Selection Sort and Insertion Sort
Data Structures and Algorithms in Python

Miriam Antona
Software engineer
Selection sort

- Determine the lowest value
Selection sort
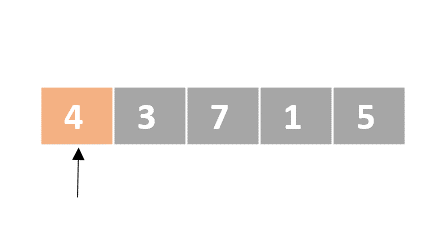
- Determine the lowest value
Selection sort
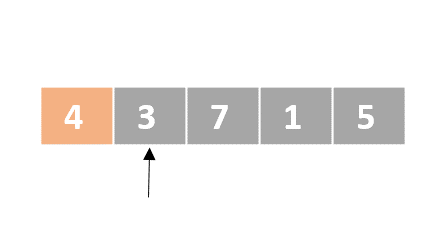
- Determine the lowest value
Selection sort
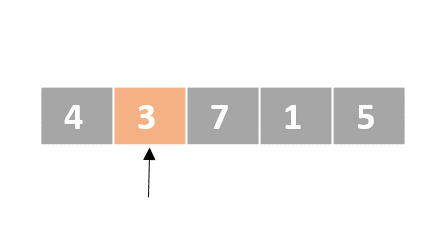
- Determine the lowest value
Selection sort
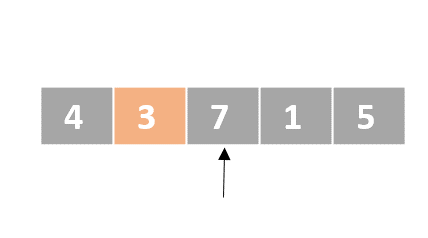
- Determine the lowest value
Selection sort
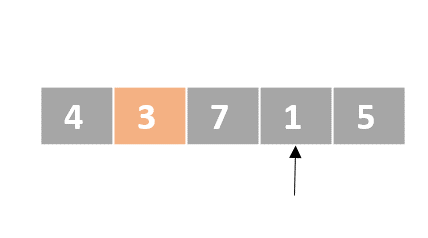
- Determine the lowest value
Selection sort
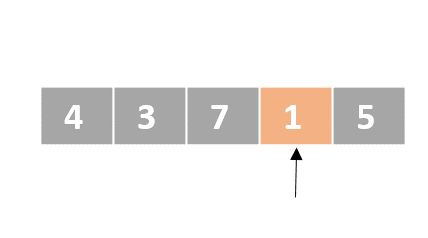
- Determine the lowest value
Selection sort
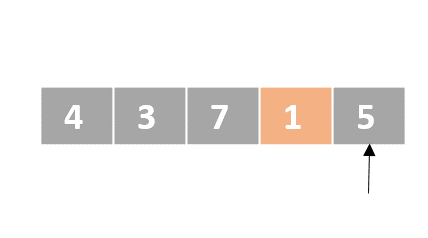
- Determine the lowest value
Selection sort
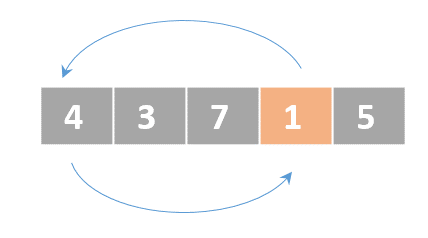
- Determine the lowest value
- Swap the lowest value with the first unordered element
Selection sort
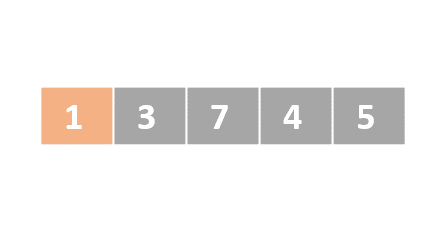
- Determine the lowest value
- Swap the lowest value with the first unordered element
Selection sort
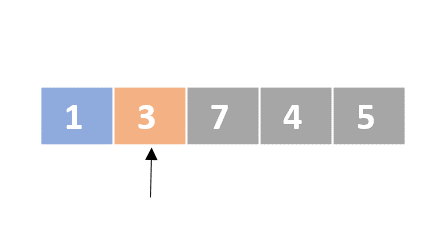
- Determine the lowest value
- Swap the lowest value with the first unordered element
Selection sort
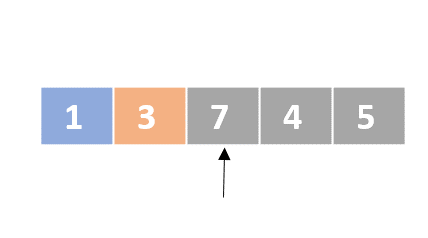
- Determine the lowest value
- Swap the lowest value with the first unordered element
Selection sort
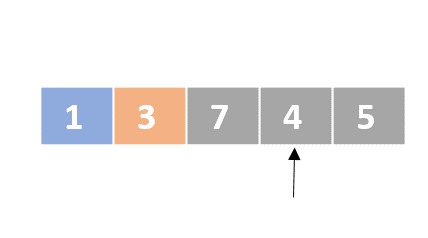
- Determine the lowest value
- Swap the lowest value with the first unordered element
Selection sort

