van den Broeck
Content Developer at DataCamp
Correlation vs. autocorrelation
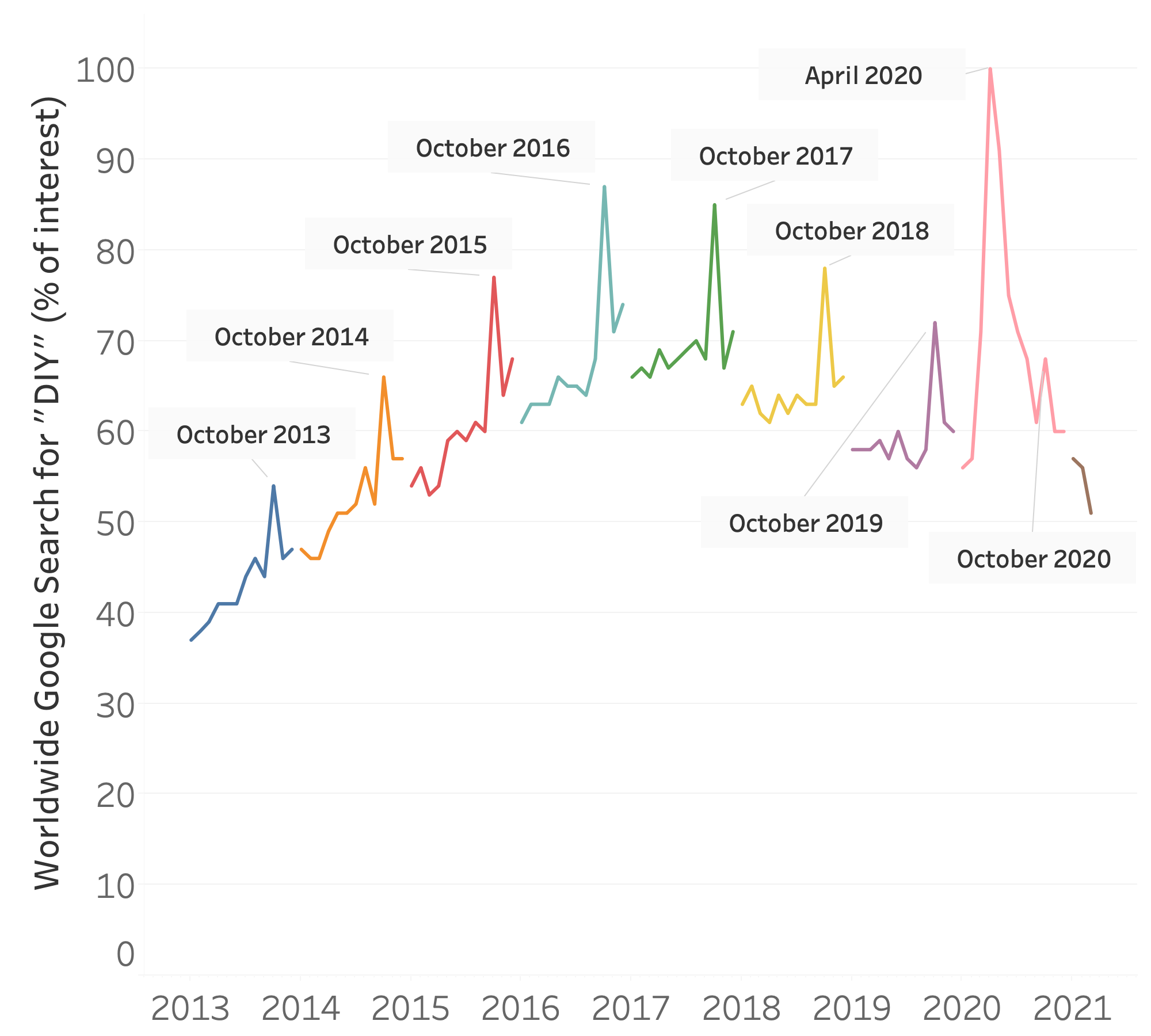
Correlation vs. autocorrelation
- Autocorrelation: repeating pattern correlates with itself
- Time series: a value measured repeatedly over time, in discrete time-intervals
- Time series analysis: general term for analysis on time series
