Discrete distributions
Introduction to Statistics

George Boorman
Curriculum Manager, DataCamp
Rolling the dice
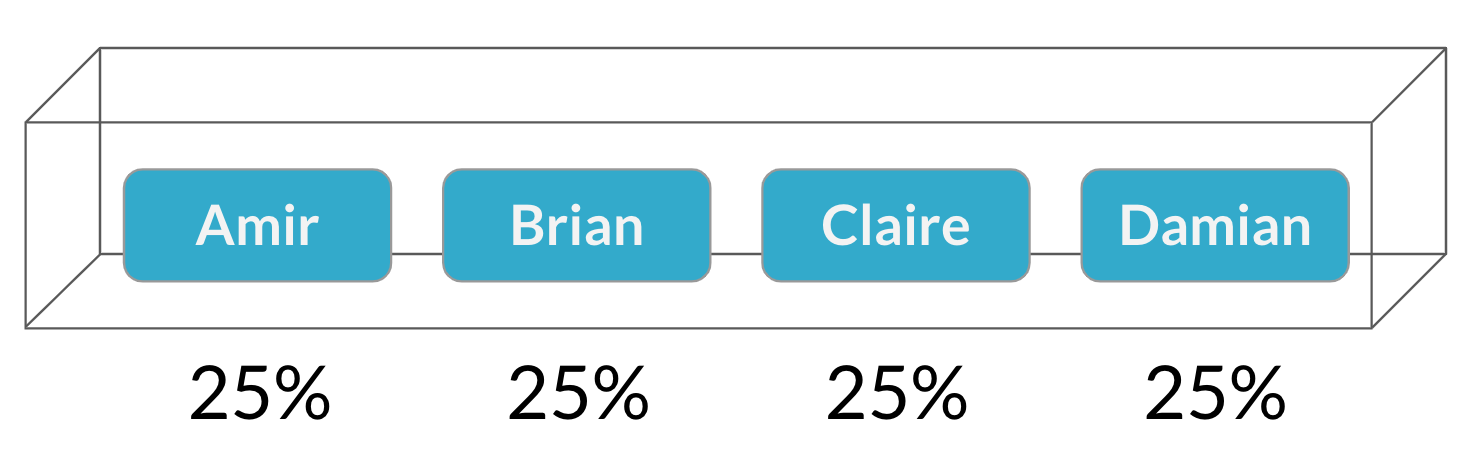
Choosing salespeople
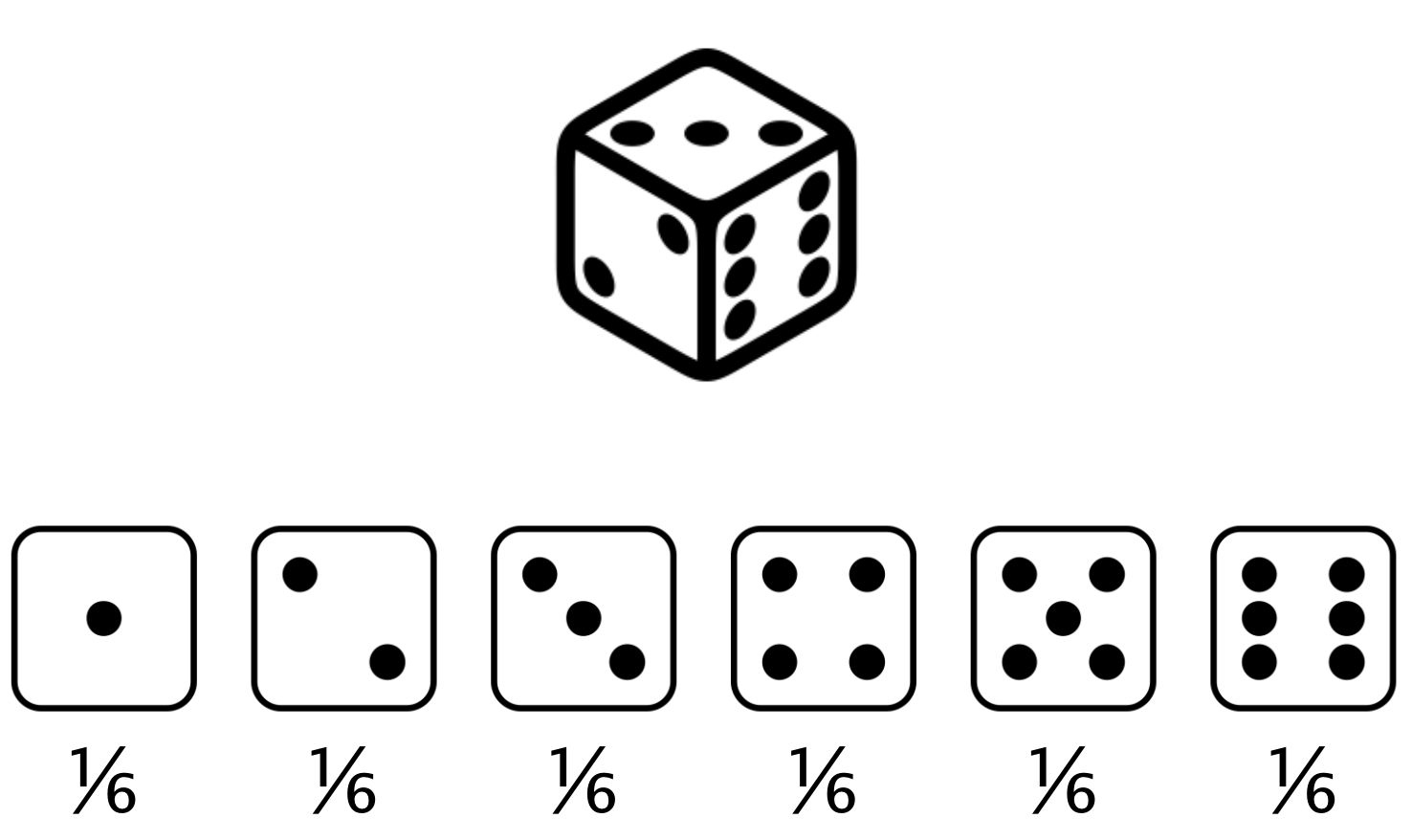
Probability distribution
Describes the probability of each possible outcome in a scenario
Expected value: The mean of a probability distribution
Expected value of a fair die roll = $(1 \times \frac{1}{6}) + (2 \times \frac{1}{6}) +(3 \times \frac{1}{6}) +(4 \times \frac{1}{6}) +(5 \times \frac{1}{6}) +(6 \times \frac{1}{6}) = 3.5$
Why are probability distributions important?
