Attribution modeling
Marketing Analytics for Business

Sarah DeAtley
Principal Data Scientist
What is attribution modeling?
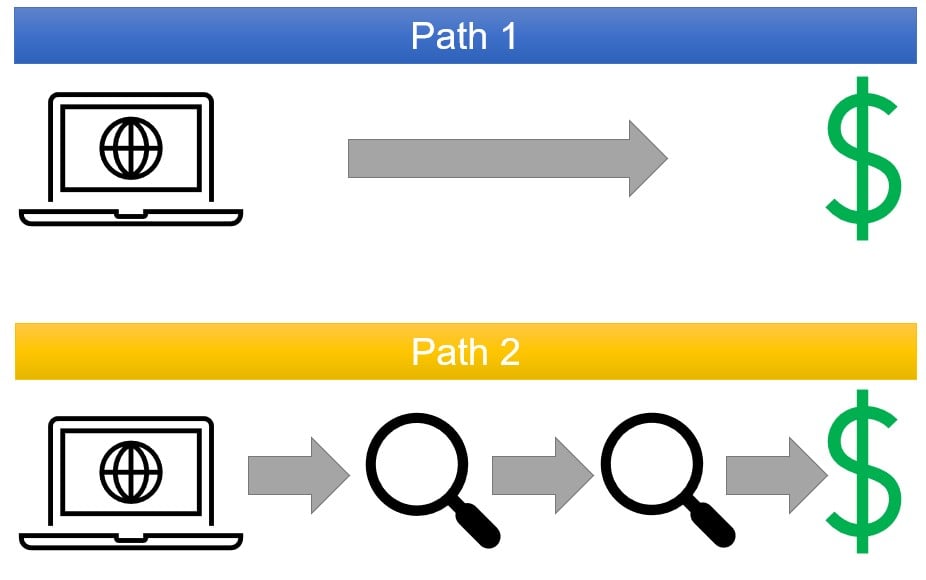
Attribution modeling: determine how much credit to give to marketing efforts upstream from decision
Analysts select attribution methodology for their marketing program
Attribution influences optimization, ROI modeling, and marketing investments
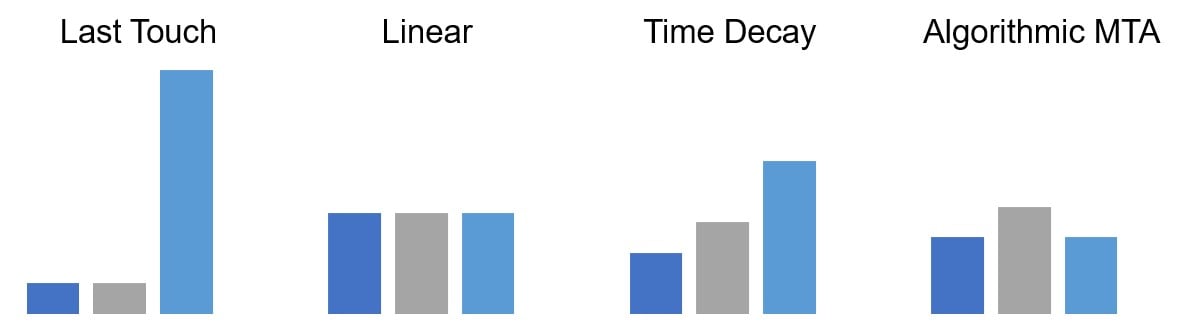
Last touch attribution
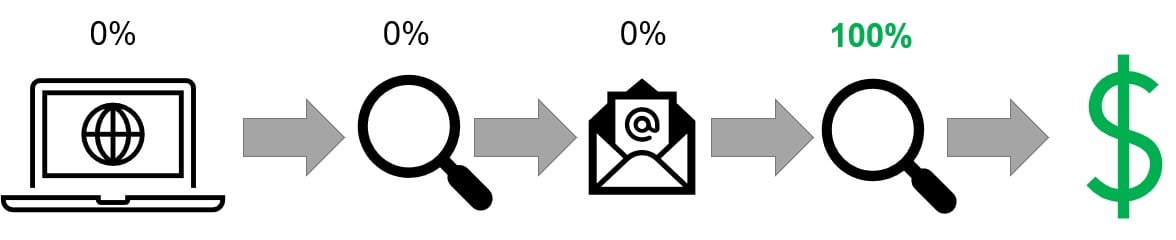
Last touch attribution (LTA): 100% of credit goes to the last channel / tactic / campaign
- It is very easy to understand this method and explain trends
- Channels with Direct impact naturally get the most credit
- Indirect channels get low credit because they are rarely last in the purchase process
Multi-touch attribution
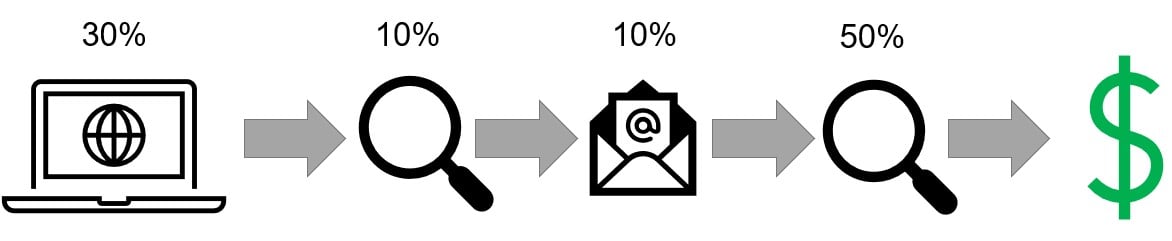
Multi-touch attribution (MTA): giving credit to multiple marketing efforts that led to a customer purchase