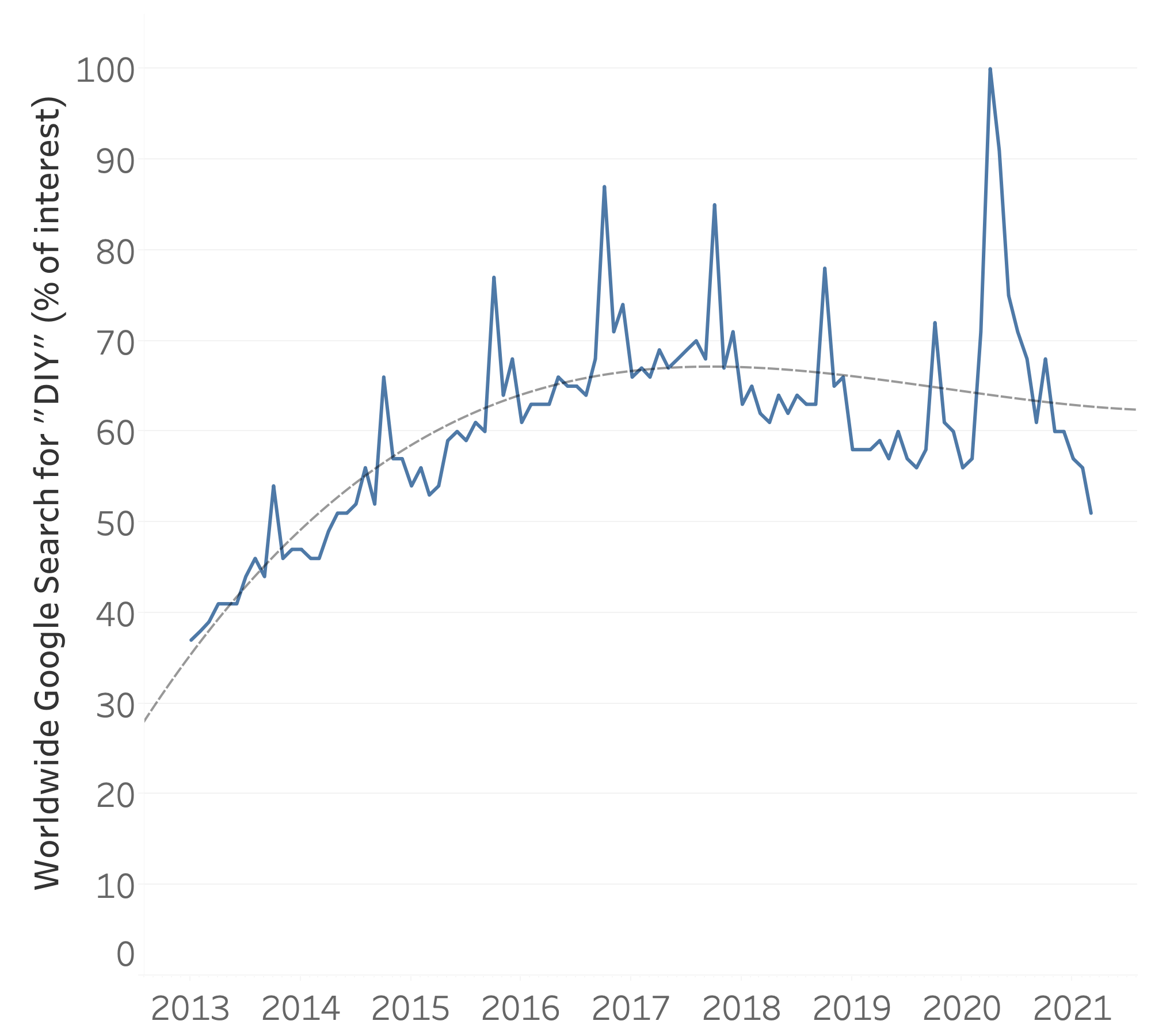
Forecasting
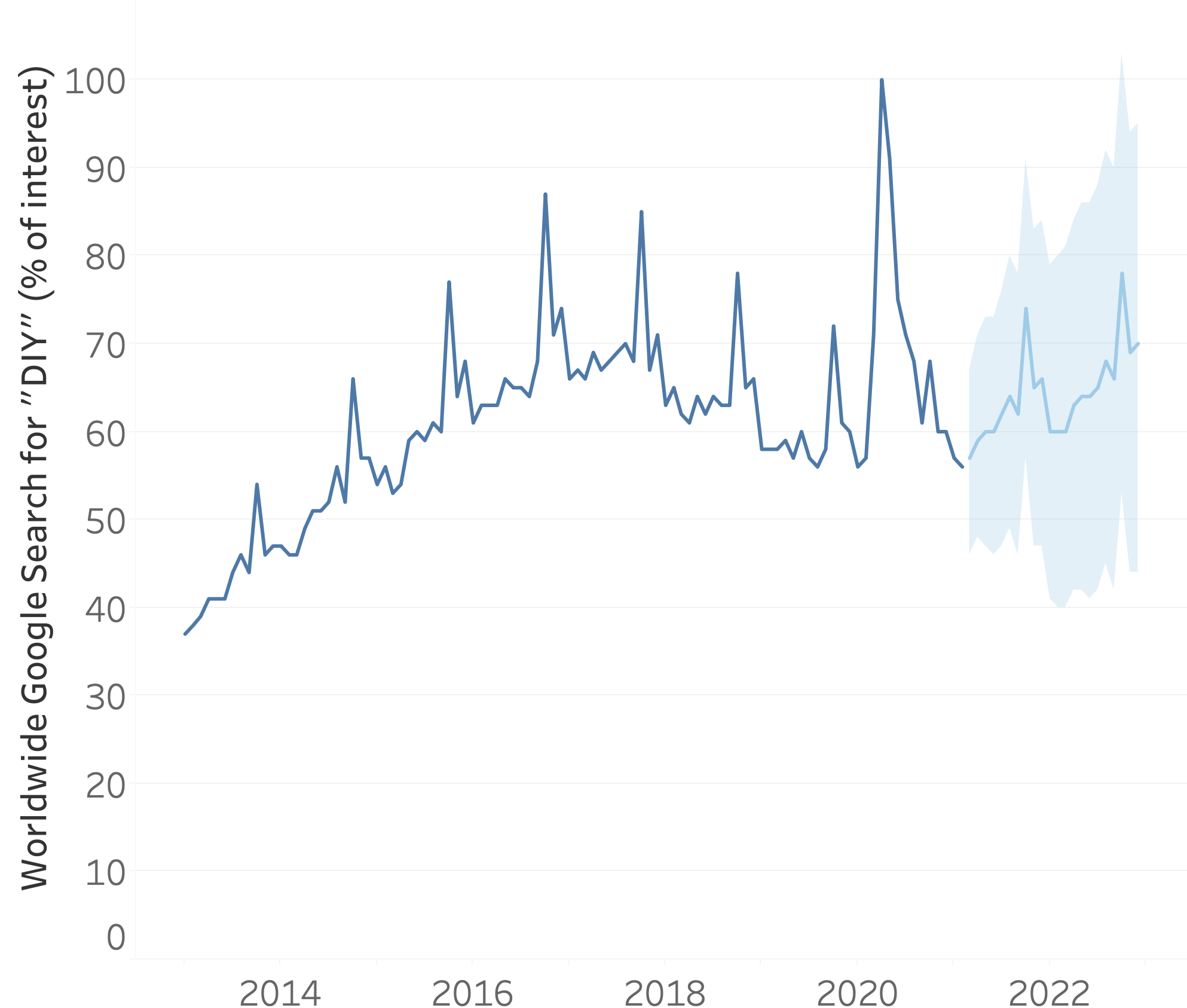
- Predictions about the future based on historical data
- Estimation: probability where future data points will fall, using confidence intervals
- Used in
- supply chain management
- earthquakes
- hormone levels
- market stocks
- sports performance
- weather
Naive forecast
$F_{t+1} = A_{t}$
