Hyperparameters of KNN
Anomaly Detection in Python

Bekhruz (Bex) Tuychiev
Kaggle Master, Data Science Content Creator
Modify evaluate_outlier_classifier
def evaluate_outlier_classifier(model, data, threshold=.75):
model.fit(data)
probs = model.predict_proba(data)
inliers = data[probs[:, 1] <= threshold]
return inliers
Modifying evaluate_regressor
def evaluate_regressor(inliers):
X, y = inliers.drop("weightkg", axis=1), inliers[['weightkg']]
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, random_state=10, train_size=0.8)
lr = LinearRegression()
lr.fit(X_train, y_train)
preds = lr.predict(X_test)
rmse = root_mean_squared_error(y_test, preds)
return round(rmse, 3)
Tuning the number of neighbors
n_neighbors = [5, 10, 15, 20] scores = dict()for k in n_neighbors: # Init a KNN knn = KNN(n_neighbors=k) # Get the inliers with KNN inliers = evaluate_outlier_classifier(knn, males_transformed, .55) # Calculate and store RMSE scores[k] = evaluate_regressor(inliers)
Inspecting the result
print(scores)
{5: 19.463, 10: 17.965, 15: 18.817, 20: 20.597}
Distance metrics
- More than 40 metrics are supported
knn = KNN(metric='euclidean')

Manhattan distance
A = np.array([9, 1, 6, ...]) B = np.array([25, 44, 85, ...])diffs = np.abs(B - A)manhattan_dist_AB = np.sum(diffs) manhattan_dist_AB
573
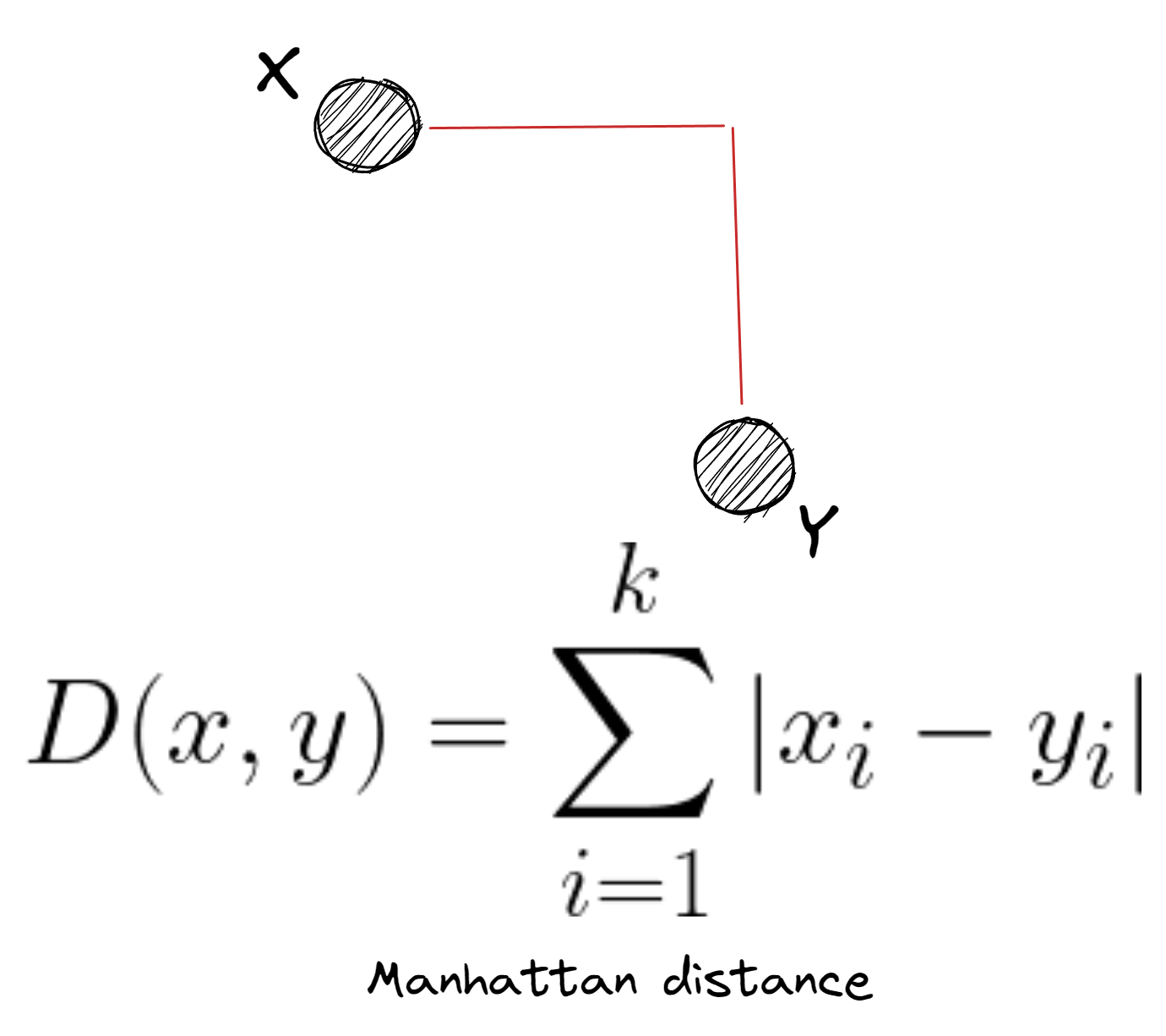
Manhattan distance
- Works well with high-dimensional data
- Returns larger values than euclidean
- Works best with categorical features

