Advantages and limitations of key-value databases
NoSQL Concepts

Miriam Antona
Software engineer
Advantages - very simple
- Key-value tuple
- No defined schema/types
- Basic operations:
- Put
- inserts a new key-value tuple
- updates a value if the key already exists
- Get
- returns the value by a given key
- Delete
- removes a key and its value
- Put
- Fast operations
Advantages - flexible
- Allow changes in data types
userID:123 = 123456userID:123 = "Miriam"
- Add additional attributes
user:457:preferences = {"language" : "en:US"}user:457:preferences = {"language" : "en:US", "color" : "green","timezone" :"GTM-4"}
Advantages - information stored in memory
- Fast reads/writes
- Can lose data
- Combination of disk and memory persistence
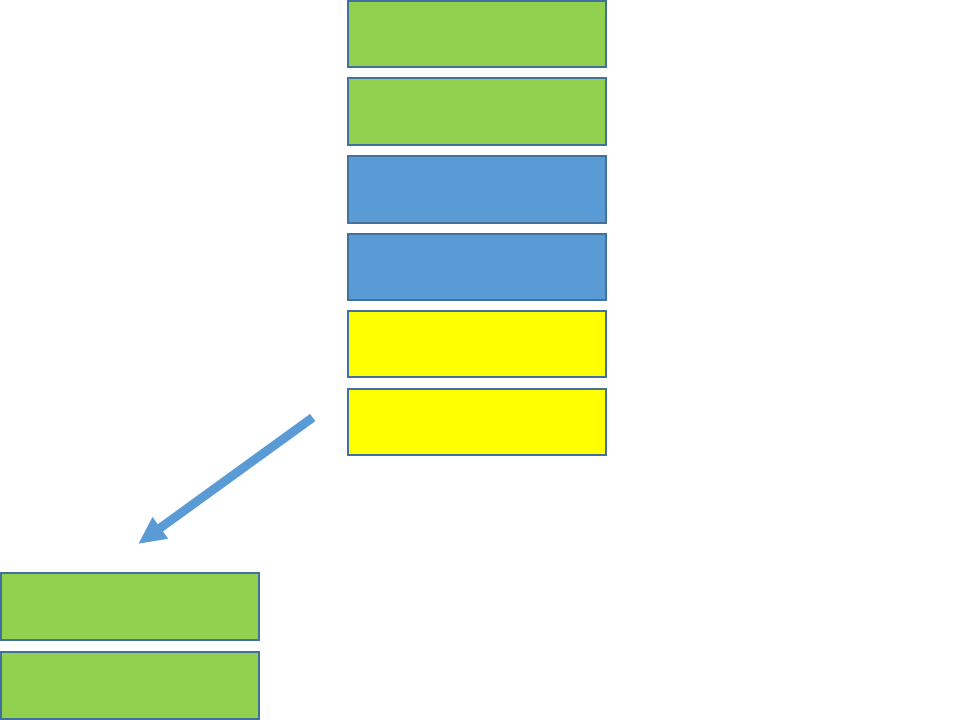
Advantages - scalability