- Help us to quantify risk and inform decision making
- Used extensively in hypothesis testing
- Probability that the results occurred by chance
Visualizing a probability distribution
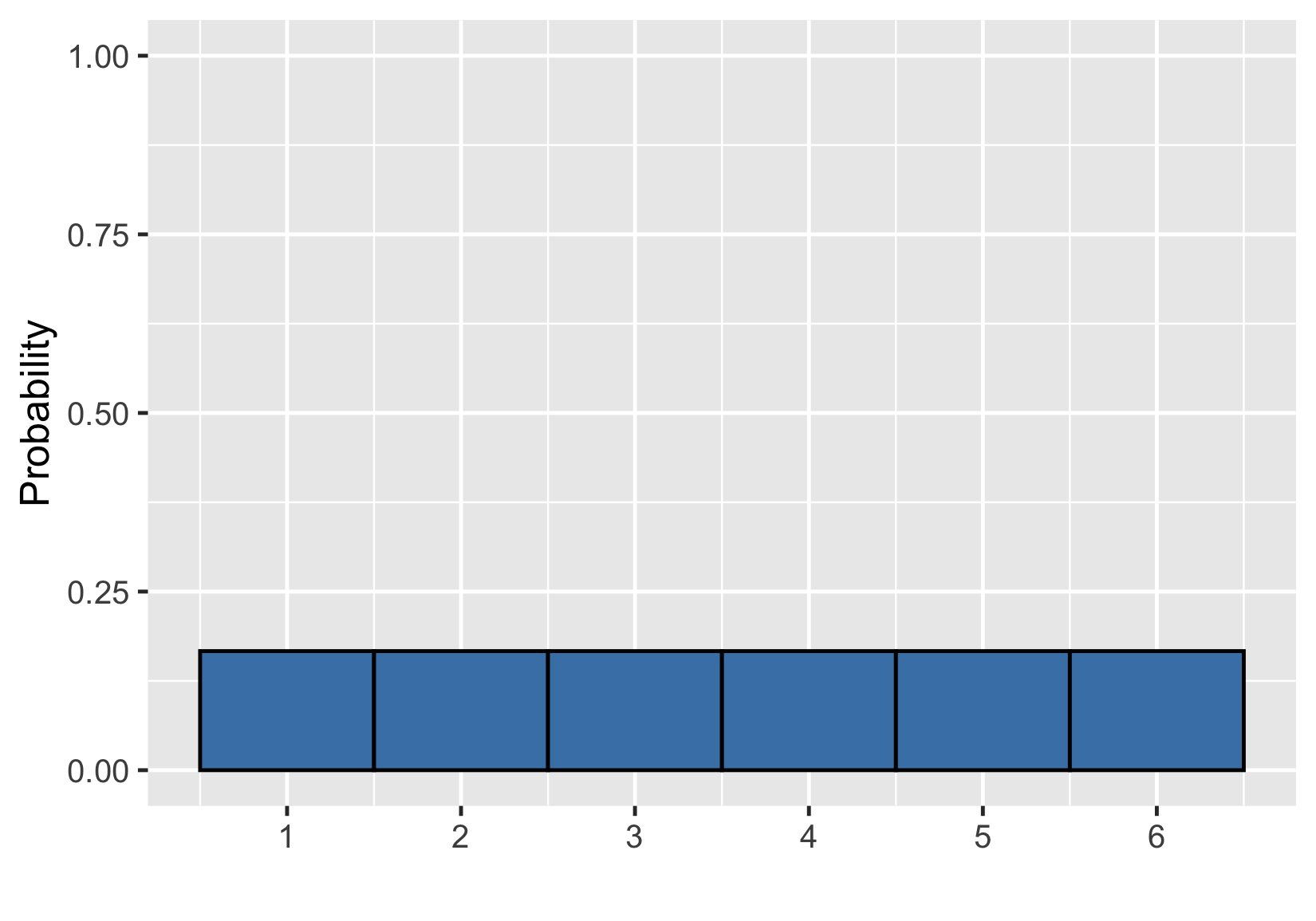
Probability = area
$$P(\text{die roll}) \le 2 = ~?$$
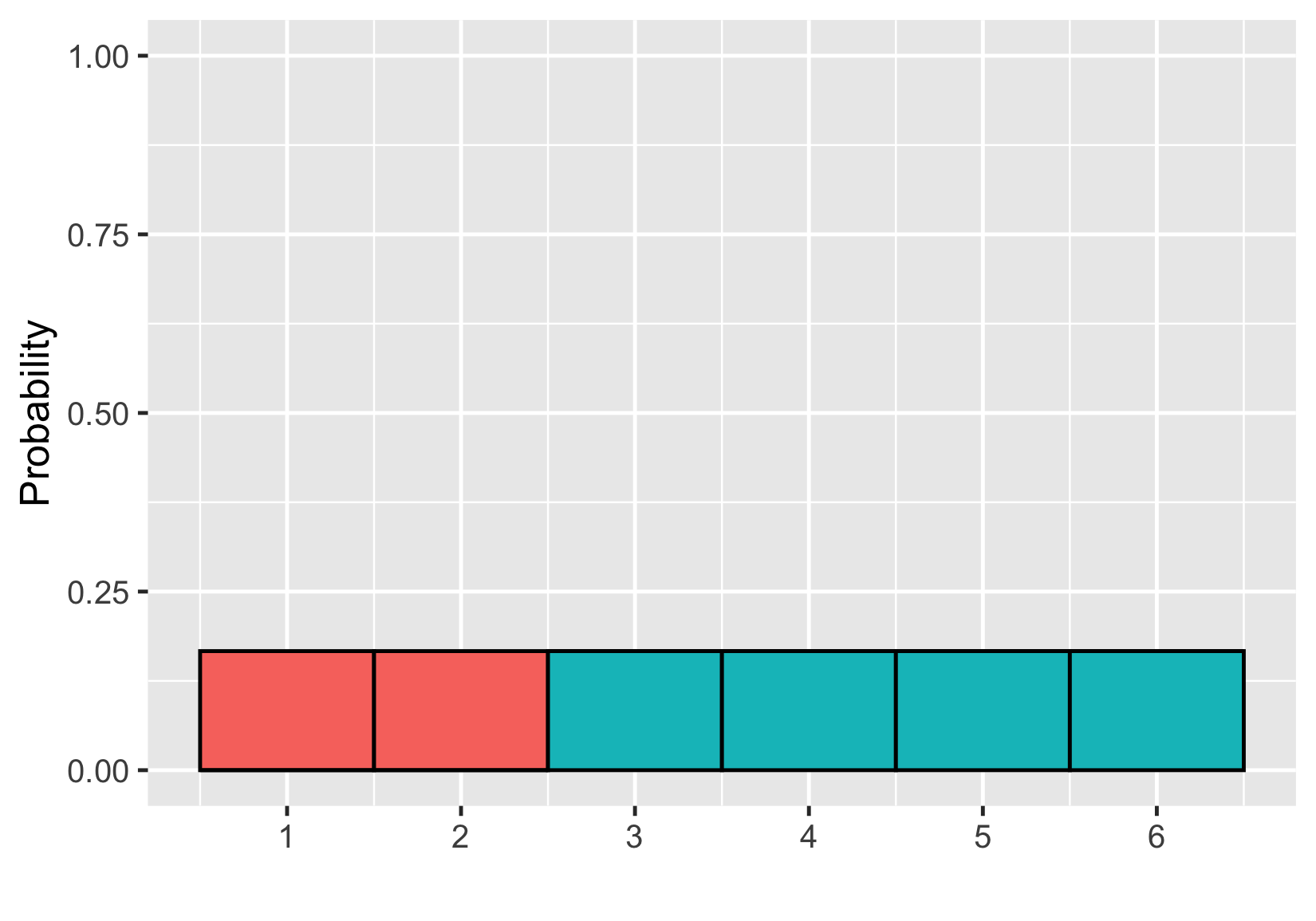
