Revenue and cost modeling
Marketing Analytics for Business

Sarah DeAtley
Principal Data Scientist
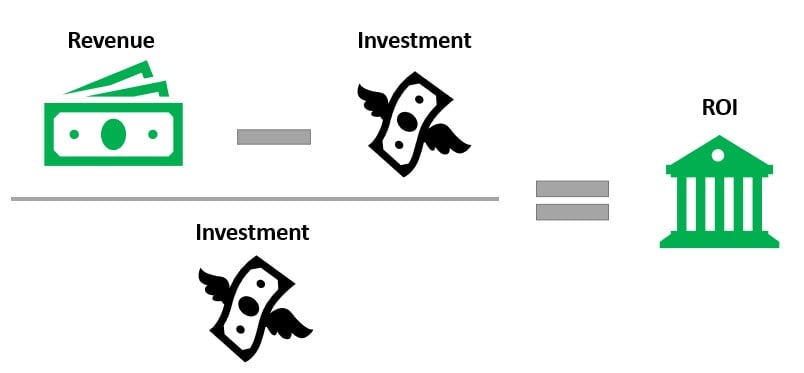
Marketing ROI
Return on Investment (ROI): net marketing revenue / marketing investment
- Ultimate goal of marketing operational excellence is positive ROI
Marketing spend

Spend model varies by channel and tactic, and can be cross-channel
Channel:
- Cost per click (paid search)
- Cost per mille (1000) (display, TV)
Tactic:
- Cost per view (video ads)
Cross-channel:
- Ad production costs
1 Pexels by Pixabay
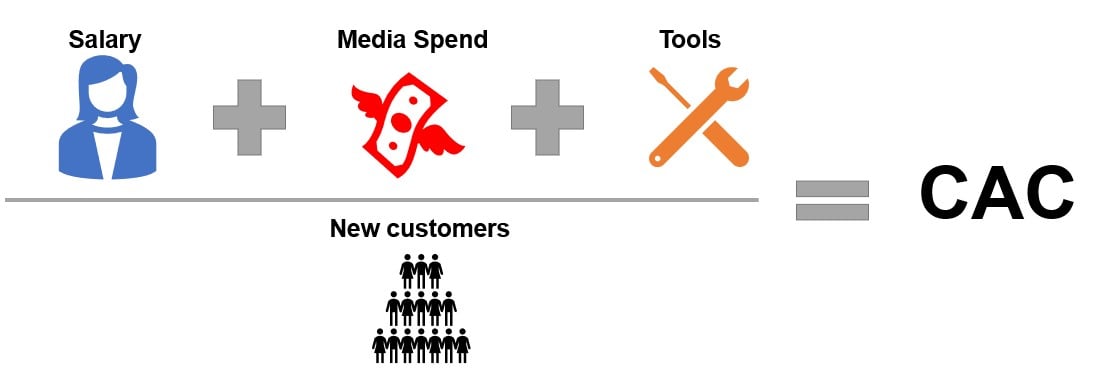
CAC
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): cost of convincing a potential customer to buy a product or service
- Accounts for all marketing spend and new customers per period
Used across multiple channels or individual channels
Finance partners can help identify marketing overhead costs
Total Marketing Costs / # of Acquired Customers
Marketing revenue
- Channel impact:
- Direct channels can associate to revenue more easily
- Indirect channels are rarely directly tied to revenue
- Product cost: expensive purchases (like a car) have delayed revenue impact
- Product type: business models can have different revenue impact depending on goods or services offered
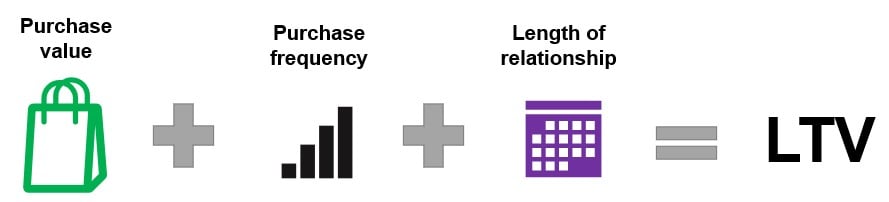
LTV
Lifetime Value: prediction of net profit attributed to future relationship with a customer
- LTV combines net revenue, customer lifespan, and churn behavior.
- Avg. purchases per customer
- Avg. value of a purchase
- Avg. length of a customer relationship
LTV to CAC ratio
- Want to spend more on customers that have a higher LTV
LTV to CAC ratio: LTV divided by CAC
- Monitoring LTV versus CAC keeps marketing accountable to positive ROI
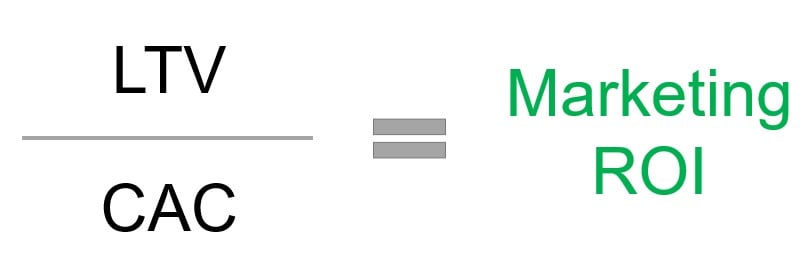
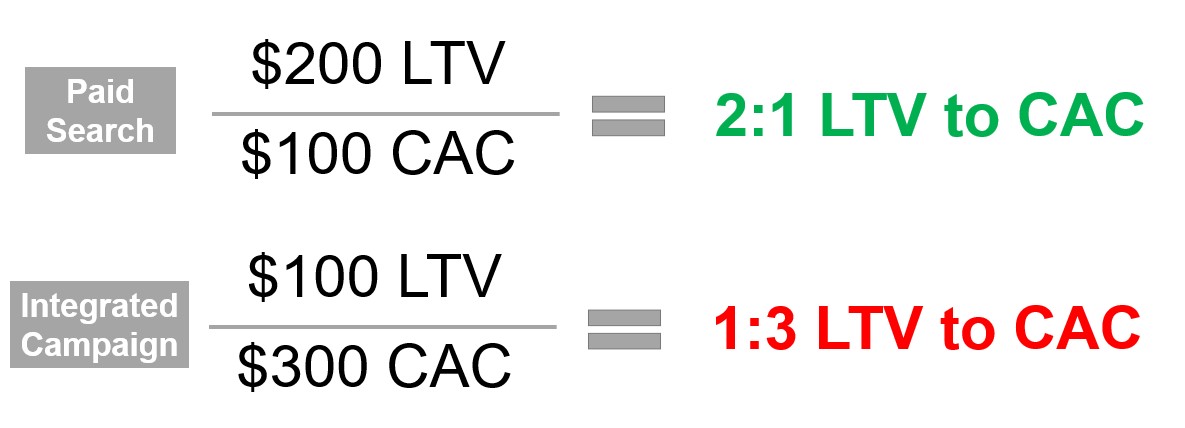
LTV to CAC example
- Minimum 1:1 LTV to CAC ratio to avoid negative ROI
- 3:1 LTV to CAC is a good starting point
Let's practice!
Marketing Analytics for Business

