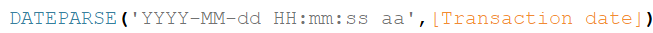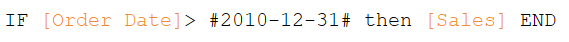Date and time functions
Calculations in Tableau

Maarten Van den Broeck
Content Developer at DataCamp
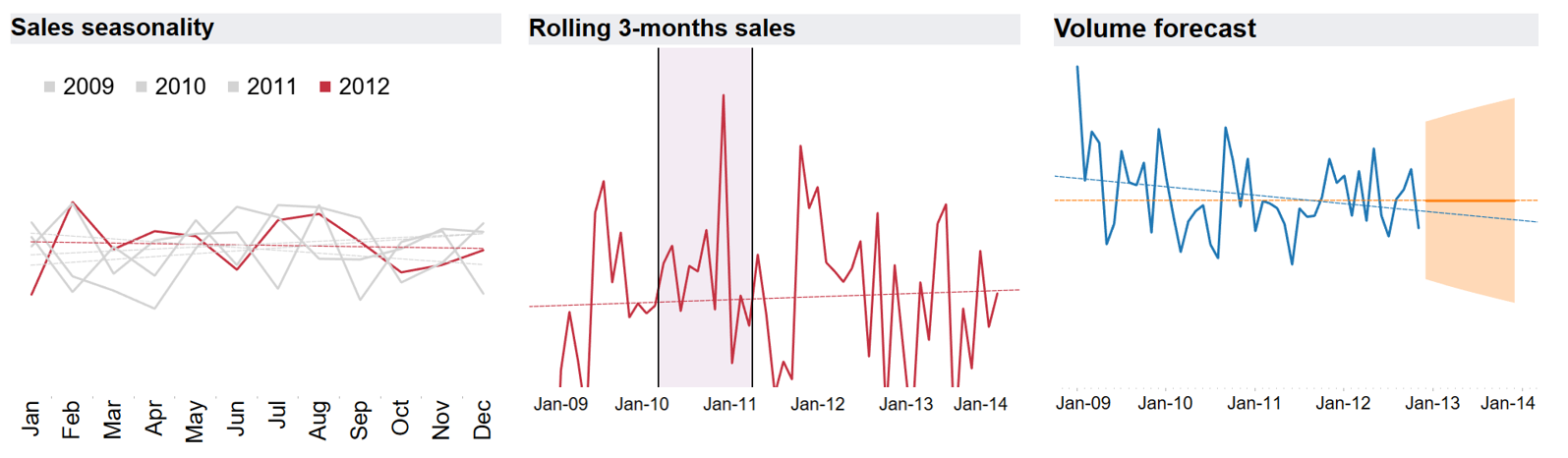
What is time series analysis?
Time series analysis - study of data in particular periods or intervals, which often includes trend analysis, seasonal comparisons of data and study of rolling time-periods
- Examples of time series analysis:
Date and time as data types
Date or DateTime data types:
- Data type storing calendar date/time
- May be auto-recognized by Tableau
- Dependent on data locale (1)
- Represented in Tableau with calendar symbol:
Date can have various output formats:
- 21-Jan-2020
- Monday, 31. December 19
- 31/10/12
- 10/31/12
- jan.22
- 2022-W05
- ...
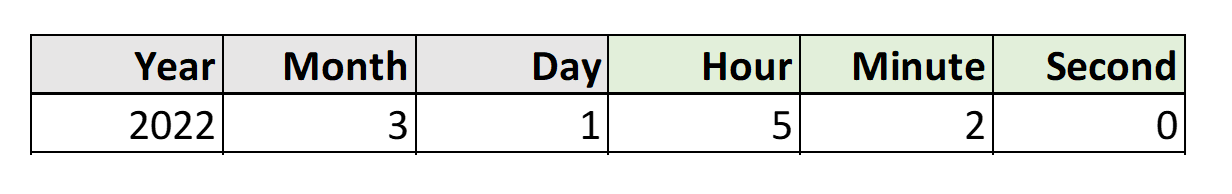
Deriving Date(Time) from other columns
Example:
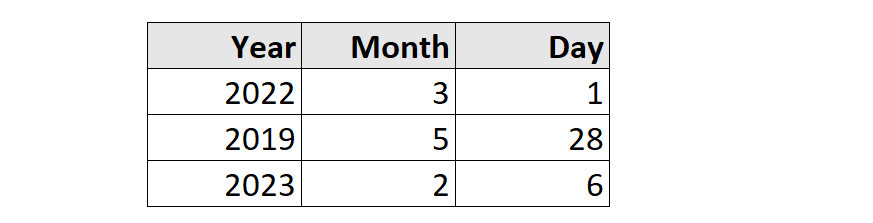
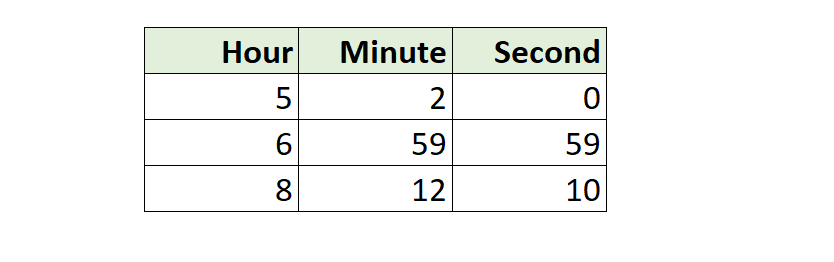