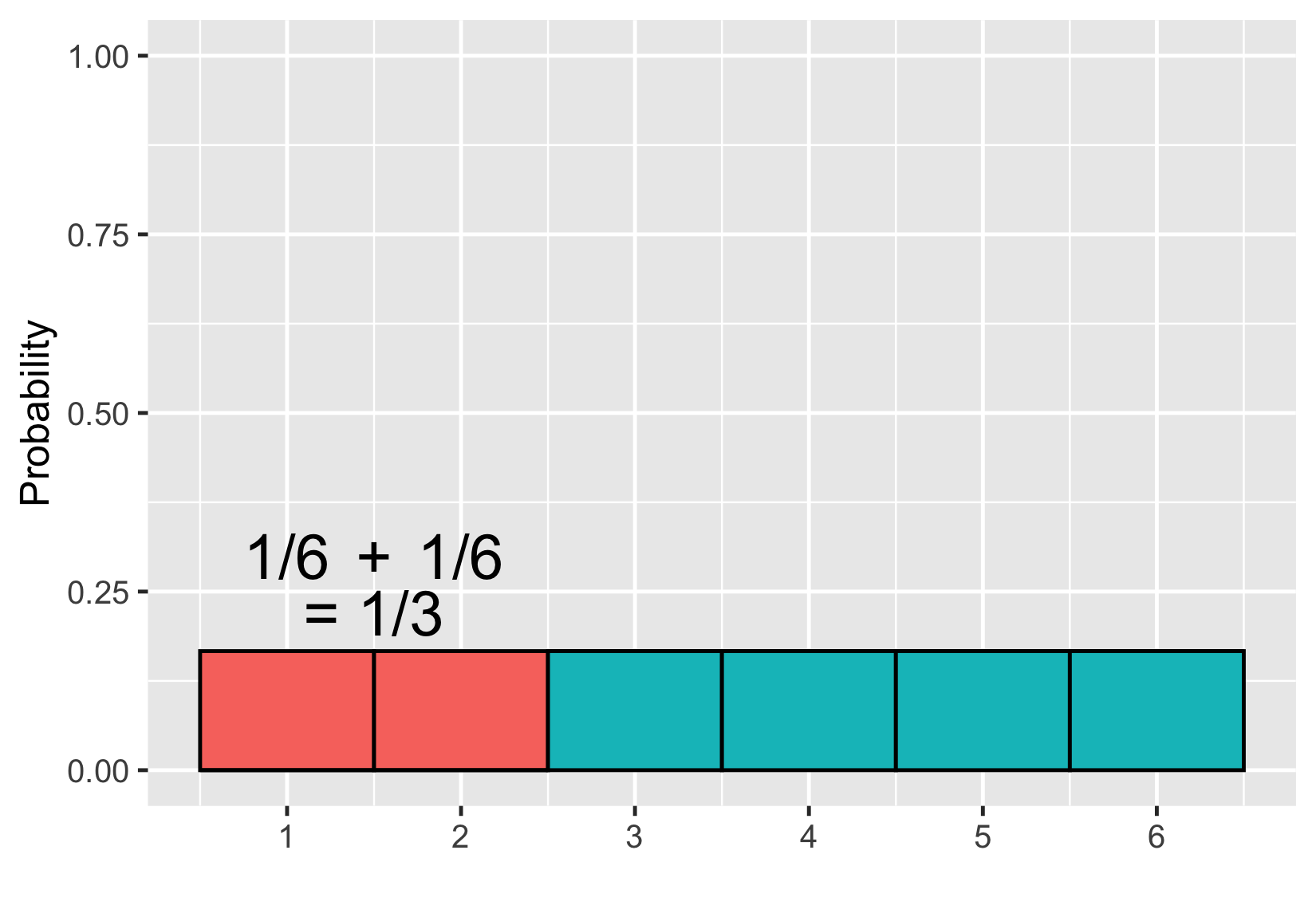
Probability = area
$$P(\text{die roll}) \le 2 = 1/3$$
Uneven die
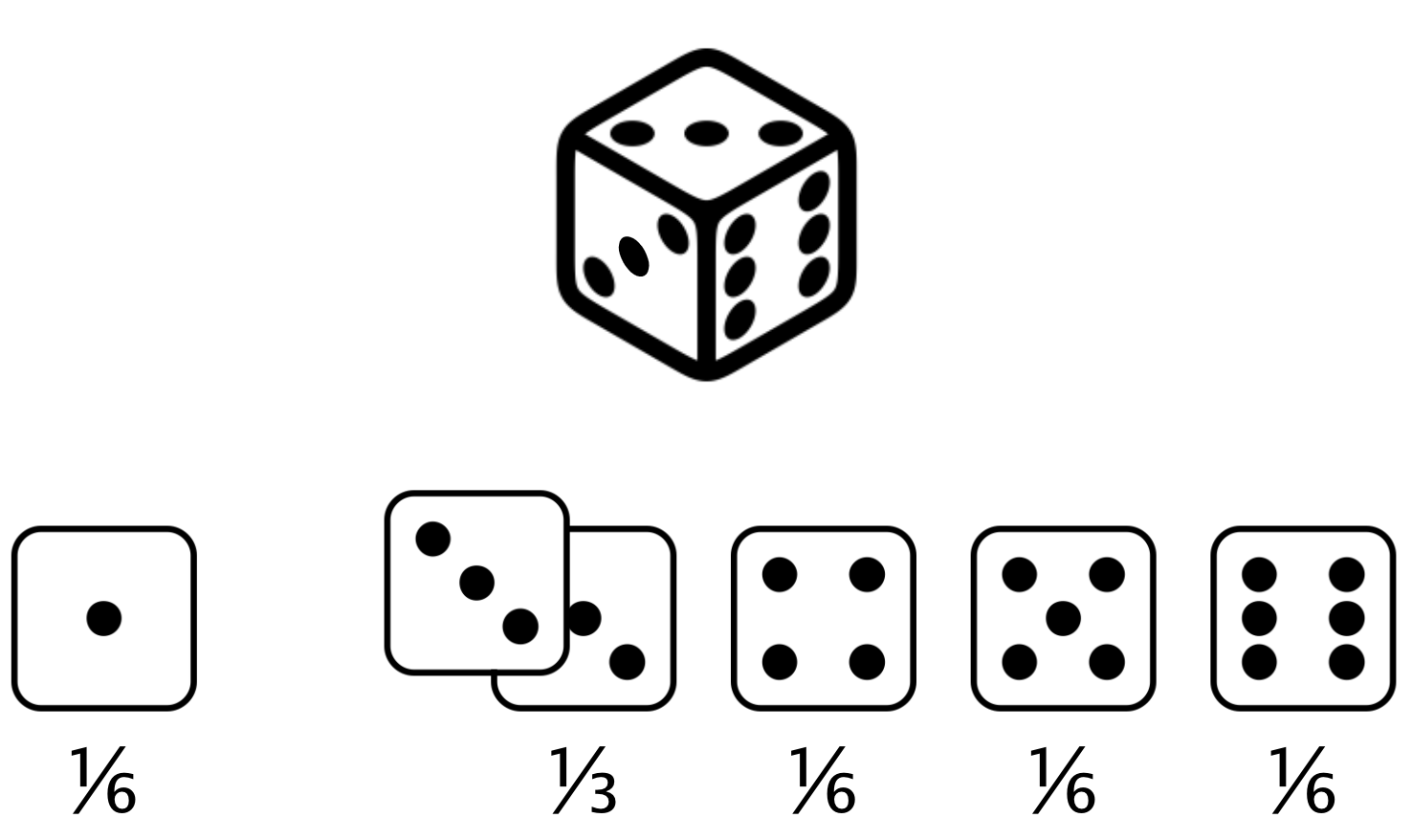
Expected value of uneven die roll = $(1 \times \frac{1}{6}) +(2 \times 0) +(3 \times \frac{1}{3}) +(4 \times \frac{1}{6}) +(5 \times \frac{1}{6}) +(6 \times \frac{1}{6}) = 3.67$
