Introduction to LOD Expressions and FIXED
Calculations in Tableau

Maarten Van den Broeck
Content Developer at DataCamp
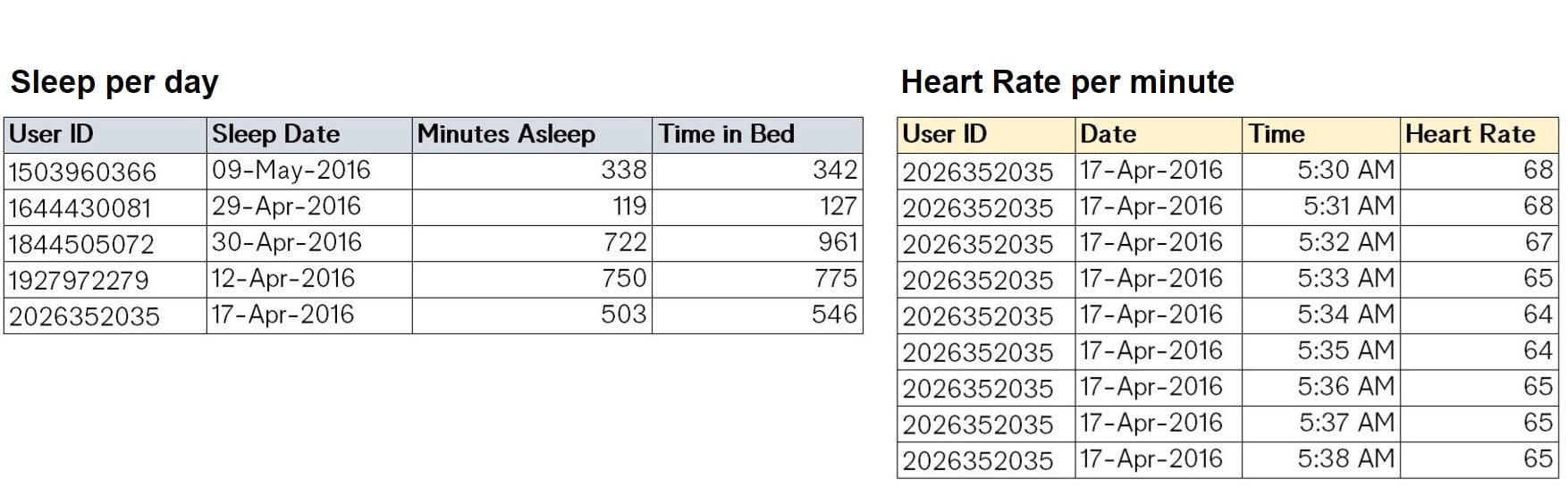
Granularity of the data
Data granularity is the level of detail in a model or decision making process. It tells you how detailed your data is (1)
e.g. Time-series analysis: per second | minute | hour | day | week | month | (...)
Granularity of the view
- Granularity and aggregation
- Aggregate = decrease the data granularity. e.g. Total
SUM(Sales)
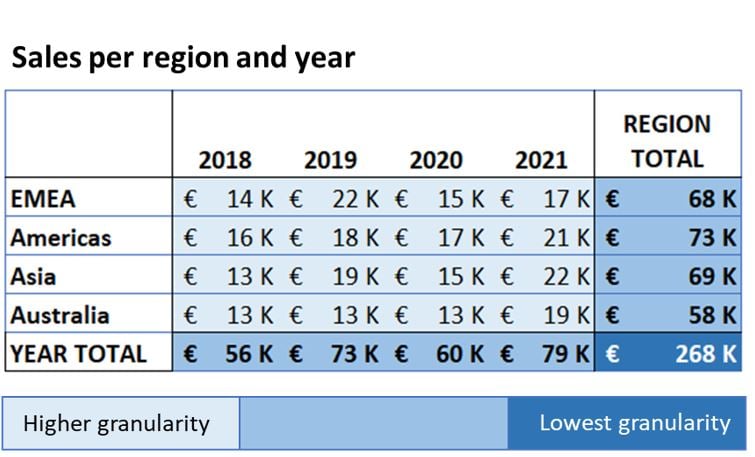
- Add dimensions = increase the data granularity, e.g.