| Month $_t$ | Actual $A$ | Forecast $F$ |
|---|---|---|
| January | 5 | |
| February | 7 | 5 |
| March | 6 | 7 |
| April | 5 | 6 |
| May | 3 | 5 |
| June | 8 | 3 |
| July | 2 | 8 |
| August | 2 |
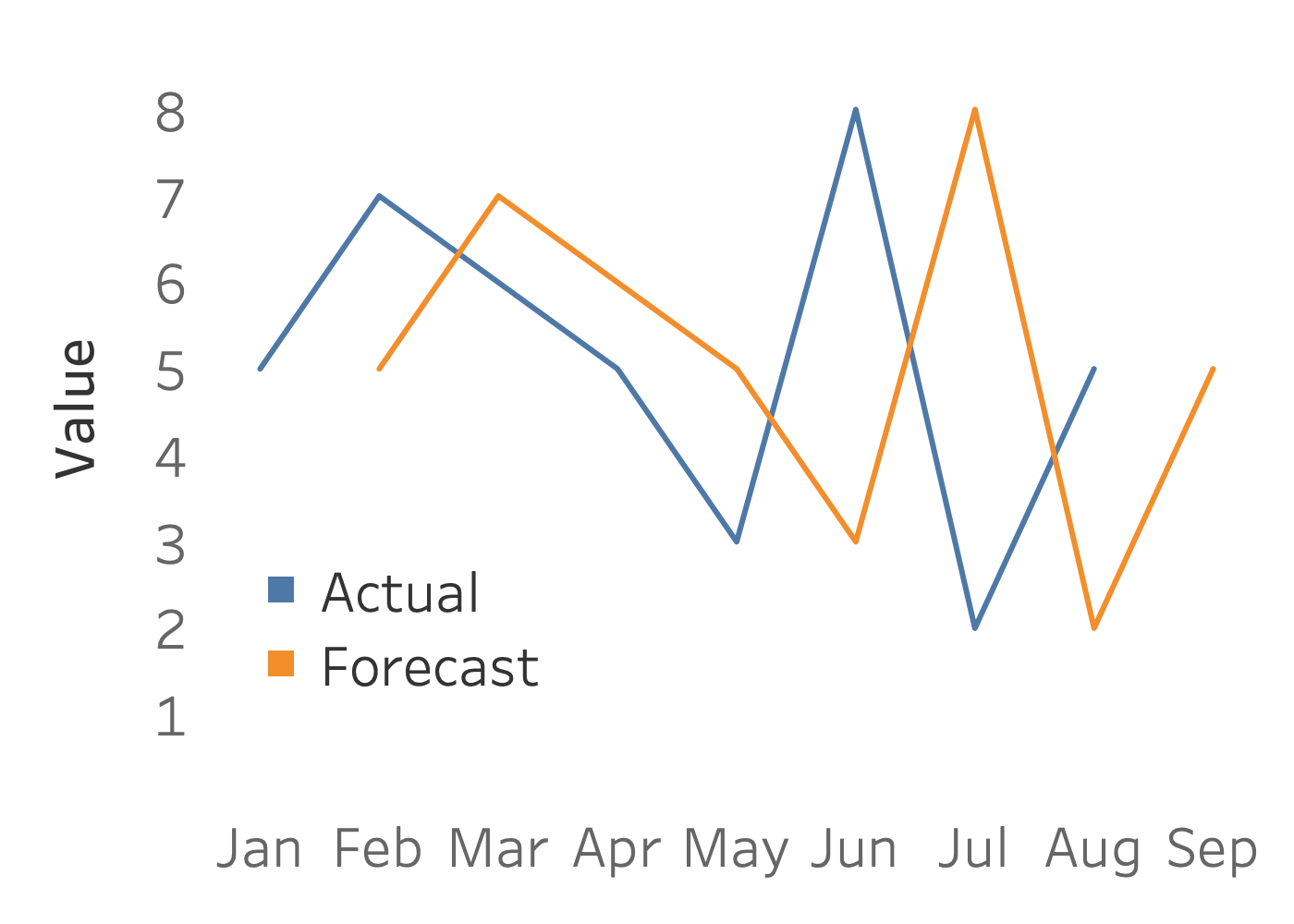
- Useful for benchmarking
Exponential smoothing
$F_{t+1} = F_t + \alpha(A_{t}-F_t)$
| Month $_t$ | Actual $A$ | Forecast $F$ |
|---|---|---|
