Automated decision making and profiling
Understanding GDPR

Shalini Kurapati, CIPP/E
Co-founder and CEO, Clearbox AI
AI: Lawfulness, fairness, and transparency
- Legal basis
- Fairness and discrimination - to infer data about people
- Transparency
- Special provisions- article 22
Article 22
- Fairness and anti-discrimination obligations
- Article 22 - automated individual decision-making, including profiling
- Right to human intervention and explanation
1 Image source: flaticon.com
Profiling

- Analyze and predict behavior, large-scale processing, using AI/machine learning
- Identify and link behavior and attributes
- Create profiles, and predict behavior based on profiles
- Examples:
- Treatment success
- Risk of re-offending
1 Information Commissioner's Office
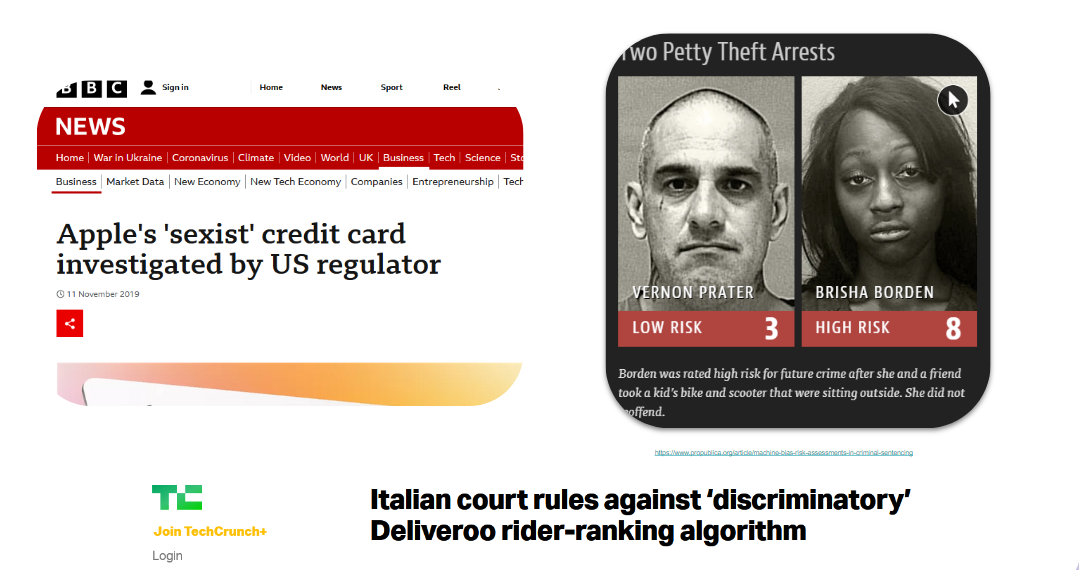
Ethical concerns related to profiling
- Propagate or reinforce bias
- Design, data, their inherent complexity/ black box
- Gender, racial discrimination
1 Image source: bbc.com, propublica.com, and techcrunch.com
The famous profiling example
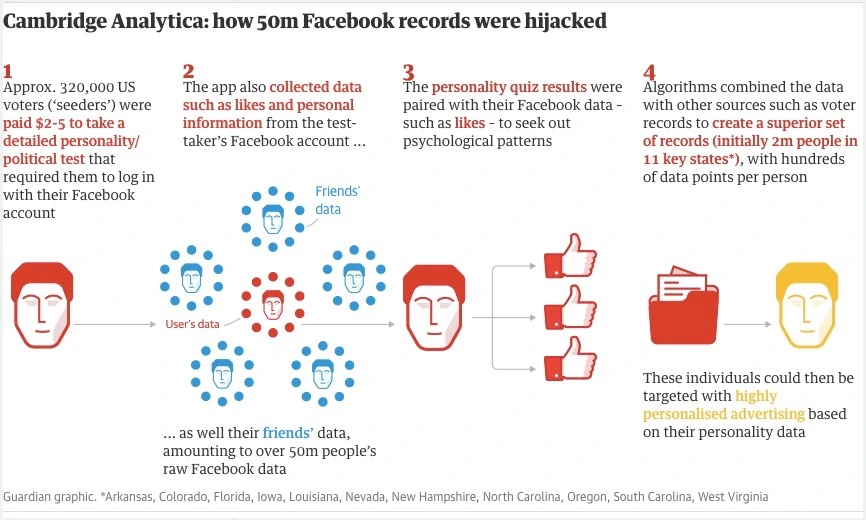
- 320,000 users took an online personality test for 'academic research'
- Collected personal data of friends of the user, up to 50m user data without consent
- Personality/political profiling, targeted ads to those likely to change mind
- Used in many elections in the US, UK, and worldwide
1 Image source: The Guardian
Automated decision making
- Decisions by automated means without human involvement
- May or may not involve profiling
- Any type of data - survey, location, profiling
- Example: Automated CV screening
1 ARTICLE 29 WORKING PARTY Guidelines on Automated individual decision-making and Profiling for the purposes of Regulation 2016/679
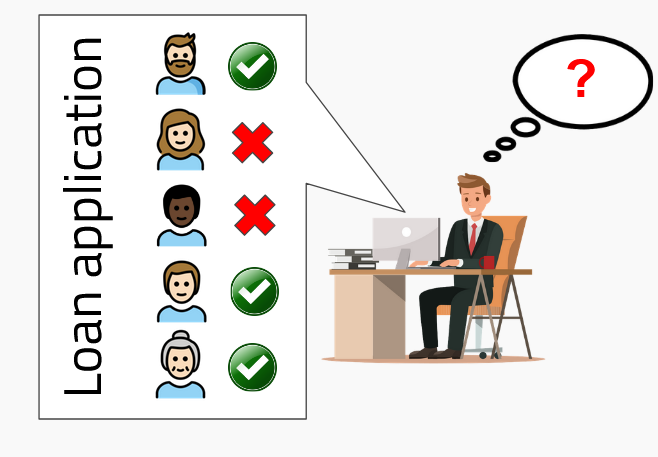
Banking example
- Automated mortgage decision
- Usually, AI gives yes or no answers, need for explanation and human intervention
- Mechanisms for preventing bias and correcting and improving AI decisions
Let's practice!
Understanding GDPR