SUM(Sales)per region and per year
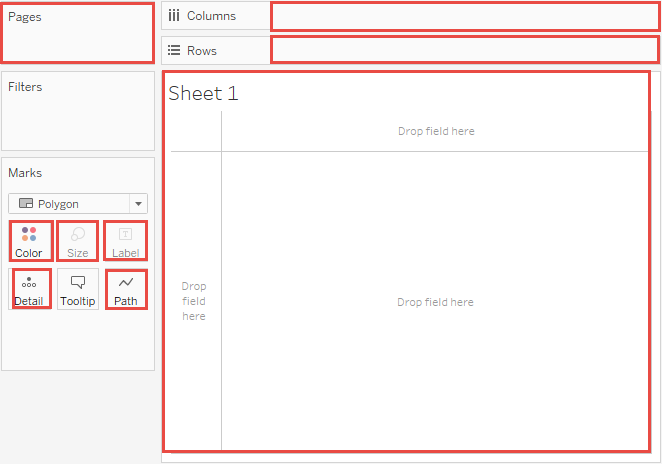
Managing granularity in Tableau worksheet
- Adding dimensions to the Shelves
Adding dimensions on the Marks:
- Detail
- Color
- Shape
- Size
- Path
- Label
More dimensions = more data points
- It becomes more difficult to visualize
LOD Expressions in Tableau
LOD Expressions provide a way to easily compute aggregations that are NOT at the level of detail of the visualization
Family of 3 functions:
INCLUDE: calculating at a lower level of detailEXCLUDE: calculating at a higher level of detailFIXED: calculating at an exactly specified level of detail
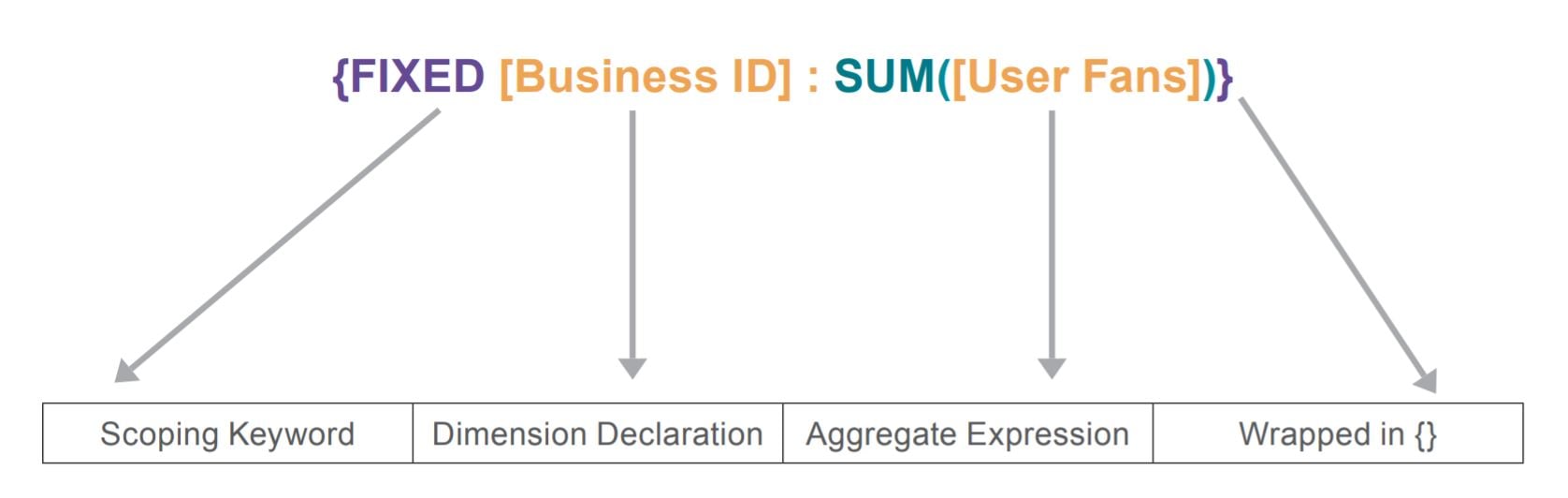
FIXED LOD Expressions
FIXED level of detail expressions compute a value using the specified dimensions, without reference to the dimensions in the view.