- Determine the lowest value
- Swap the lowest value with the first unordered element
Selection sort
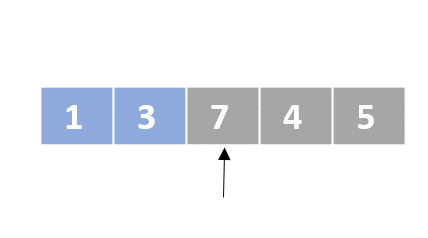
- Determine the lowest value
- Swap the lowest value with the first unordered element
Selection sort
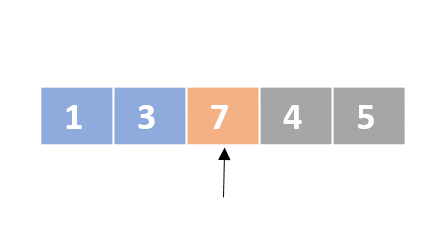
- Determine the lowest value
- Swap the lowest value with the first unordered element
Selection sort
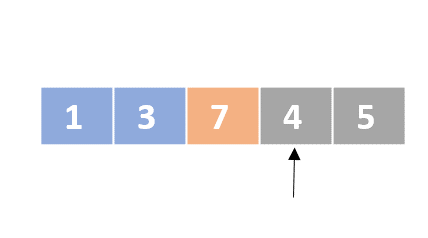
- Determine the lowest value
- Swap the lowest value with the first unordered element
Selection sort
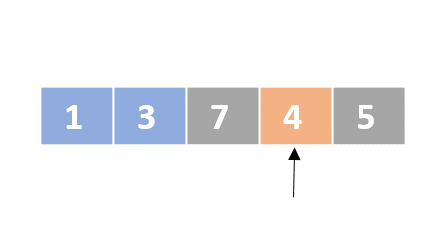
- Determine the lowest value
- Swap the lowest value with the first unordered element
Selection sort

- Determine the lowest value
- Swap the lowest value with the first unordered element
Selection sort
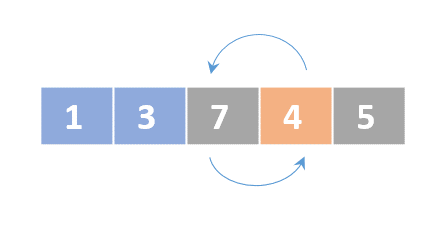
- Determine the lowest value
- Swap the lowest value with the first unordered element
Selection sort

- Determine the lowest value
- Swap the lowest value with the first unordered element
Selection sort
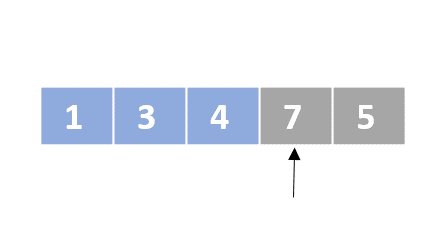
- Determine the lowest value
- Swap the lowest value with the first unordered element
Selection sort
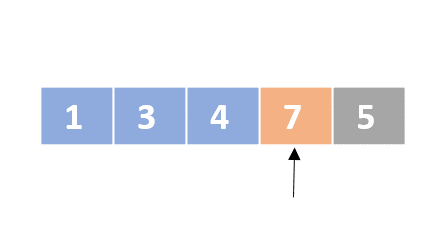
- Determine the lowest value
- Swap the lowest value with the first unordered element
Selection sort

- Determine the lowest value
- Swap the lowest value with the first unordered element
Selection sort

- Determine the lowest value
- Swap the lowest value with the first unordered element
Selection sort
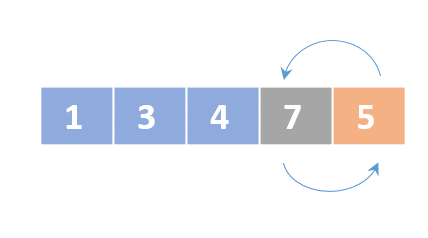
- Determine the lowest value
- Swap the lowest value with the first unordered element
Selection sort
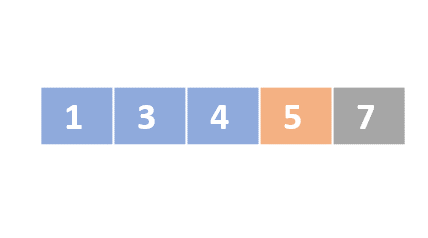
- Determine the lowest value
- Swap the lowest value with the first unordered element
Selection sort

- Determine the lowest value
- Swap the lowest value with the first unordered element
Selection sort

- Determine the lowest value
- Swap the lowest value with the first unordered element
Selection sort - implementation
def selection_sort(my_list): list_length = len(my_list) for i in range(list_length - 1):lowest = my_list[i]index = ifor j in range(i + 1, list_length):if my_list[j] < lowest:index = jlowest = my_list[j]my_list[i] , my_list[index] = my_list[index] , my_list[i]return my_list
Selection sort - complexity
- Worst case: $O(n^2)$
- Average case: $\Theta(n^2)$
- Best case: $\Omega(n^2)$
Insertion sort

