The central limit theorem
Introduction to Statistics

George Boorman
Curriculum Manager, DataCamp
Rolling a die five times

| Roll | Result |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 3 |
| 3 | 4 |
| 4 | 1 |
| 5 | 1 |
$Mean(Results) = 2 $
Rolling a die five times
| Roll | Result |
|---|---|
| 1 | 4 |
| 2 | 4 |
| 3 | 5 |
| 4 | 3 |
| 5 | 6 |
$Mean(Results) = 4.4 $
| Roll | Result |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 3 |
| 3 | 1 |
| 4 | 5 |
| 5 | 6 |
$Mean(Results) = 3.2 $
10 sets of five die rolls
- Roll a die five times
- Record the mean
- Repeat 10 times
| Set | Mean |
|---|---|
| 1 | 3.8 |
| 2 | 4.0 |
| 3 | 3.8 |
| 4 | 3.6 |
| 5 | 3.2 |
| 6 | 4.8 |
| 7 | 2.6 |
| 8 | 3.0 |
| 9 | 2.6 |
| 10 | 2.0 |
Sampling distributions
Sampling distribution of the sample mean
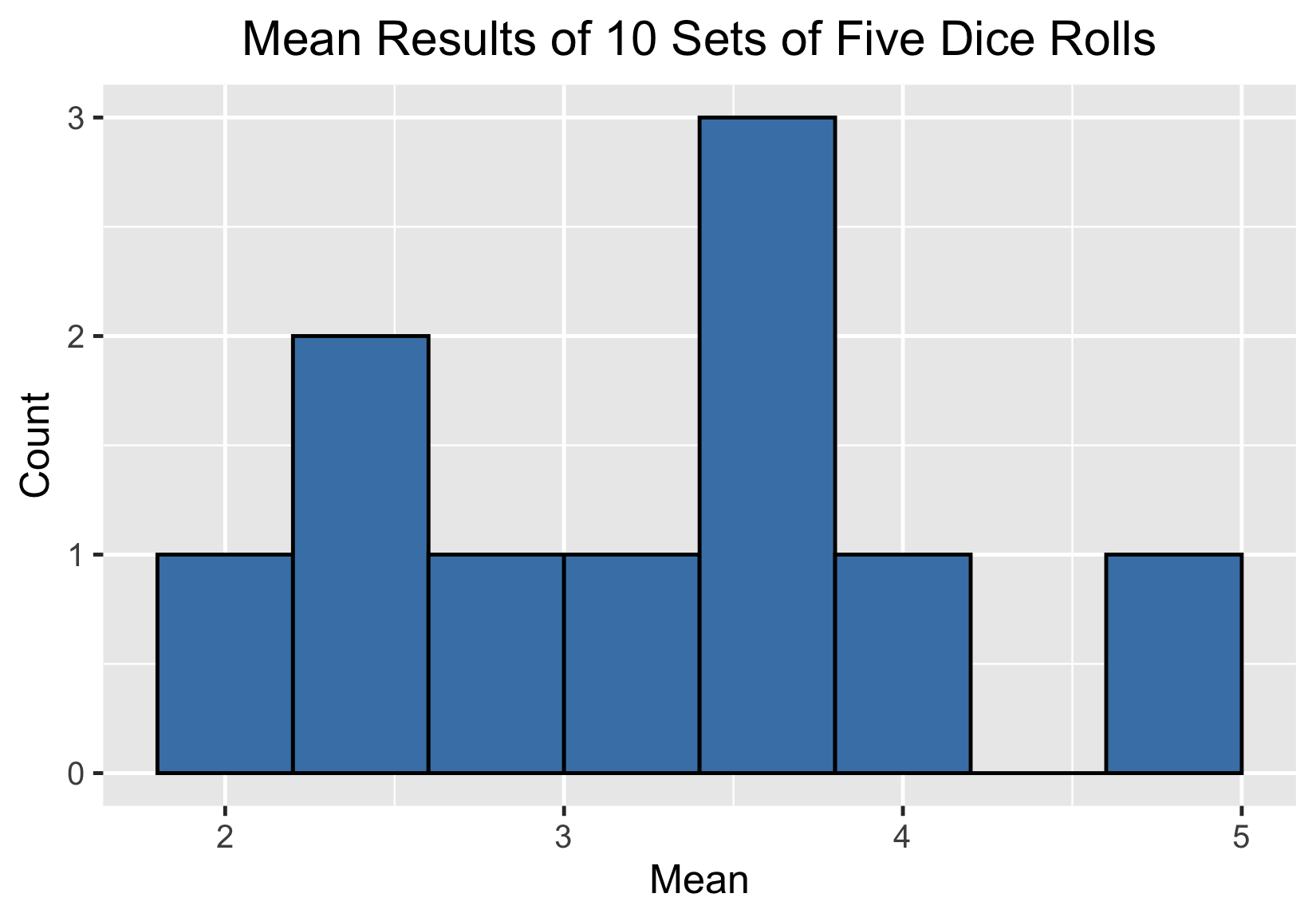
100 sample means
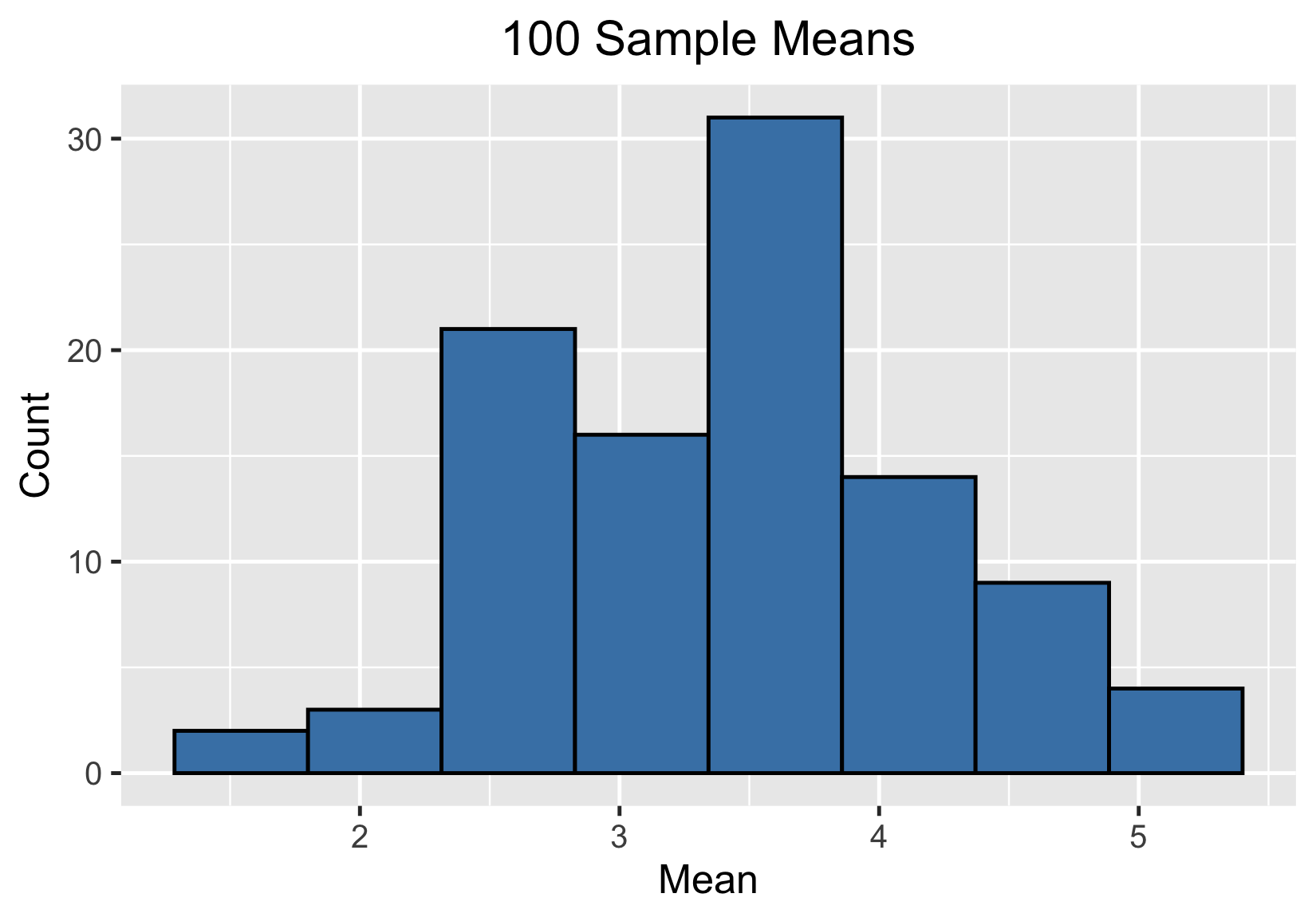