- Works with 0, 1, 2 or more dimensions, in any order
- Result of the LOD calculation can be either a dimension or a measure
- Dimensions of interest are contained in the calculation and do not clutter the view
Practical applications of FIXED LOD expressions
Calculating measures between various time dimensions:
e.g Swapping between daily and weekly calculations
{ FIXED [Day] : SUM(Sales)}
Calculating (sub) totals per categories:
e.g. % of Total { FIXED [Product] : SUM(Costs) } / { FIXED : SUM(Costs) }
Computing first or last data point per data subject:
e.g. First order date per customer
{ FIXED [Customer] : MIN([Order Date]) }
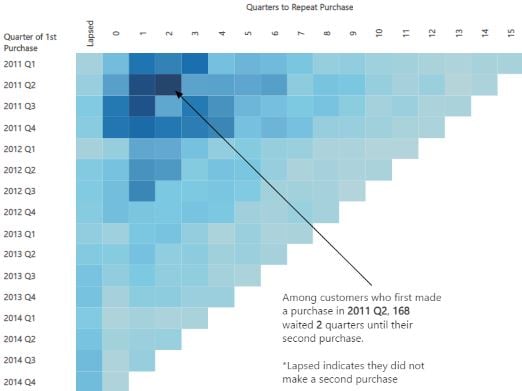
Cohort and survival analysis
Cohort analysis:
- Analyzing repetitive behavior of a group
- e.g. Usage of a product by various client groups (cohorts)
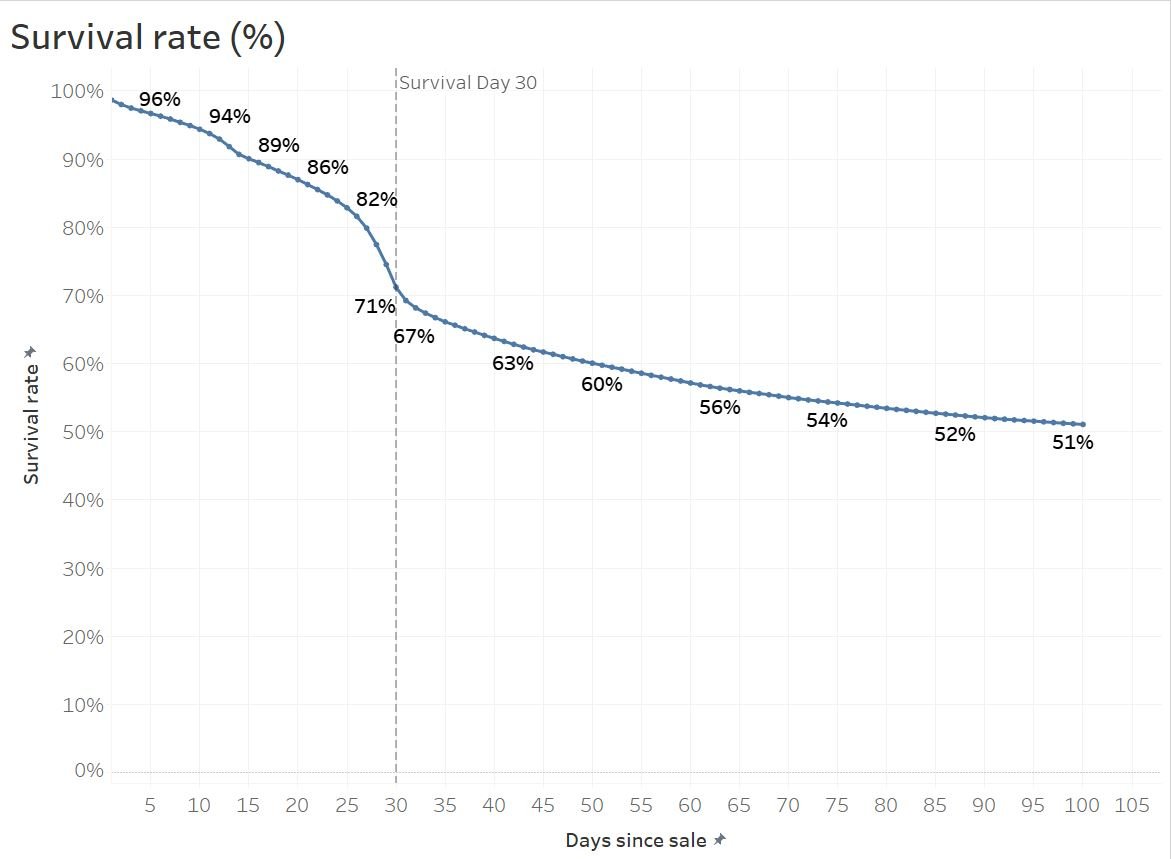
Survival analysis:
- Analyzing how many subject remain in dataset on a given day
- e.g. Who still keeps the New Year resolutions in February?