Visualizing uneven probabilities
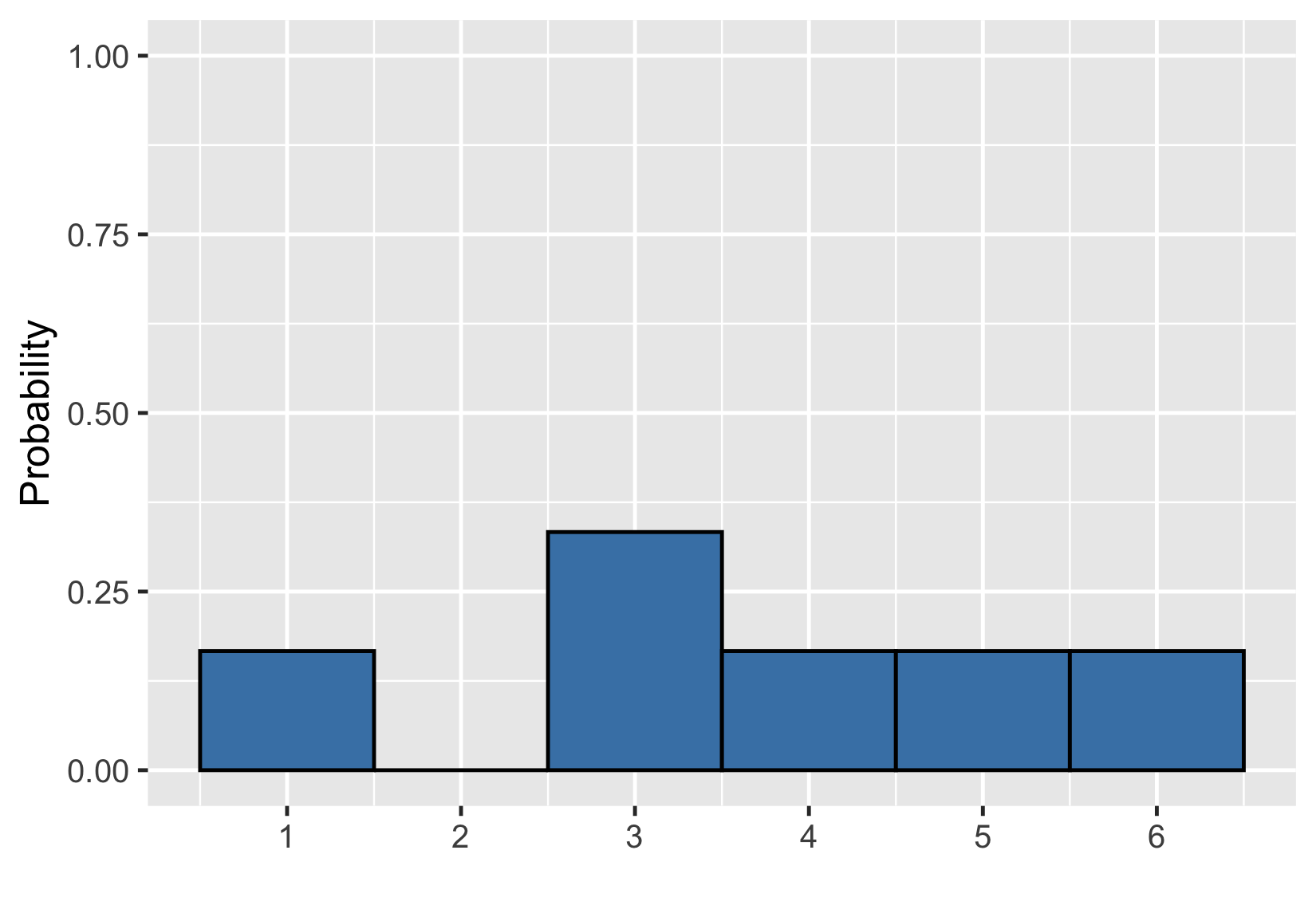
Adding areas
$$P(\text{uneven die roll}) \le 2 = ~?$$
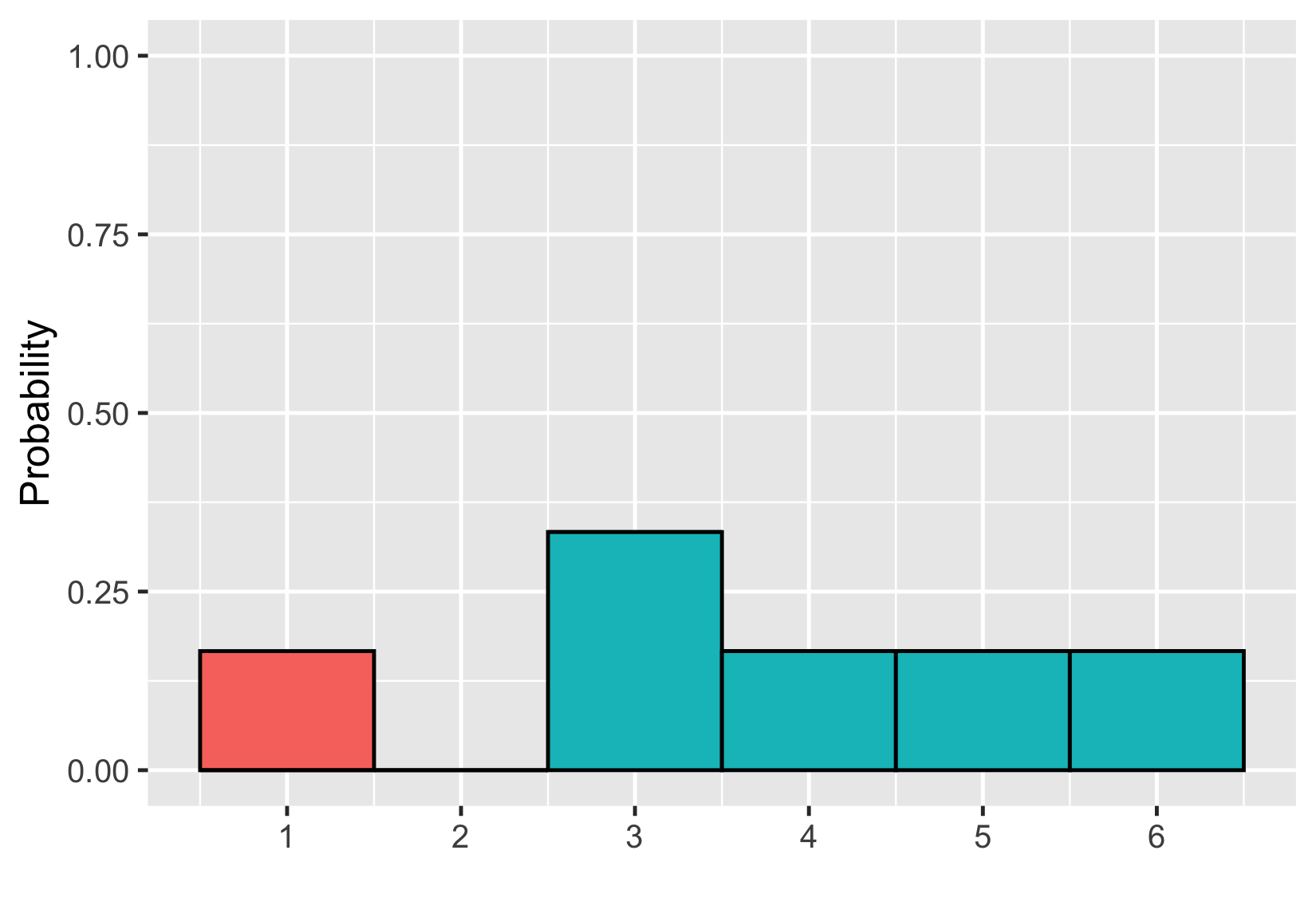
Adding areas
$$P(\text{uneven die roll}) \le 2 = 1/6$$
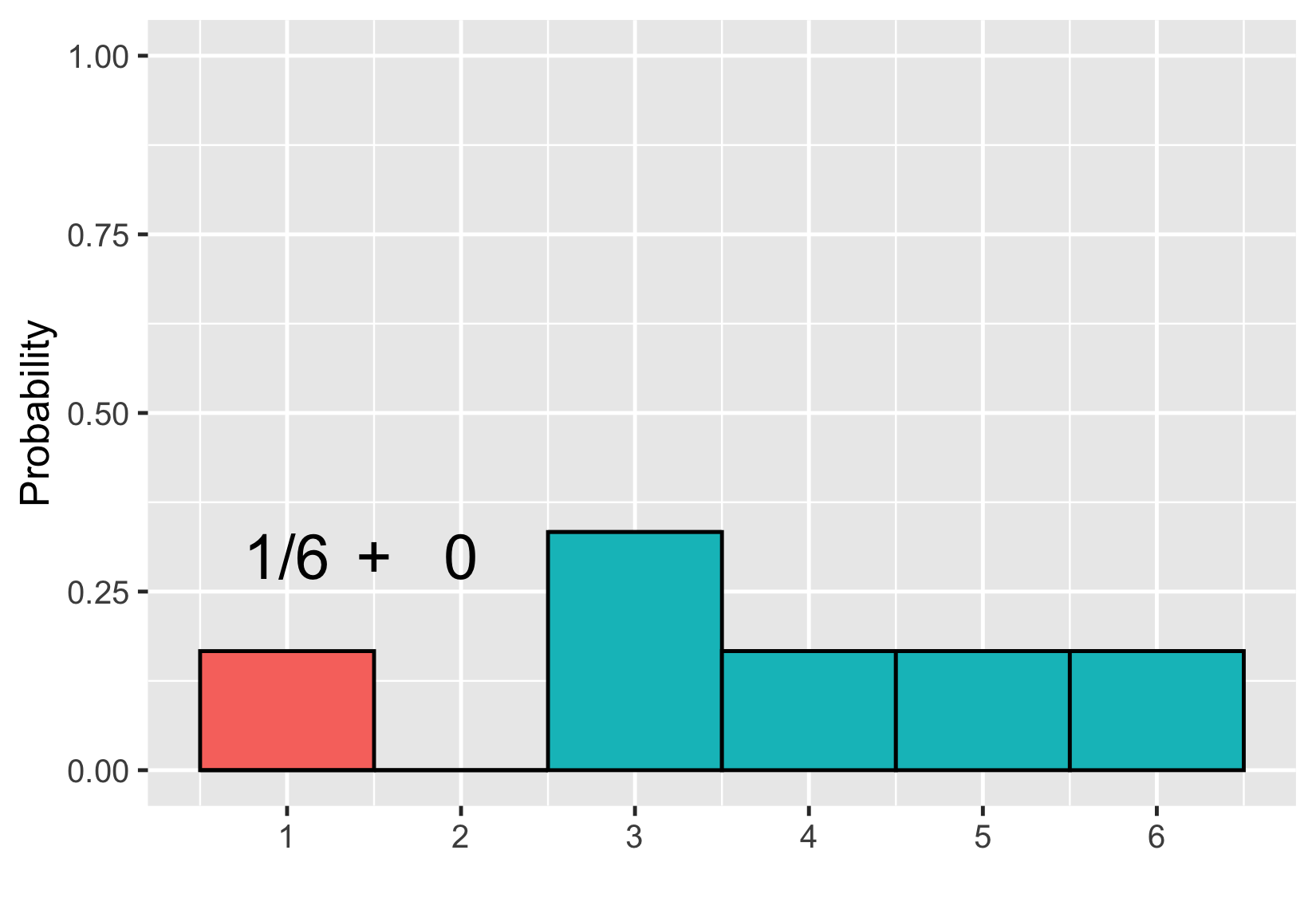