Insertion sort
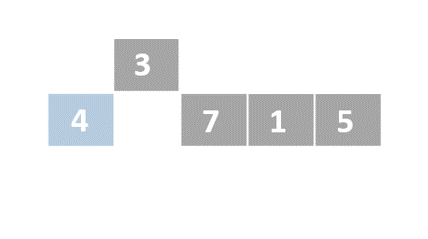
Insertion sort
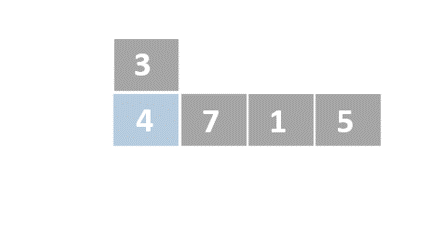
Insertion sort

Insertion sort

Insertion sort
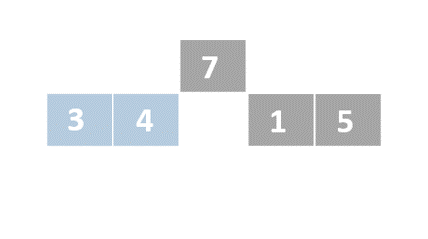
Insertion sort

Insertion sort
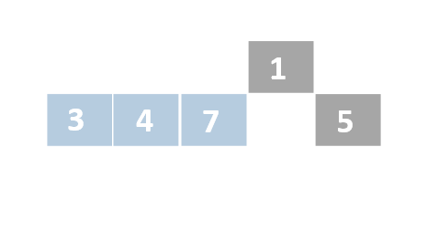
Insertion sort
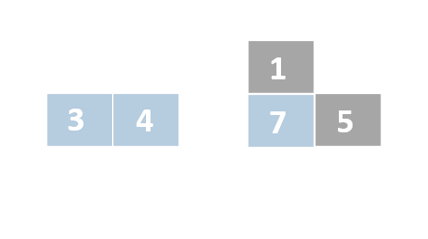
Insertion sort
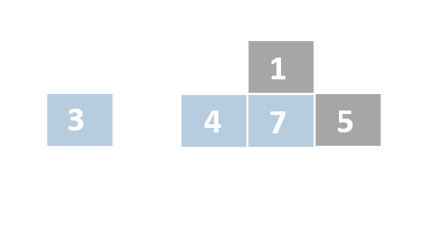
Insertion sort
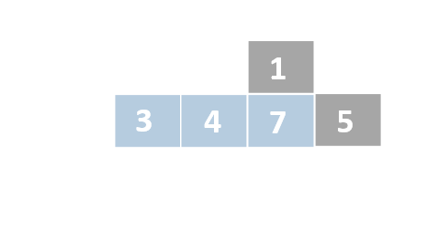
Insertion sort
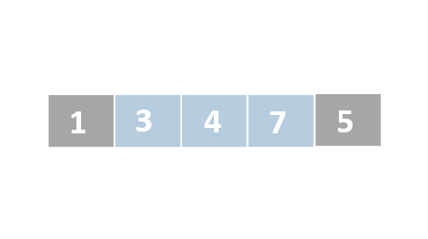
Insertion sort
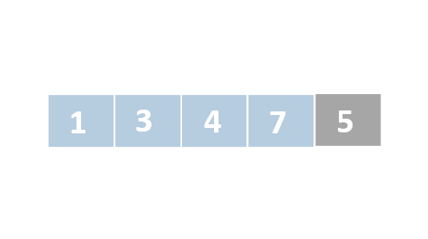
Insertion sort
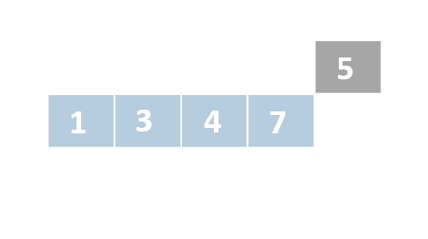
Insertion sort
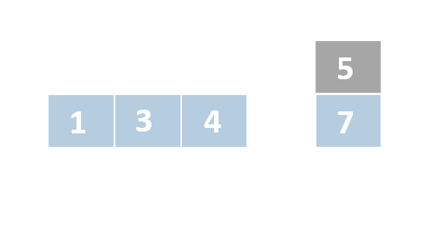
Insertion sort

Insertion sort - implementation
def insertion_sort(my_list): for i in range(1, len(my_list)):number_to_order = my_list[i]j = i - 1while j >= 0 and number_to_order < my_list[j]:my_list[j + 1] = my_list[j]j -= 1my_list[j + 1] = number_to_orderreturn my_list
Insertion sort - complexity
- Worst case: $O(n^2)$
- Average case: $\Theta(n^2)$
- Best case: $\Omega(n)$
Let's practice!
Data Structures and Algorithms in Python