1000 sample means
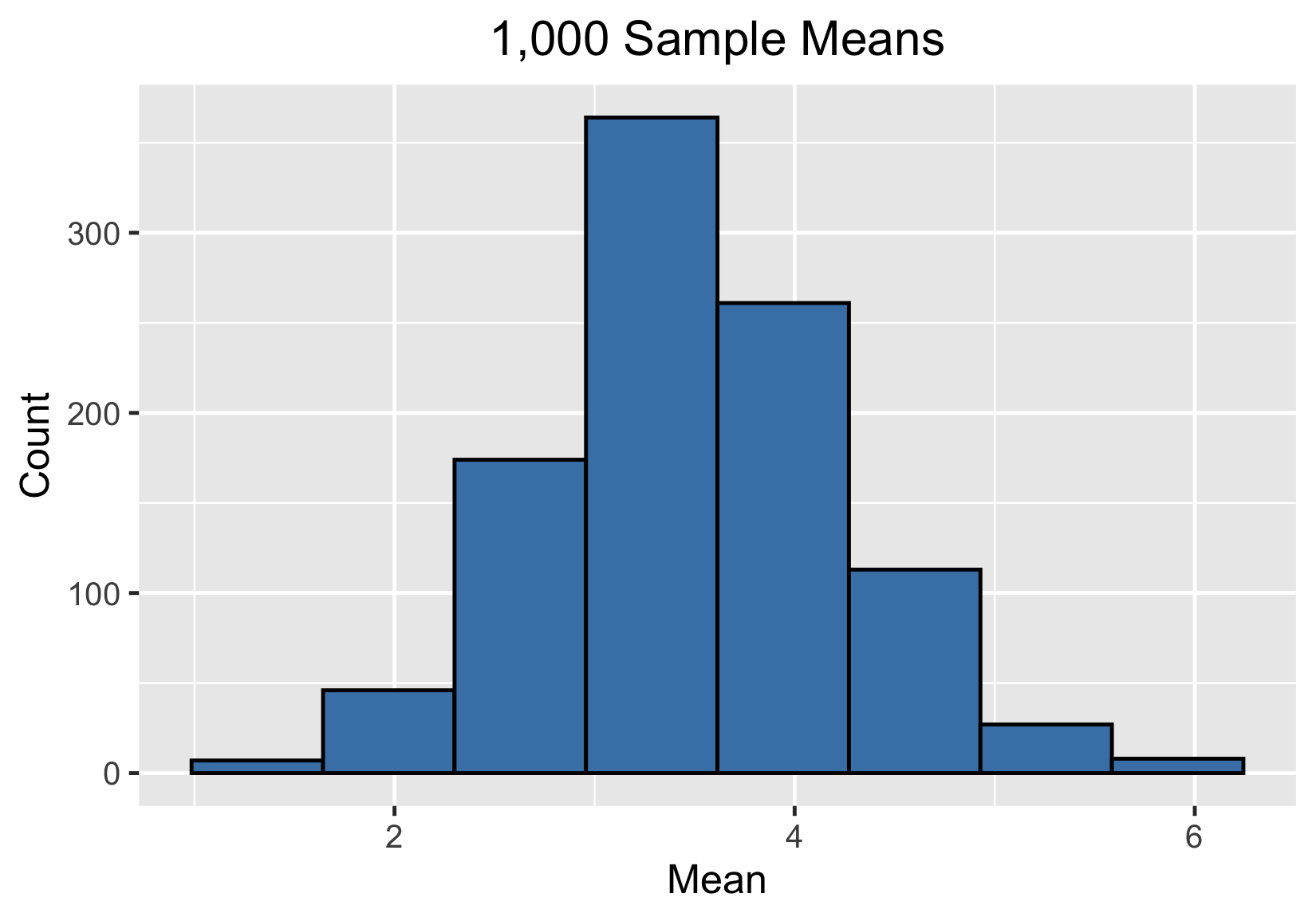
10000 sample means
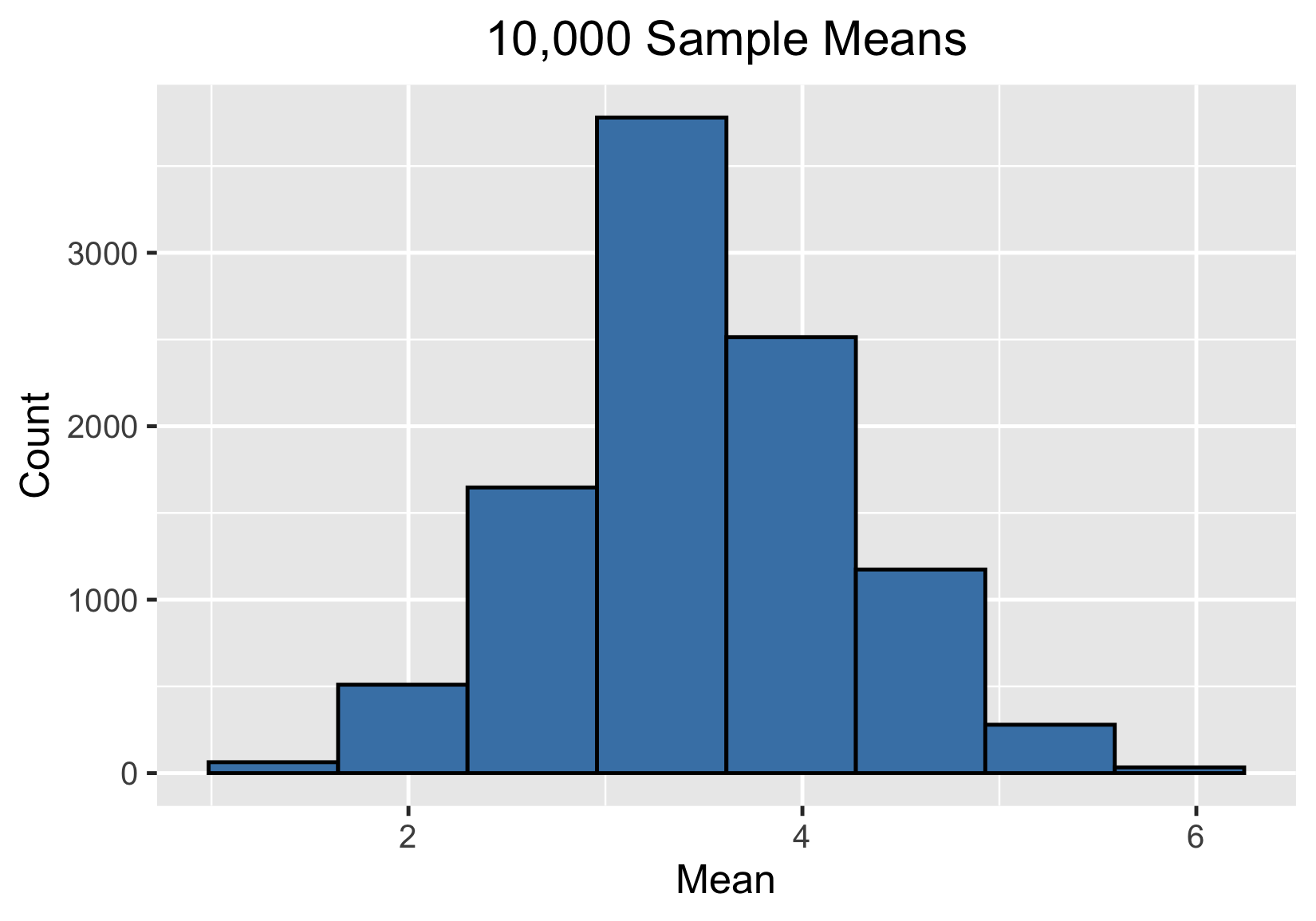
100000 sample means
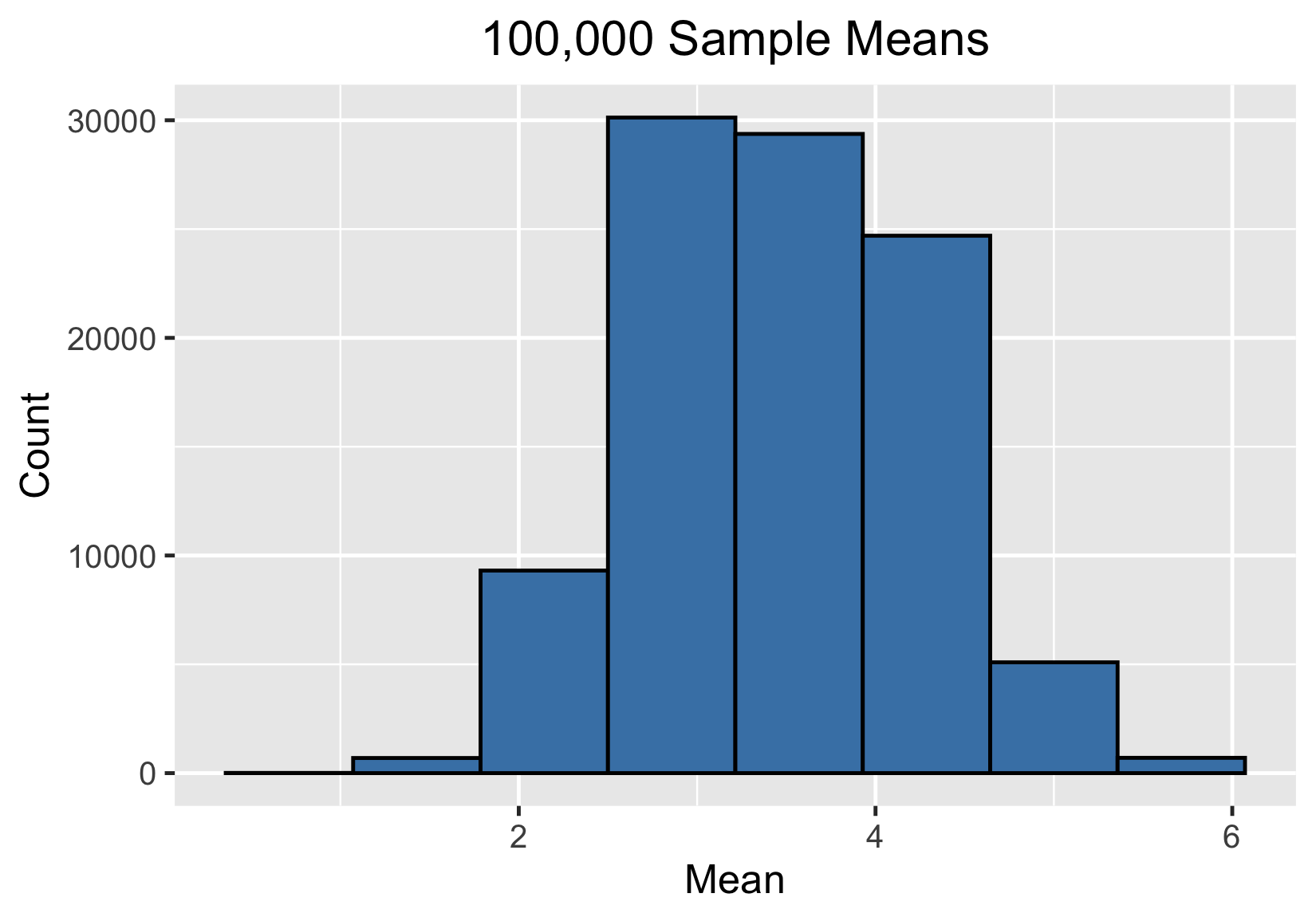
One million sample means
