Trends, seasonality, and cyclicity
Forecasting in R

Rob J. Hyndman
Professor of Statistics at Monash University
Time series patterns
| Pattern | Description |
|---|---|
| Trend | A pattern exists involving a long-term increase OR decrease in the data |
| Seasonal | A periodic pattern exists due to the calendar (e.g., the quarter, month, or day of the week) |
| Cyclic | A pattern exists where the data exhibits rises and falls that are not of fixed period (duration usually of at least 2 years) |
Examples of time series patterns
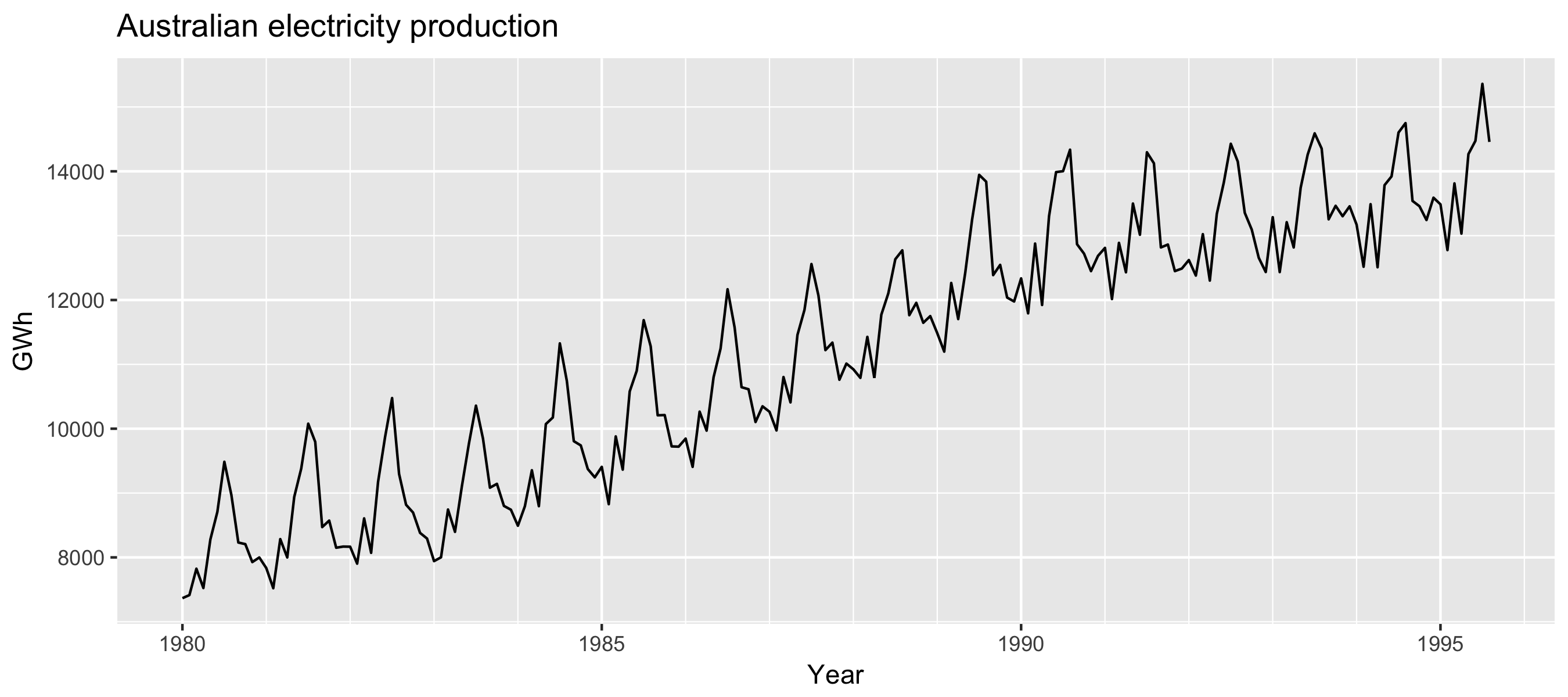
Examples of time series patterns
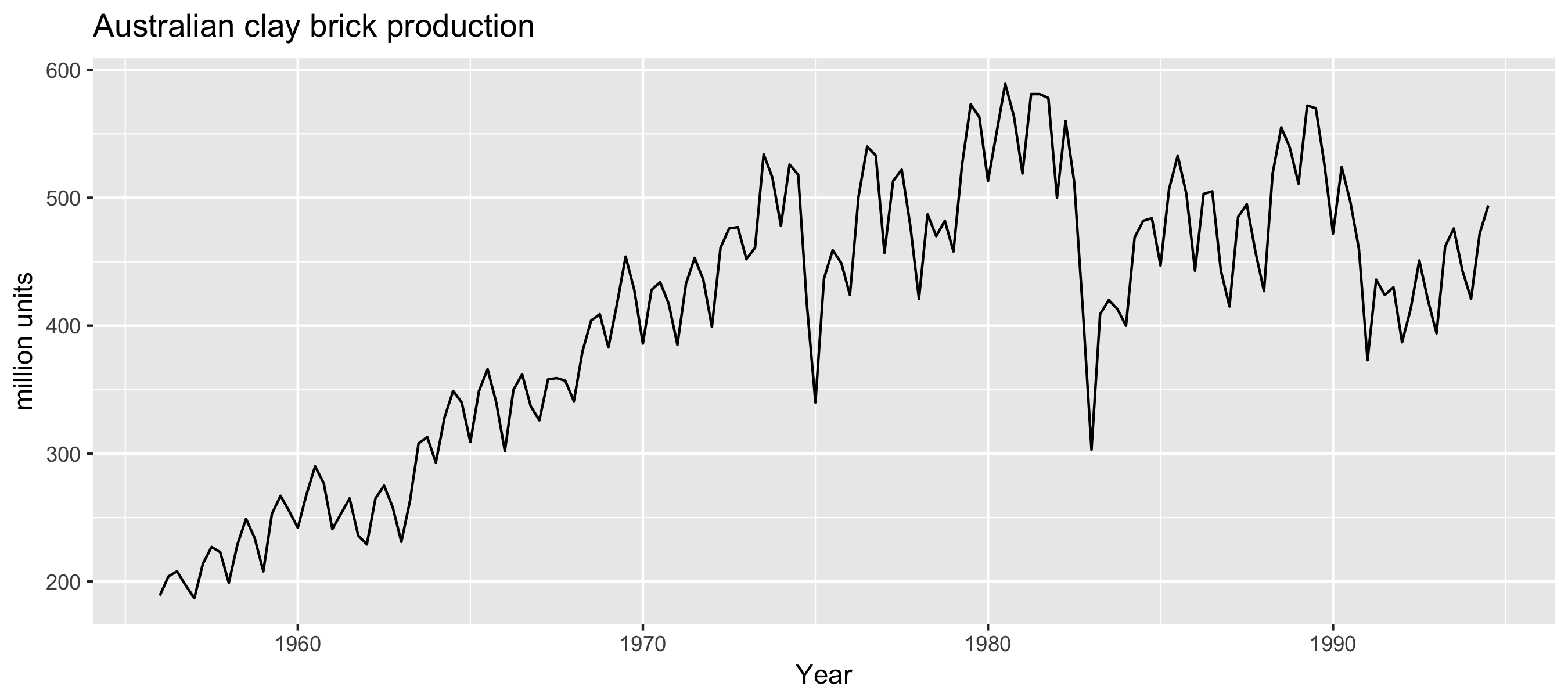
Examples of time series patterns
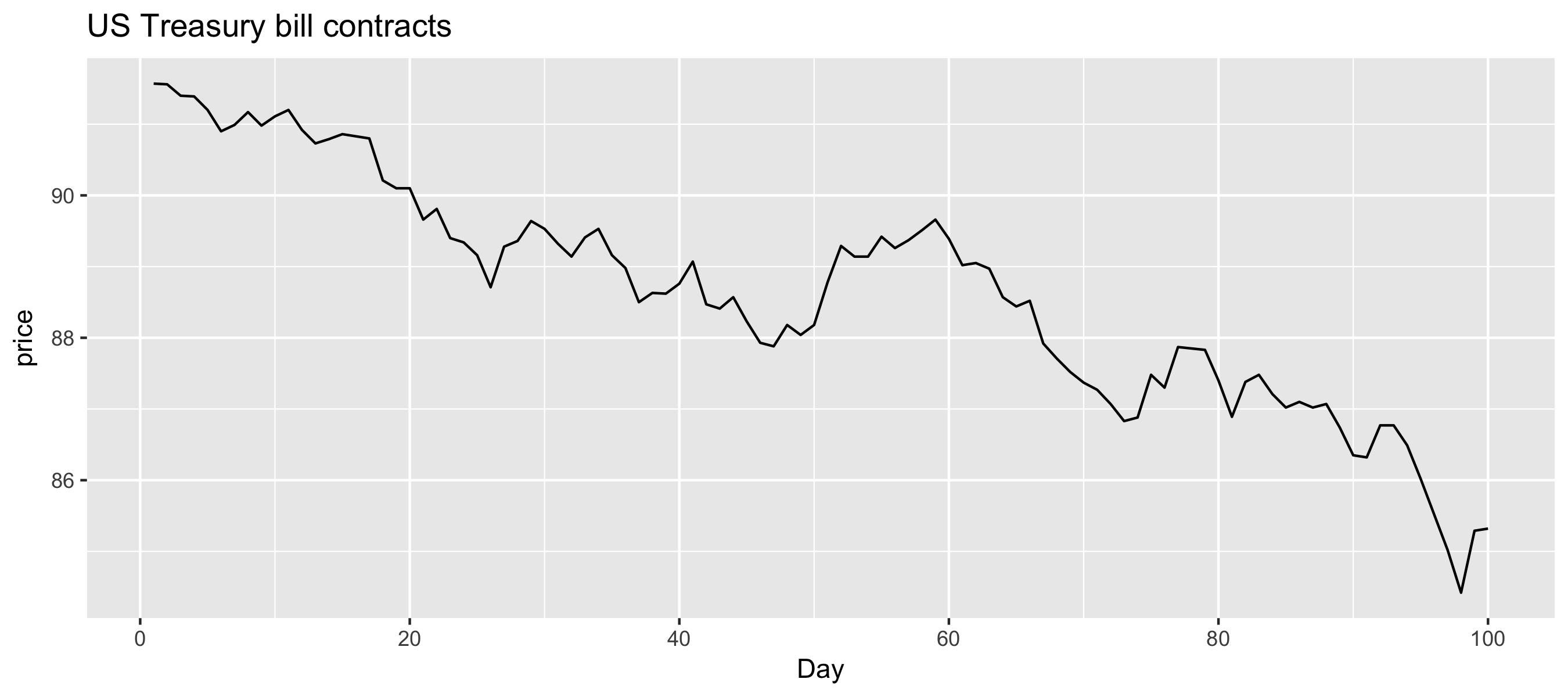
Examples of time series patterns
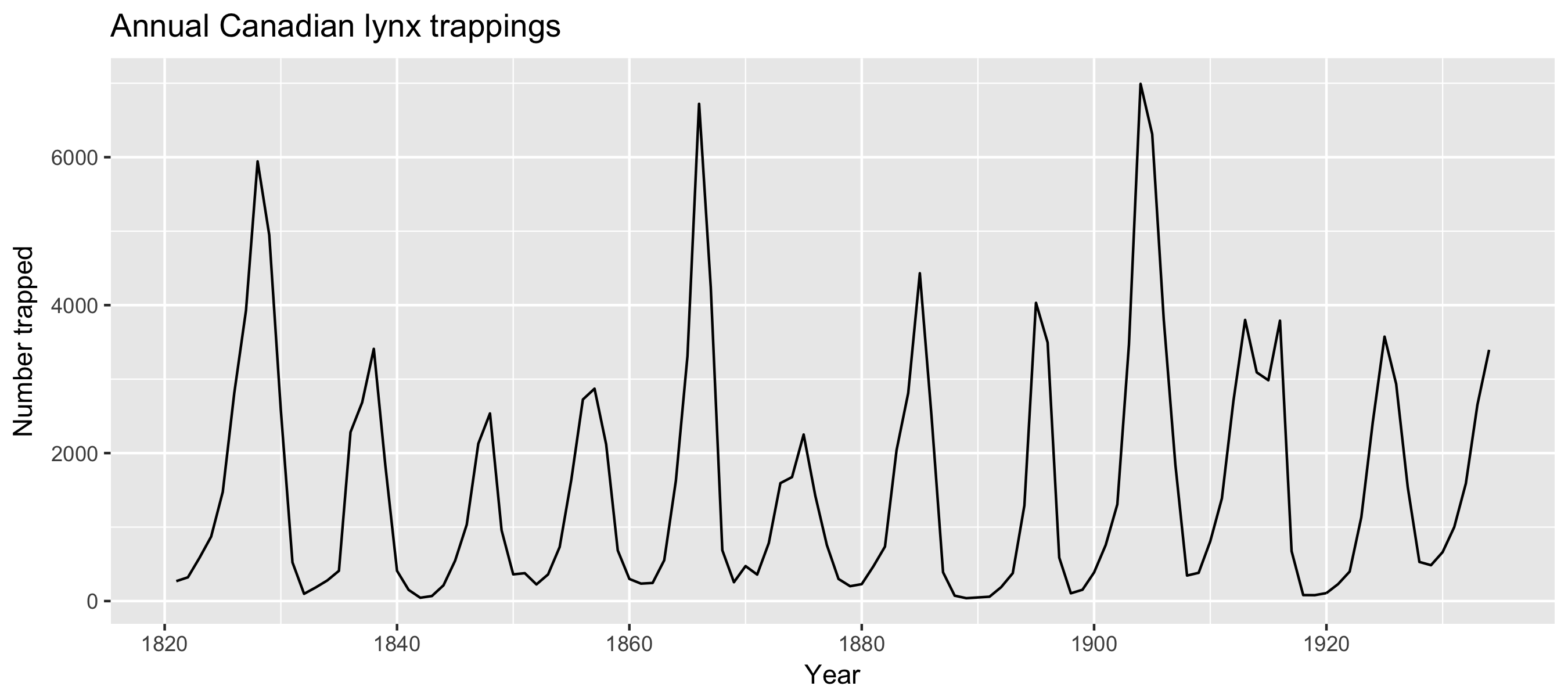
Seasonal or cyclic?
Differences between seasonal and cyclic patterns:
Seasonal pattern constant length vs. cyclic pattern variable length
Average length of cycle longer than length of seasonal pattern
Magnitude of cycle more variable than magnitude of seasonal pattern
The timing of peaks and troughs is predictable with seasonal data, but unpredictable in the long term with cyclic data.
Let's practice!
Forecasting in R