- Can scale horizontally
- Sharding
- distributes different parts of the data across multiple servers

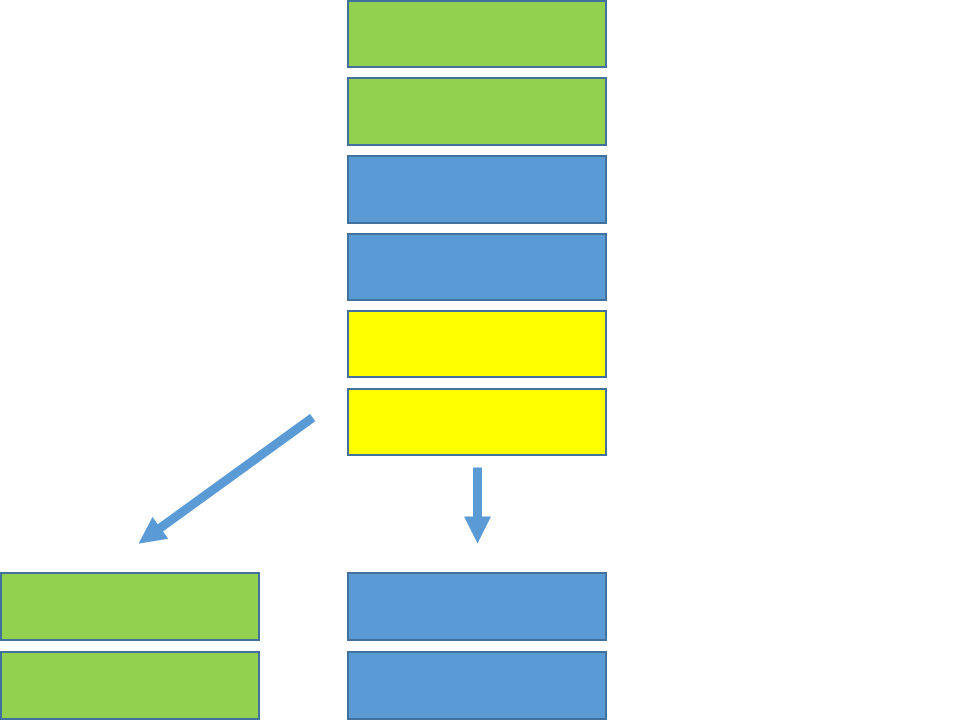
Advantages - scalability
- Can scale horizontally
- Sharding
- distributes different parts of the data across multiple servers
Advantages - scalability
- Can scale horizontally
- Sharding
- distributes different parts of the data across multiple servers
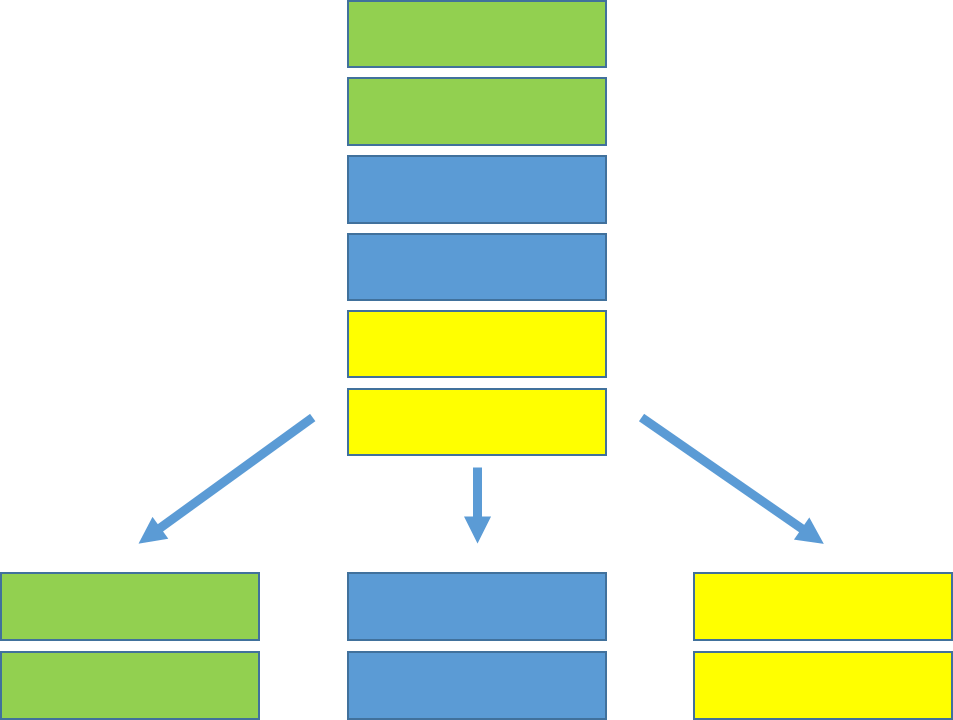
Advantages - scalability
- Can scale horizontally
- Sharding
- distributes different parts of the data across multiple servers
Limitations
- Just search by key
- Problem if we don't know the key
- Some key-value databases added functionalities
- search by value
- add secondary indexes
- search by several keys simultaneously
- Not complex queries
Let's practice!
NoSQL Concepts