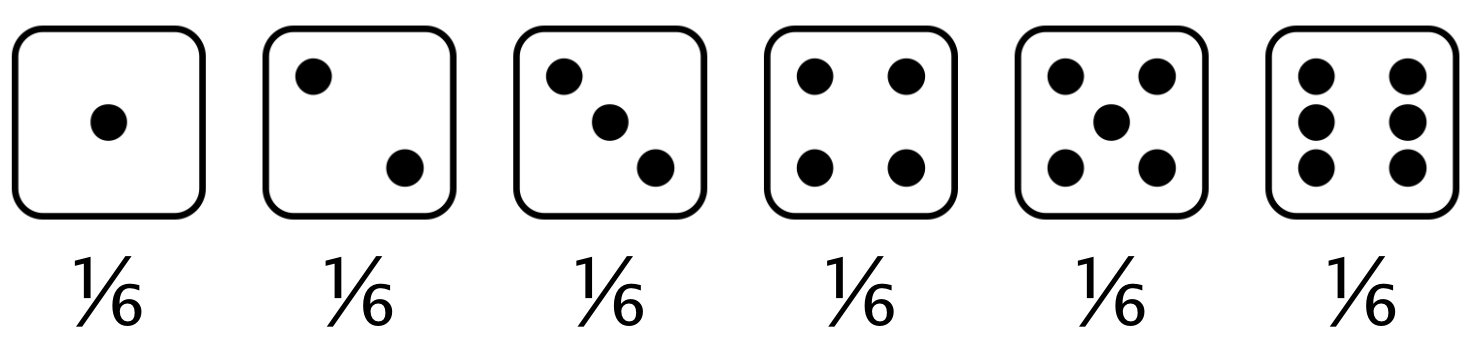
Discrete probability distributions
Describe probabilities for discrete outcomes
Fair die
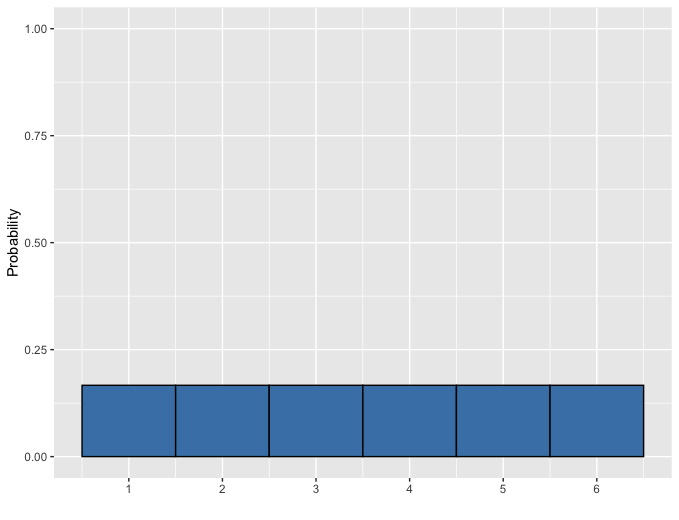
Discrete uniform distribution
Uneven die
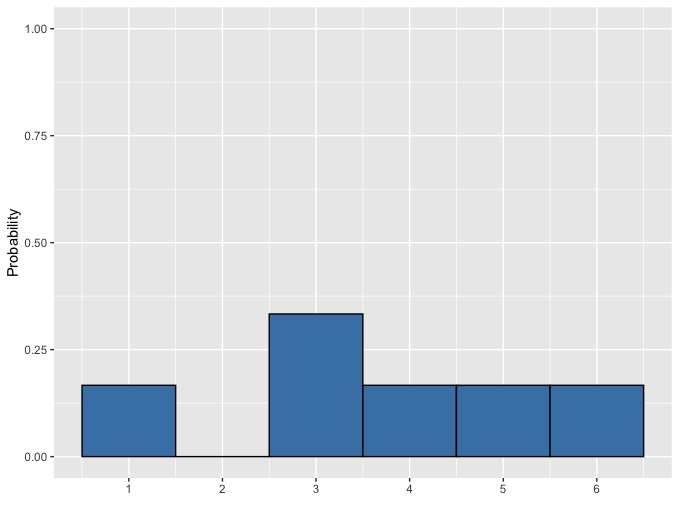
Sampling from a discrete distribution