- Multi-touch attribution can account for Direct and Indirect impact
- MTA makes it challenging to identify which channel is driving marketing trends
Heuristic and algorithmic MTA
MTA can be heuristic (rules-based) or algorithmic (statistical model-based), while adding up to 100%
- Heuristic example: linear splits credit equally between all channels
- Algorithmic example: regression modeling ranks influence of channels based on strength of relationship to KPI
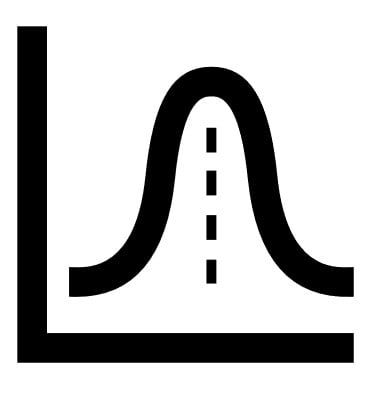
Time decay attribution
Time decay attribution: heuristic MTA where rules assign gradually more credit based on recency
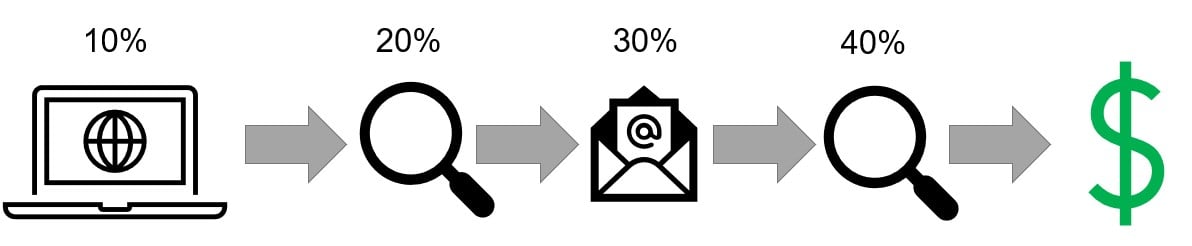
Choosing an attribution model
"All attribution models are wrong."
- No single correct model, but need to evaluate trade-offs of each
- Consider need for precision, ease of interpretation, customer behavior, channel mix, and data availability
- Privacy law impact: algorithmic can mitigate when data is not tied to customer directly
Let's practice!
Marketing Analytics for Business