| January | 5 | 5 |
| February | 7 | 5 |
| March | 6 | 4,6 |
| April | 5 | 4,32 |
| May | 3 | 4,184 |
| June | 8 | 4,4208 |
| July | 2 | 3,70496 |
| August | 5 | 4,045952 |
- Predictions will be influenced more by recent value changes than the past
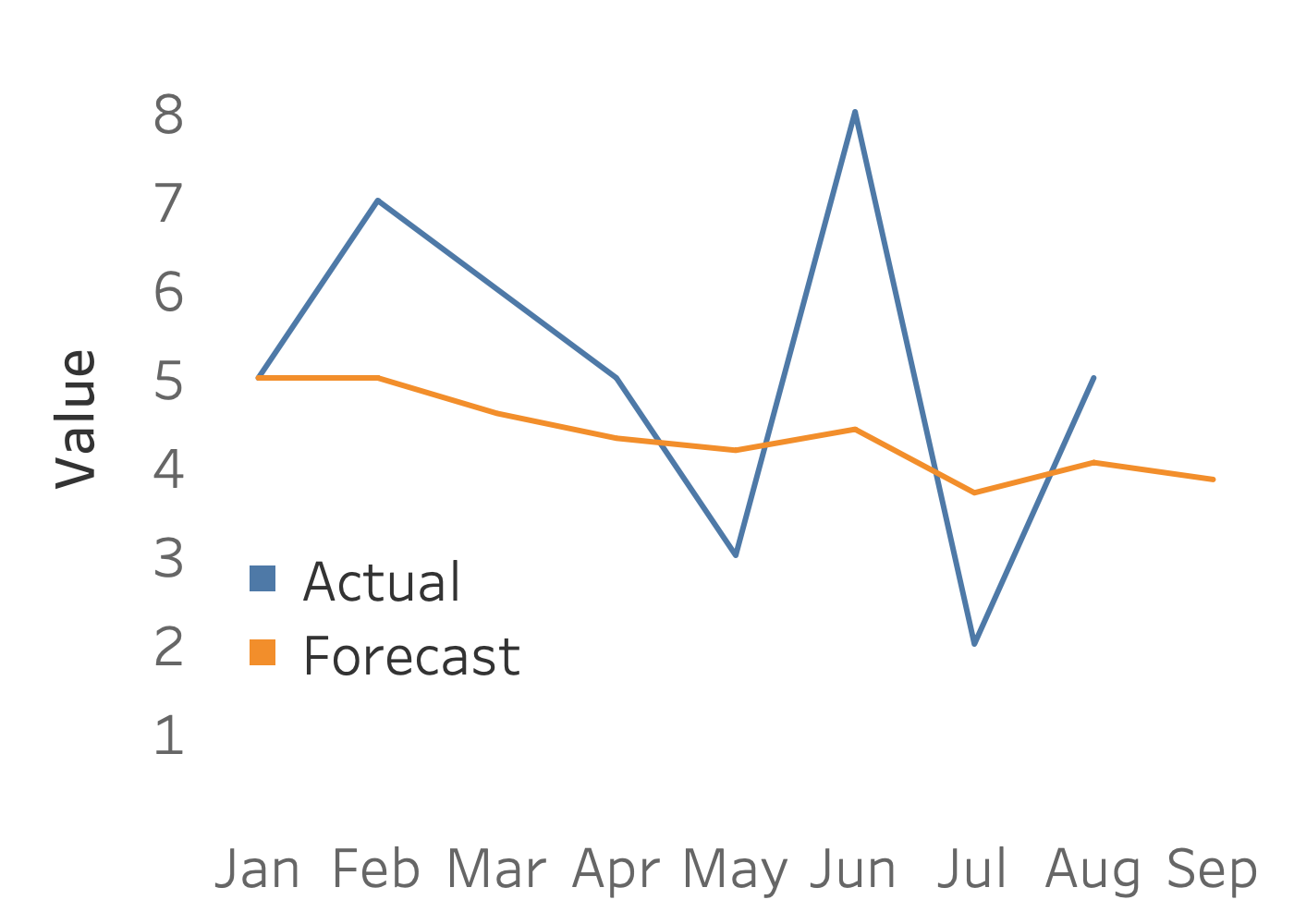
- Tableau will run many models and select the best one
Mean absolute error (MAE)