MakeDate ([Year], [Month], [Day])

MakeTime ([Hour], [Minute], [Second])


MakeDateTime ([Date], [Time])

Parsing dates
Parsing: analyzing a string into logical syntactic components
Example:
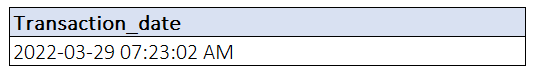
DateParse ( format, string )
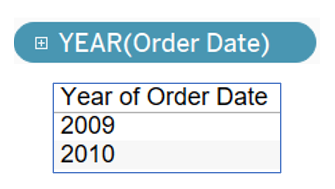
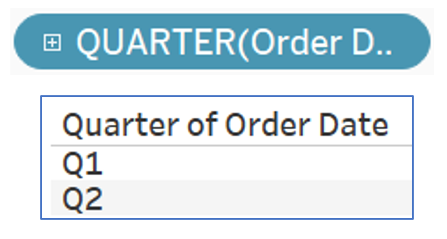
Extracting date parts
Extracting a discrete year, but also possible with quarter, month, day, dayofyear, weekday, hour, minute, etc.
Example:
DATEPART ( 'year', [Order Date] )
DATEPART ( 'quarter', [Order Date] )
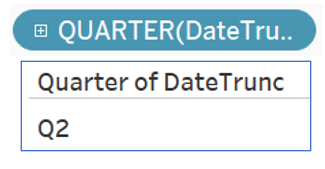
Truncating dates
Truncating: shortening, cutting
Truncating the specified date to the accuracy specified by the date part.
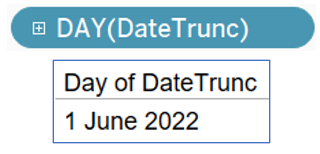
DATETRUNC ( 'month', #2022-06-15# )
DATETRUNC ( 'quarter', #2022-06-15# )
Calculating with dates
Adding intervals to dates:
DATEADD (date_part, interval, [Date])
Adds specified amount of intervals (e.g., 3 months, 2 days, 10 weeks, etc.) to the date
Subtracting intervals from dates:
DATEDIFF ( date_part, date1, date2 )
- Returns the difference between two dates, expressed in requested date part intervals
E.g.
DATEADD ('month', 3, [Date])DATEADD ('week', 10, [Date])Returns a date
E.g.
DATEDIFF ('month', [Start], [End])DATEDIFF ('day', [Start], [End])- Returns a number
Referring to a date in a calculation
Using hard-coded dates in calculations:
Enclose the date value between # #
E.g. #2010-12-31#
Let's practice!
Calculations in Tableau