Sampling and bias
Foundations of Inference in Python

Paul Savala
Assistant Professor of Mathematics
Bias
- Biased sample: A group occurs more/less often in sample than in population
Biased samples
all_salaries = [75000, 82000, ...] friends_salaries = [93000, 87000, 103000, 101000]np.mean(friends_salaries)
96000
Sampling distribution
sampling_distribution = []for i in range(100):random_sample = np.random.choice(salaries, size=10) sample_mean = np.mean(random_sample)sampling_distribution.append(sample_mean)plt.hist(sampling_distribution) plt.xlabel('Mean salary') plt.ylabel('Percent of samples') plt.title('Sampling distribution of mean salaries') plt.show()
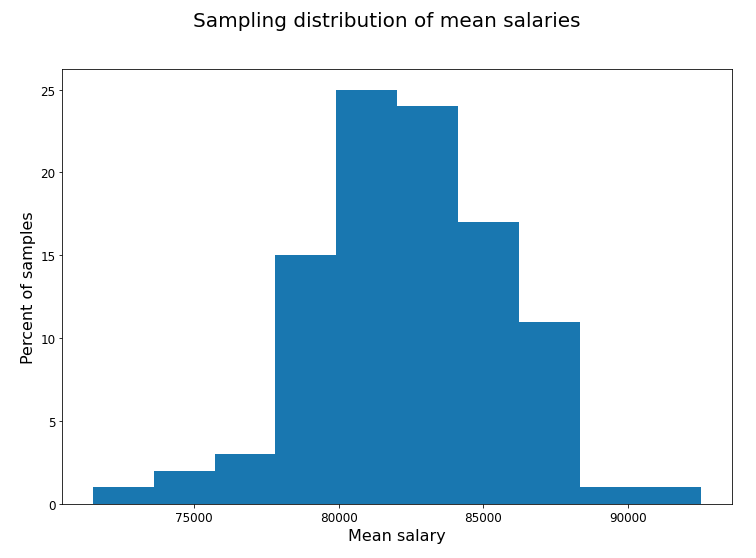
Depends on the sample
- Samples affect point estimates
- Point estimates affect inference
- Samples affect p-value calculations
Doesn't depend on the sample
- Population statistic
- Is unaffected by sample chosen
- Conclusion from test
- Given a p-value, conclusion is unaffected by sample chosen
Let's practice!
Foundations of Inference in Python