Cohort and Survival analysis - FIXED
Cohort analysis:
- Analyzing repetitive behavior of a group.
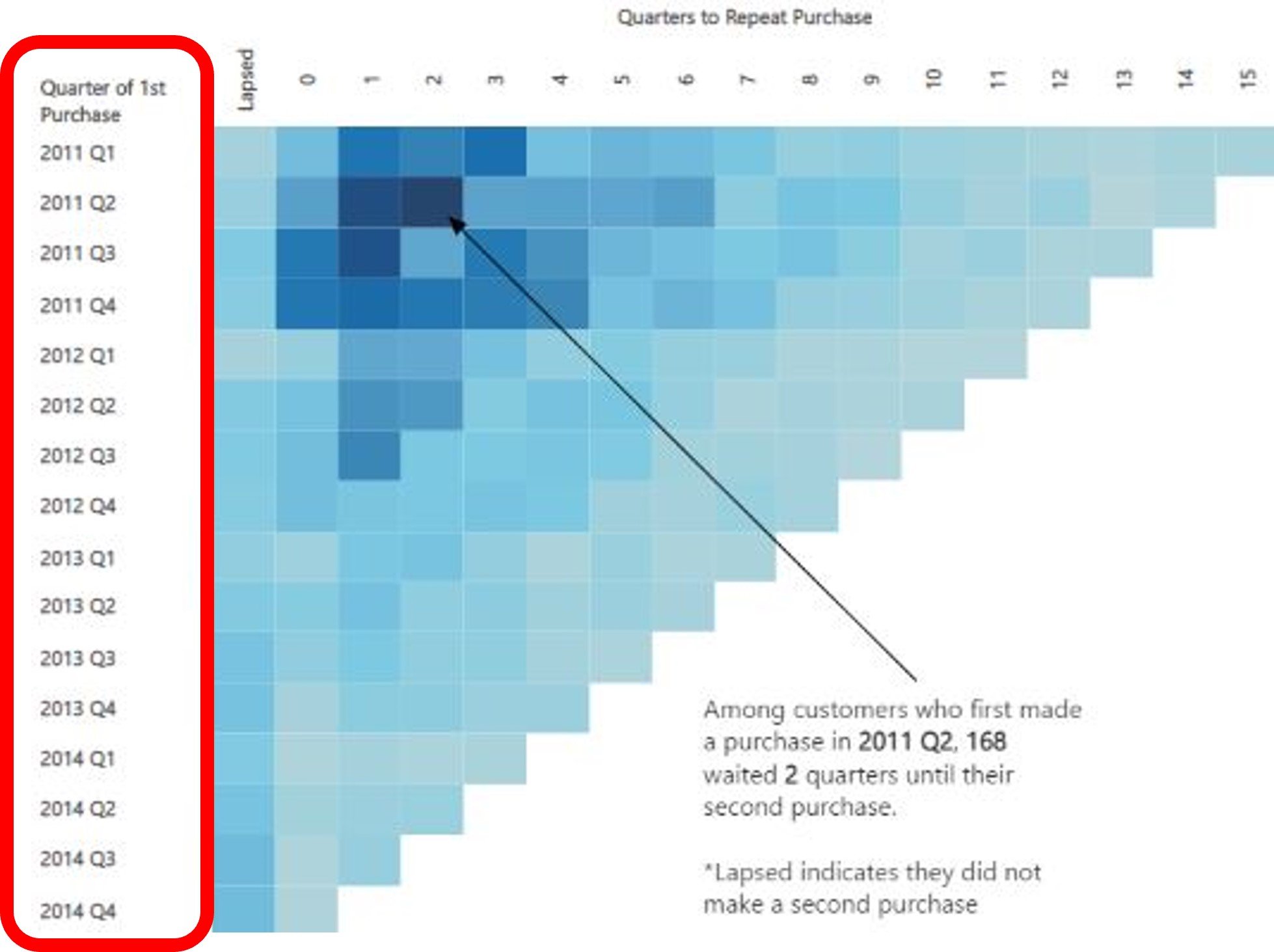
- e.g. Usage of a product by various client groups
Survival analysis:
- Analyzing how many subject remain in dataset on a given day.