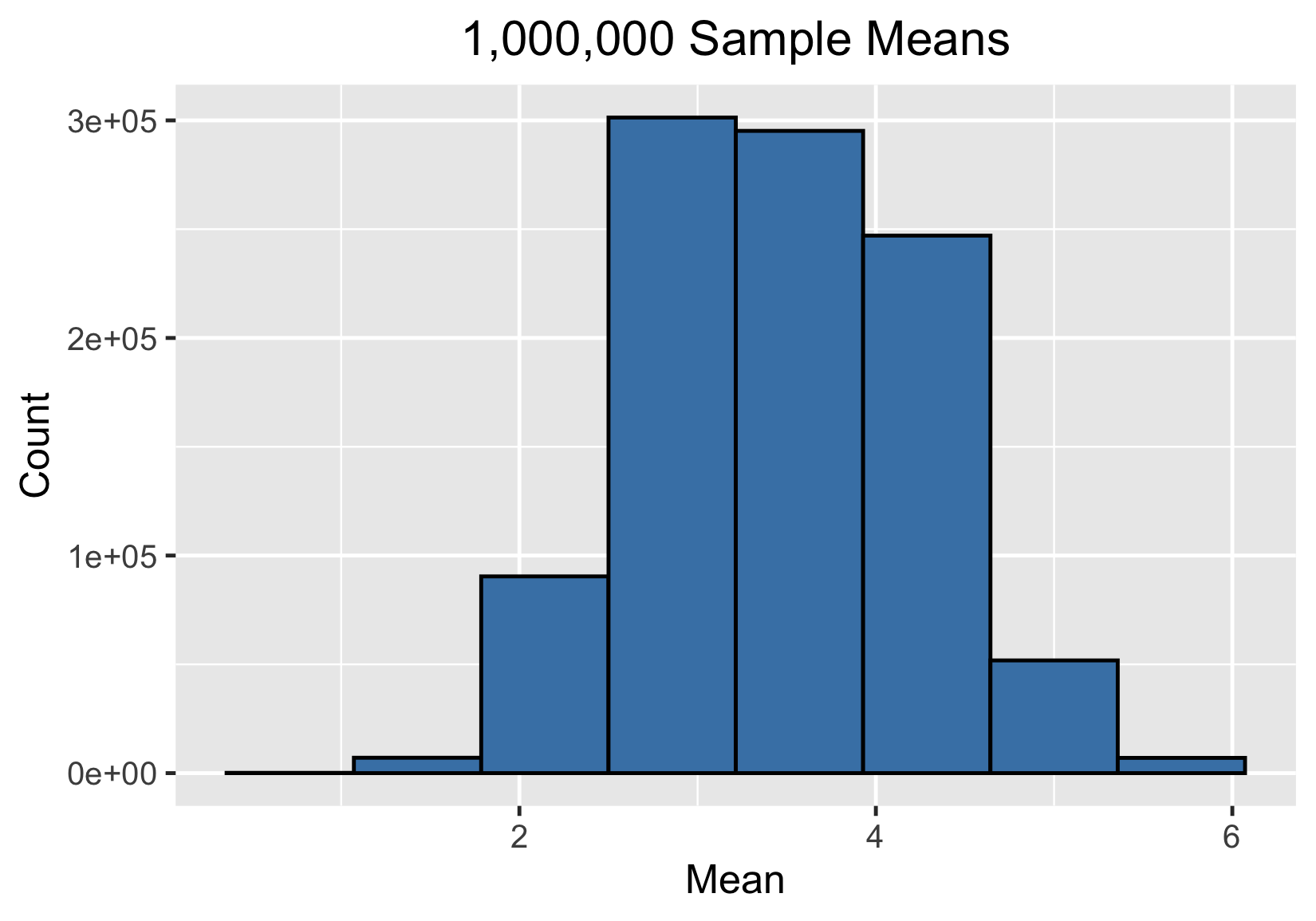
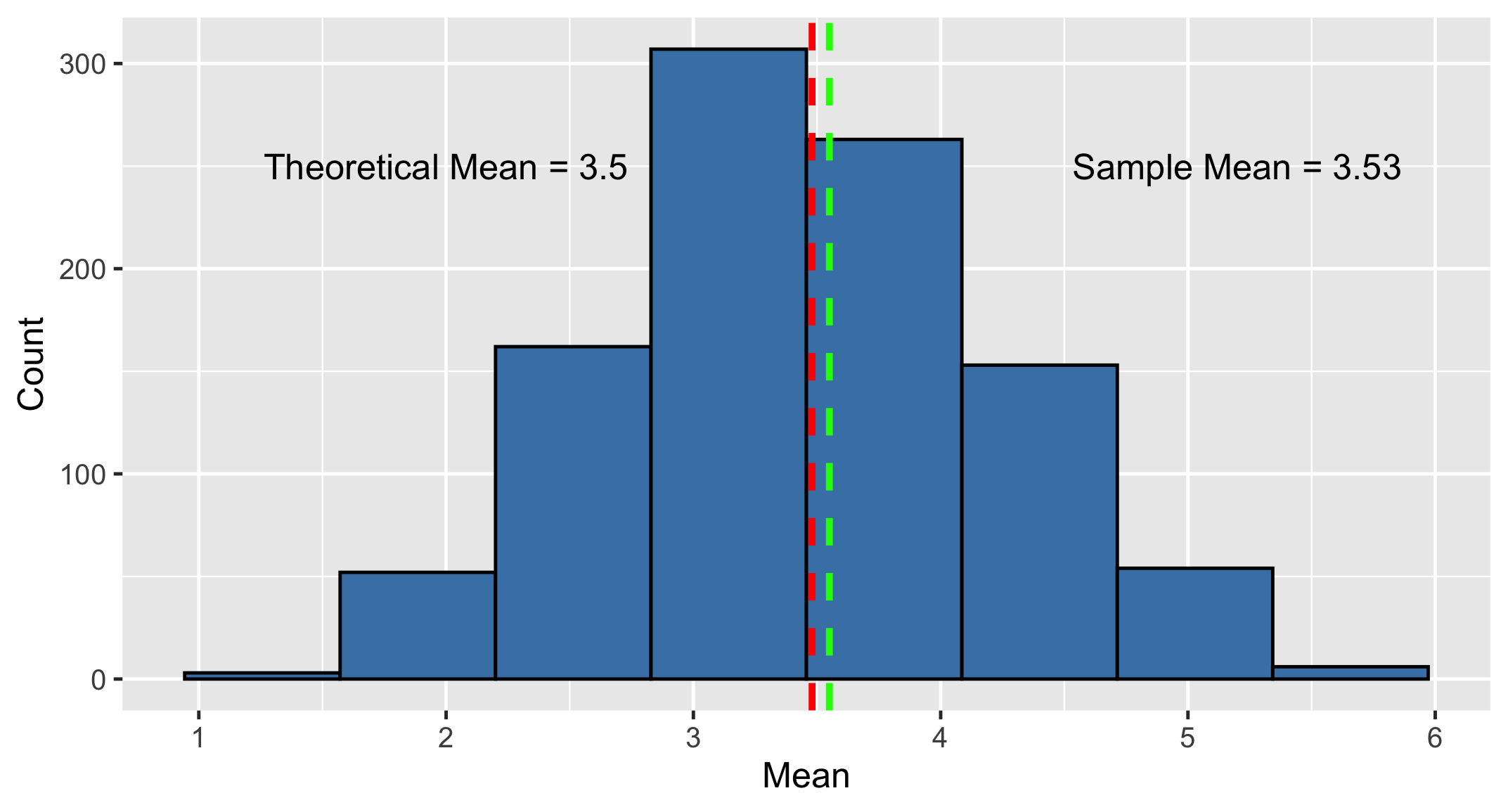
Central limit theorem
The sampling distribution of a statistic becomes closer to the normal distribution as the size of the sample increases.