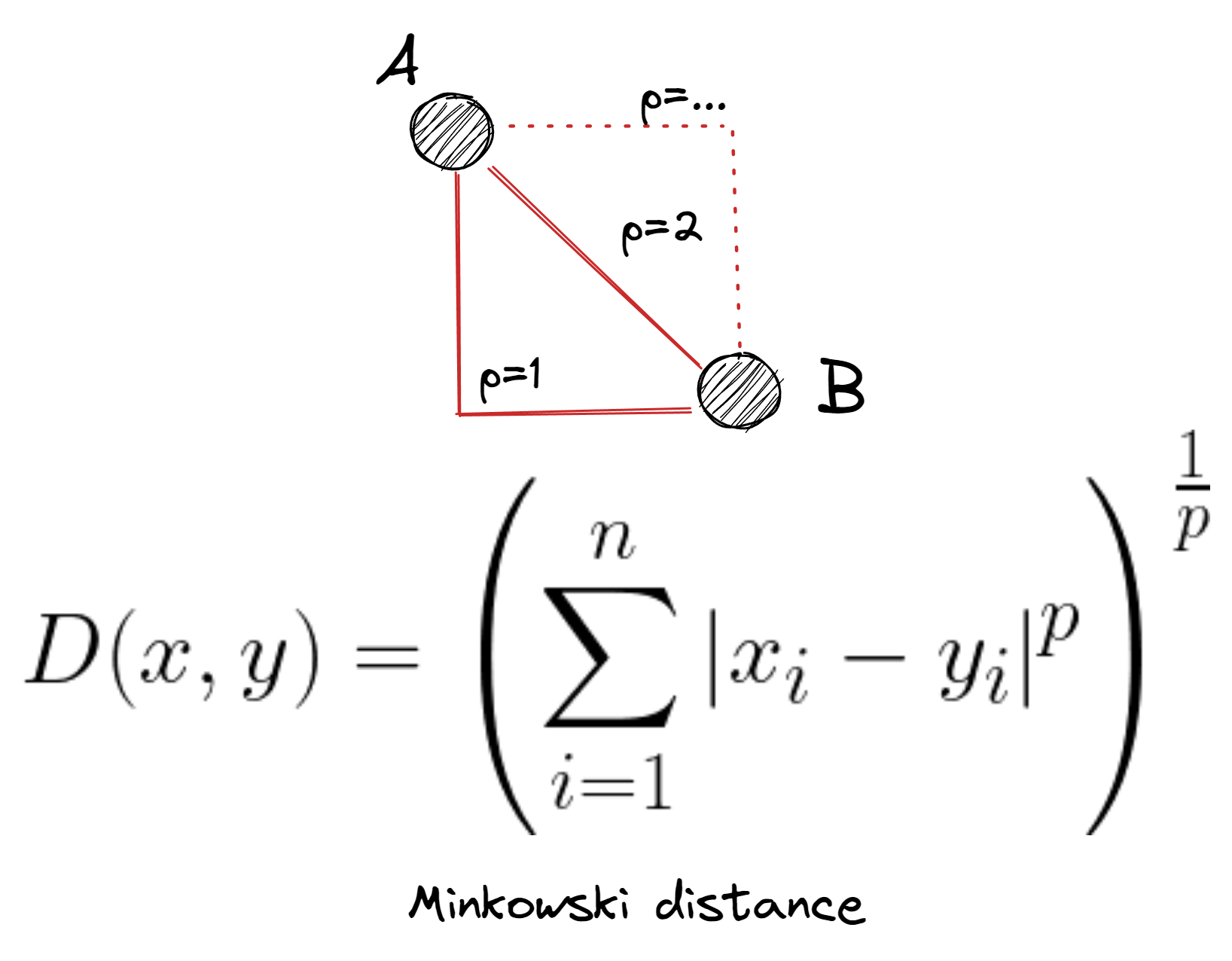
Minkowski distance
# Euclidean distance
knn = KNN(metric="minkowski", p=2)
# Manhattan distance
knn = KNN(metric="minkowski", p=1)
Distance aggregation
knn_largest = KNN(n_neighbors=10, method="largest")knn_mean = KNN(n_neighbors=10, method="mean") knn_median = KNN(n_neighbors=10, method="median")
Tuning distance and method
ps = [1, 2, 3, 4] methods = ["largest", "mean", "median"] scores = dict()for p, method in product(ps, methods): # Init an instance of KNN knn = KNN(n_neighbors=10, method=method, p=p, n_jobs=-1) # Find the inliers with the current KNN inliers = evaluate_outlier_classifier(knn, males_transformed, .55) # Calculate and store RMSE into scores scores[(p, method)] = evaluate_regressor(inliers)
Inspecting the result
print(scores)
{(1, 'largest'): 23.188,
(1, 'mean'): 23.188,
(1, 'median'): 23.188,
(2, 'largest'): 17.965,
(2, 'mean'): 19.463,
(2, 'median'): 19.463,
(3, 'largest'): 17.965,
(3, 'mean'): 19.463,
(3, 'median'): 19.463, ...
}
Let's practice!
Anomaly Detection in Python