| Roll | Result |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 3 |
| 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 5 |
| 6 | 6 |
$ {Mean} = 3.5 $
| Roll | Result |
|---|---|
| 1 | 3 |
| 2 | 1 |
| 3 | 2 |
| 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 6 |
| 6 | 3 |
| 7 | 2 |
| 8 | 2 |
| 9 | 2 |
| 10 | 5 |
Visualizing a sample
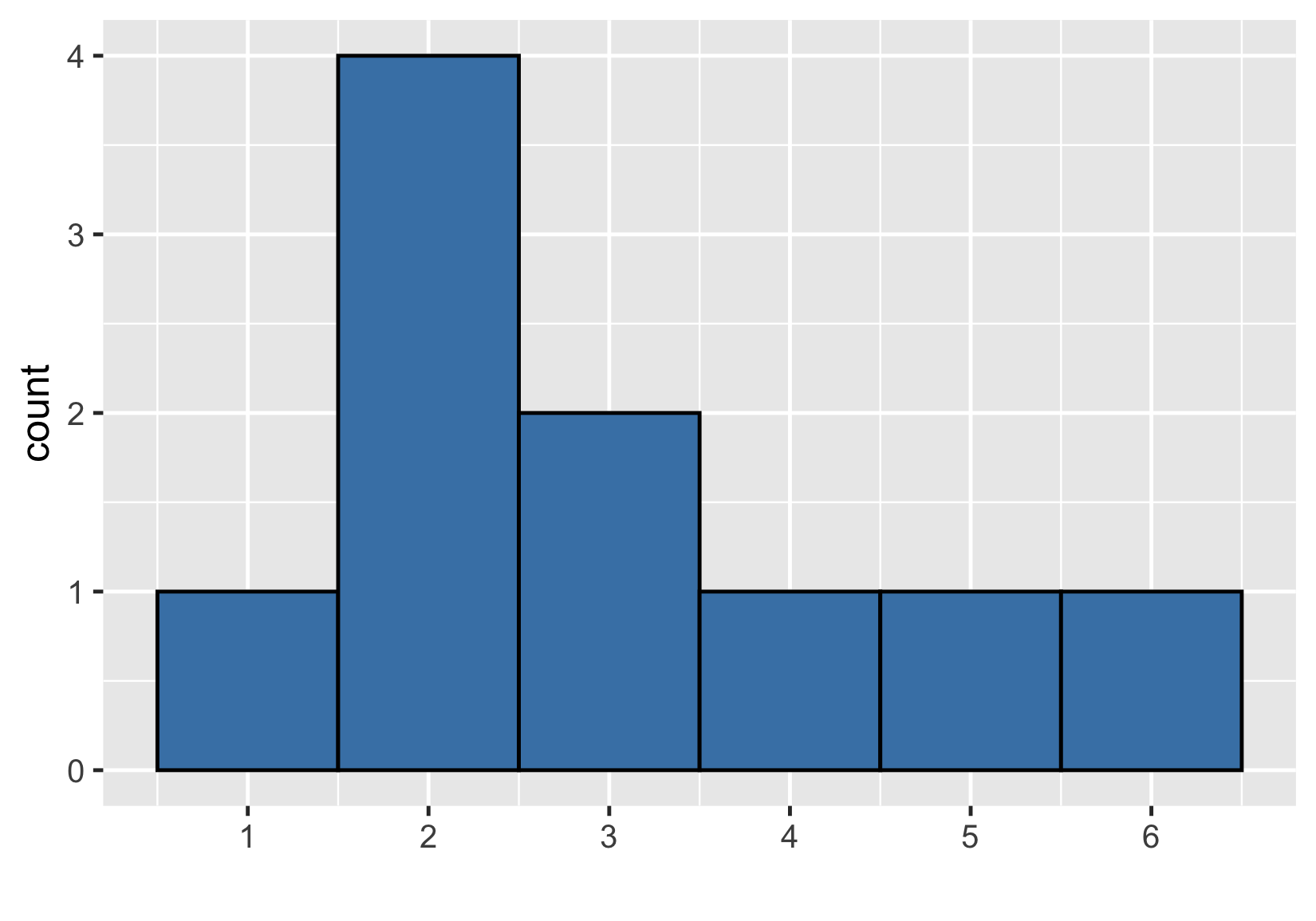
Sample distribution vs theoretical distribution

$ {Mean} = 3.0 $

$ {Mean} = 3.5 $
A bigger sample
Sample of 100 rolls
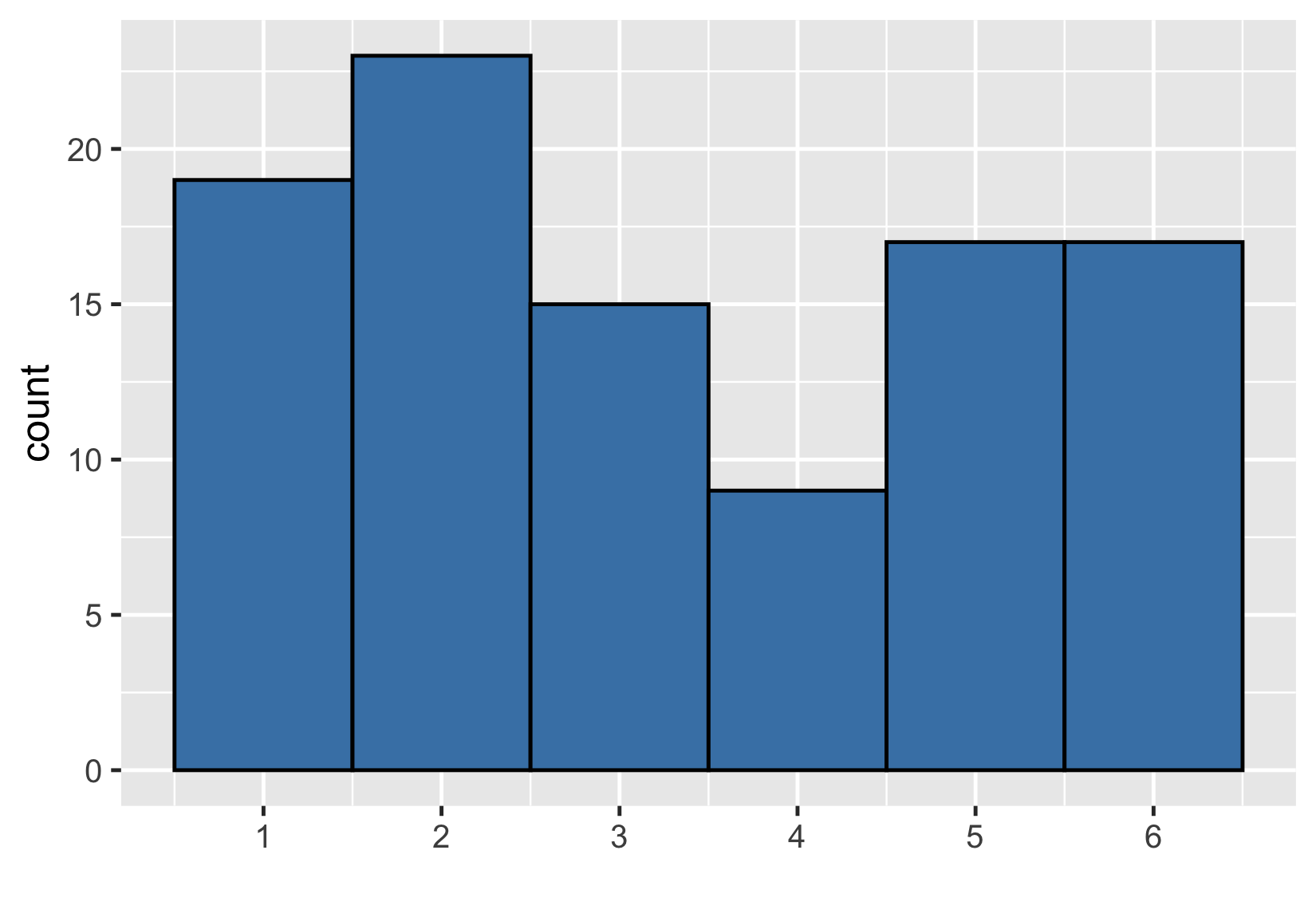
$ {Mean} = 3.33 $
An even bigger sample