| Month | Actual | Forecast | Error | Absolute Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| January | 5 | |||
| February | 7 | 5 | 2 | 2 |
| March | 6 | 7 | -1 | 1 |
| April | 5 | 6 | -1 | 1 |
| May | 3 | 5 | -2 | 2 |
| June | 8 | 3 | 5 | 5 |
| July | 2 | 8 | -6 | 6 |
| August | 5 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| September | 5 | MAE | 2.86 |
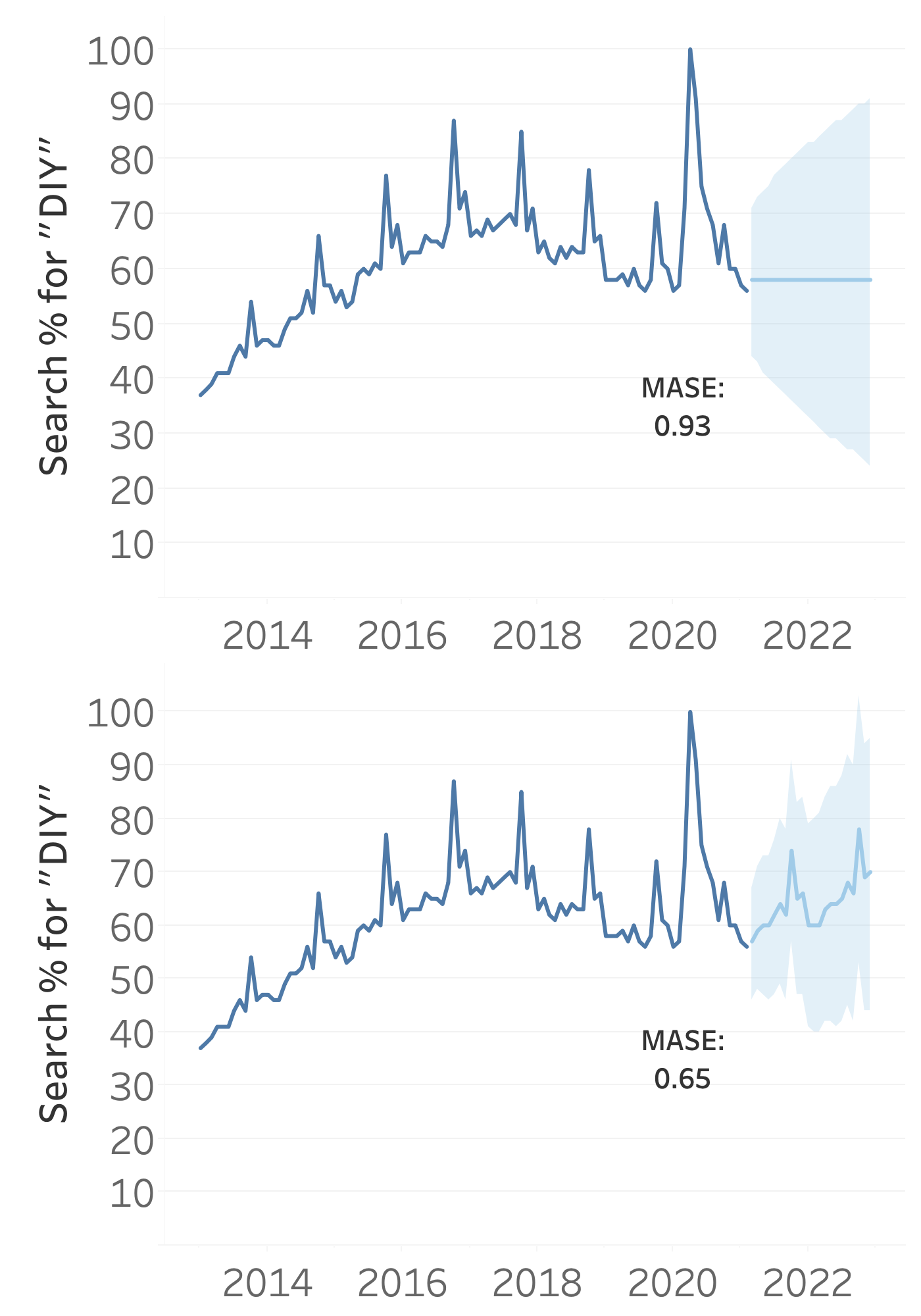
Mean absolute scaled error (MASE)
$MASE = \frac{MAE_{model}}{MAE_{naive}}$
- MASE compares MAE of your model with MAE of naive forecast
- Typically between
0(good) and1(bad), or higher (even worse) - You can customize options in Tableau, but out-of-the-box forecast is acceptable by default
Let's practice!
Statistical Techniques in Tableau