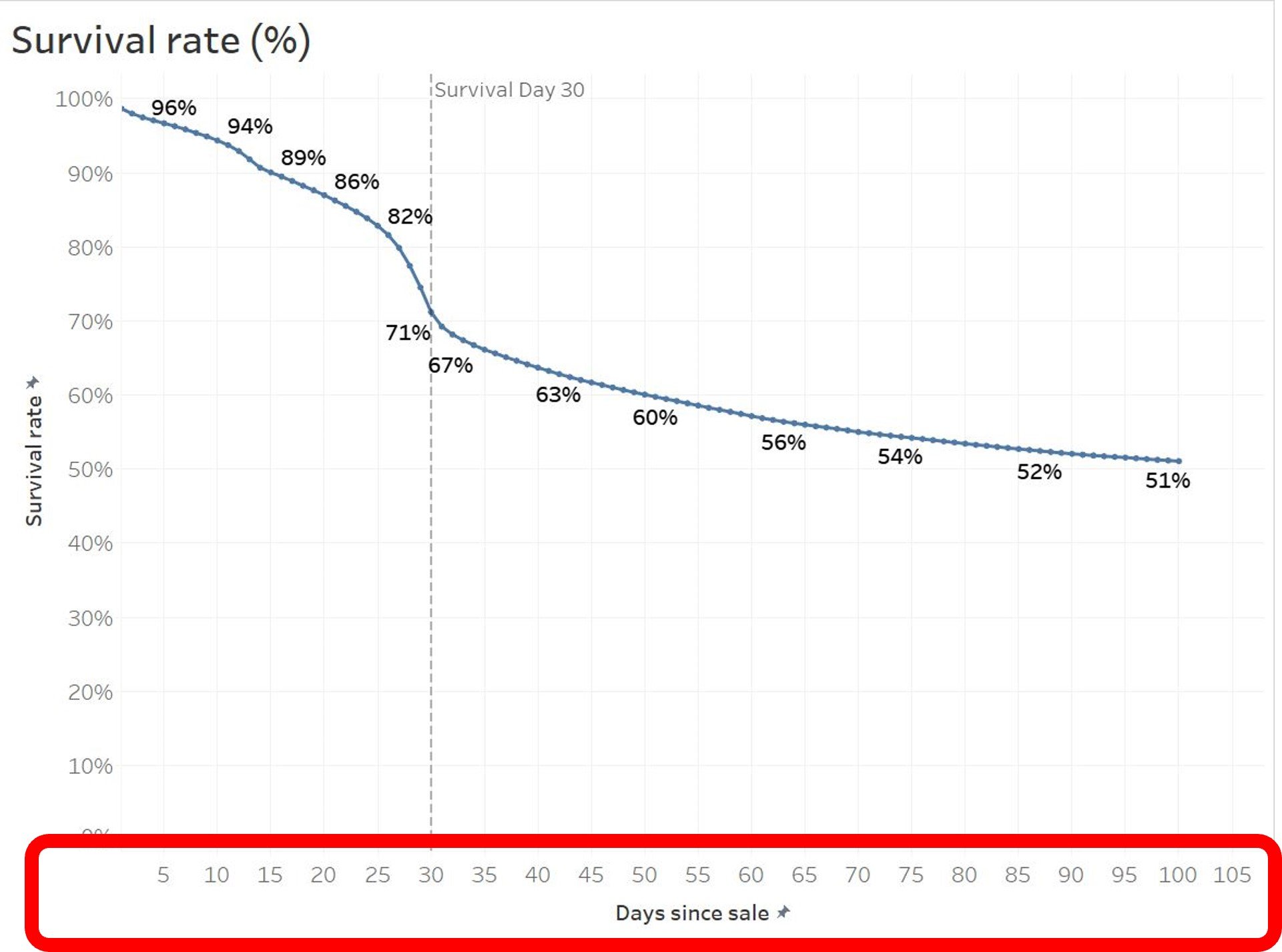
- e.g. Who still keeps the New Year resolutions in February?
Let's practice!
Calculations in Tableau