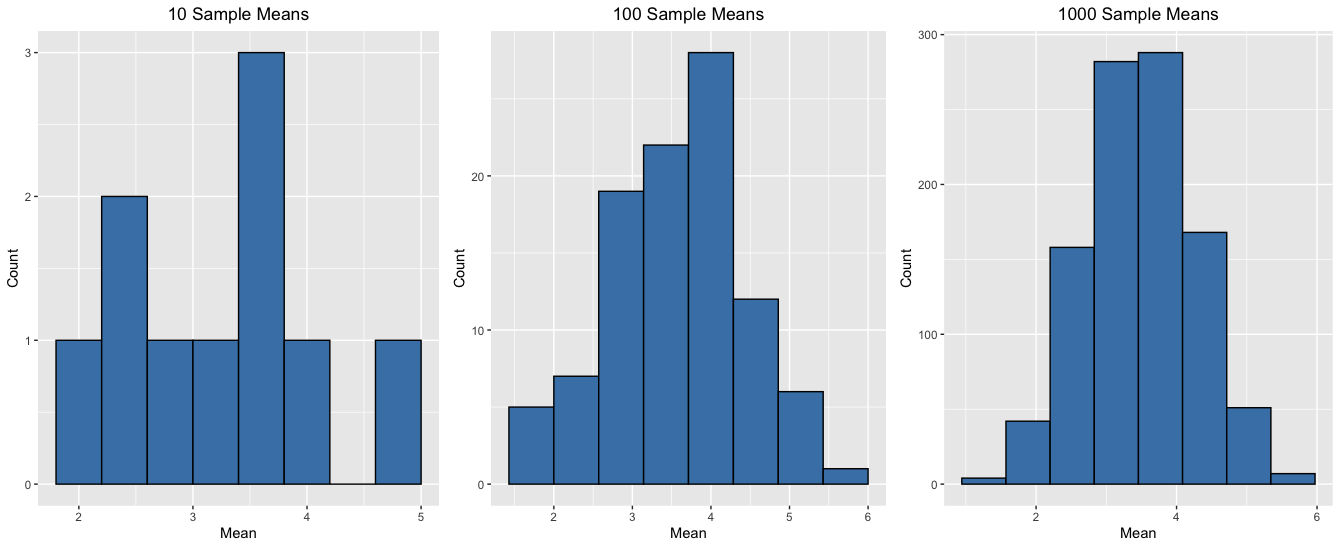
* Samples should be random and independent
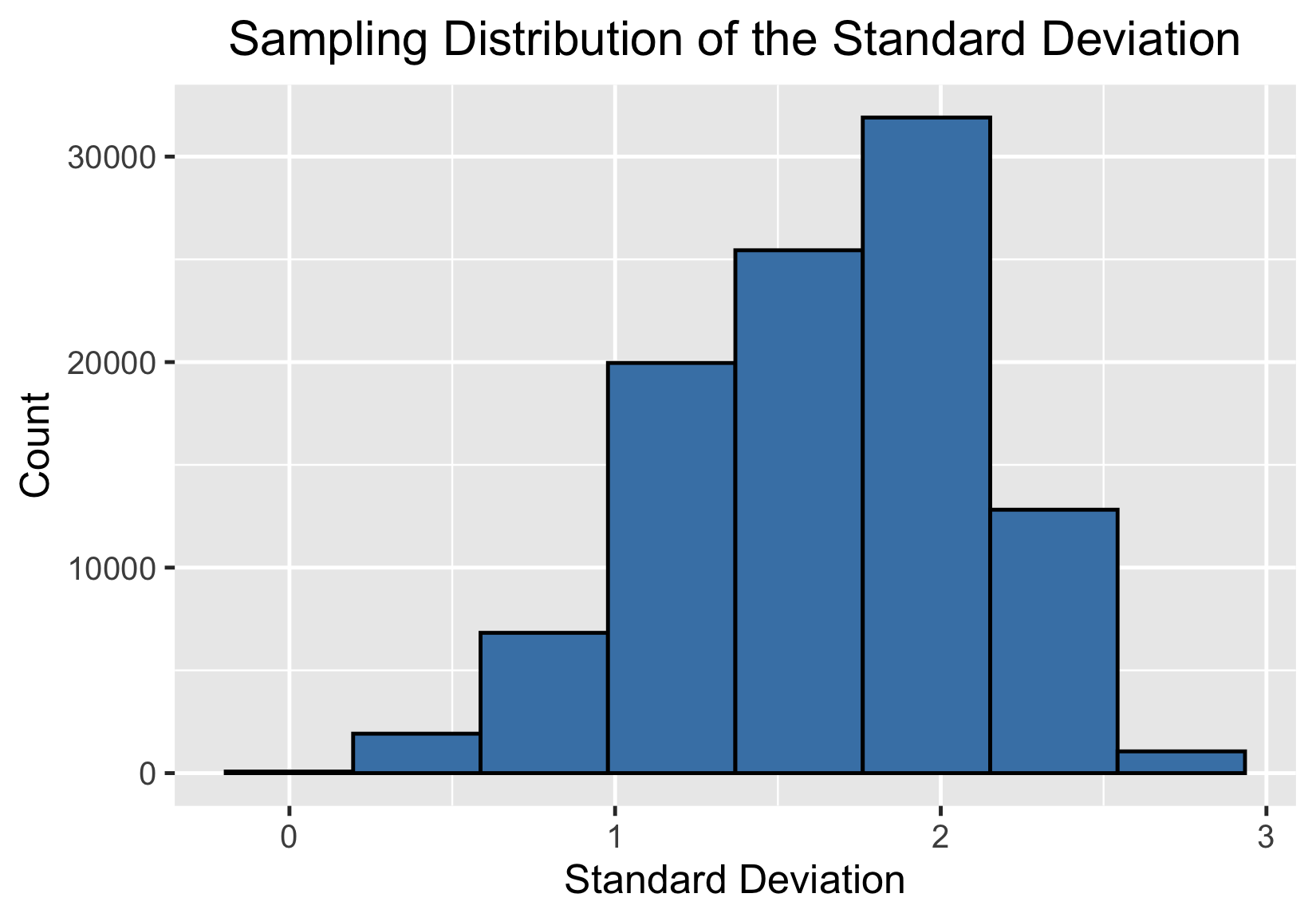
Standard deviation and the CLT
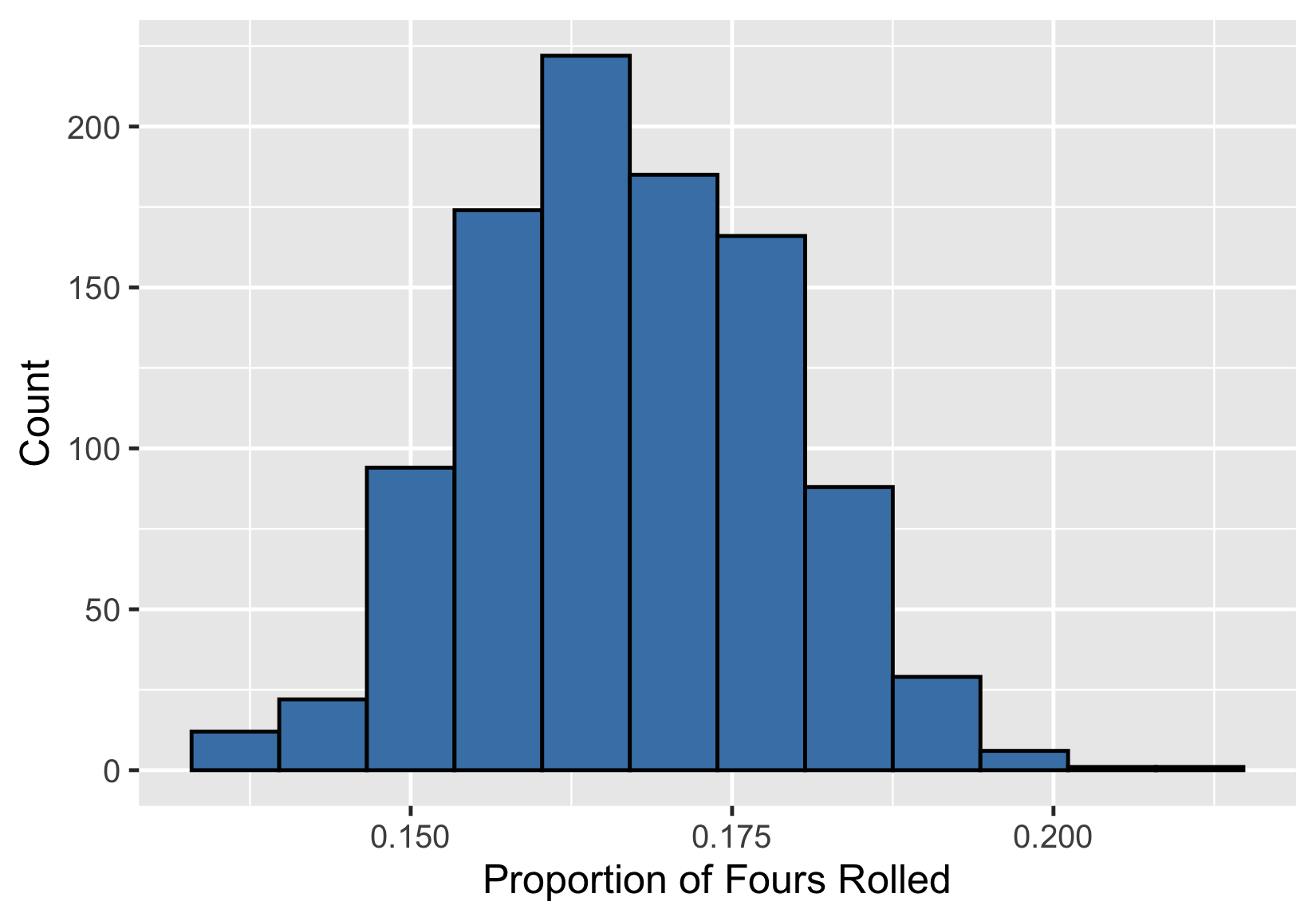
Proportions and the CLT
| Roll | Result |
|---|---|
| 1 | 2 |
| 2 | 1 |
| 3 | 4 |
| 4 | 2 |
| 5 | 6 |
- $\frac{1}{5}$ or 20% are a 4
| Set | Mean |
|---|---|
| 1 | 4 |
| 2 | 4 |
| 3 | 1 |
| 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 3 |
- $\frac{3}{5}$ or 60% are a 4
Sampling distribution of proportion
Mean of the sampling distribution
Benefits of the central limit theorem
Let's practice!
Introduction to Statistics