Sample of 1000 rolls
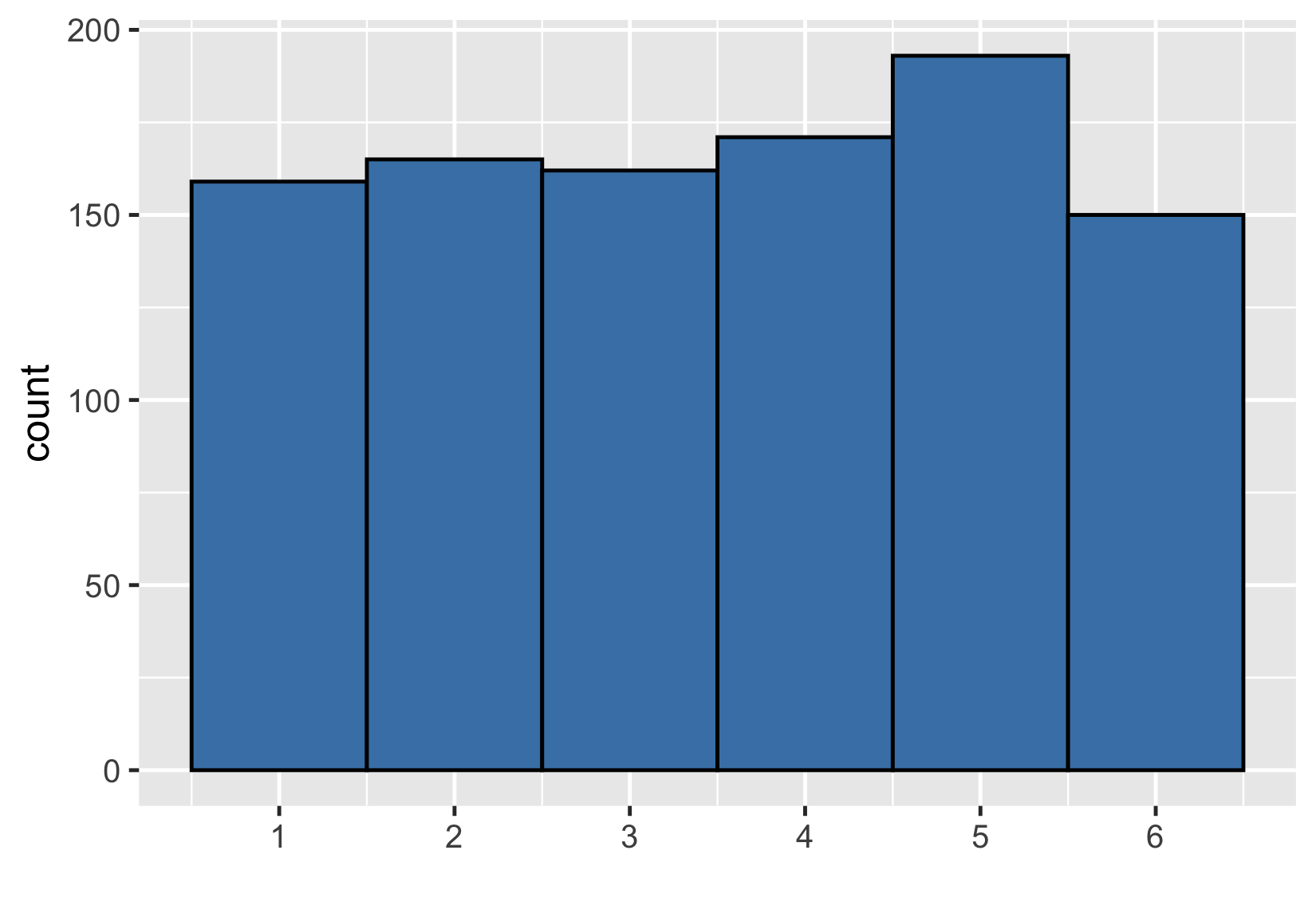
$ {Mean} = 3.52 $
Law of large numbers
As the size of your sample increases, the sample mean will approach the expected value.
| Sample size | Mean |
|---|---|
| 10 | 3.00 |
| 100 | 3.33 |
| 1000 | 3.52 |
Let's practice!
Introduction to Statistics

